-
What is the muscular system?
- refers to skeletal muscle system
- primarily attached to bone
- produce movement by contracting
-
What makes up a skeletal muscle?
- a muscle is a group of fascicles
- a fascicle is a group of muscle fibers
- a muscle fiber cell is multinucleate, this is whats made of sarcomere
-
What are the CT components of skeletal muscle?
- fascia (CT surrounding muscles or other organs), diff names within muscle
- tendons and aponeuroses
-
What are the different names for fascia?
- epimysium (surrounds entire skeletal muscle)
- perimysium (surrounds fascicles within muscle)
- endomysium (surrounds each muscle fiber cell)
-
What are the different names for fascia? And where are they? (image)
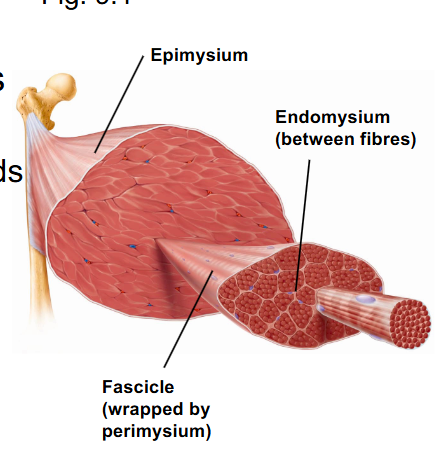
-
What do the tendons and aponeuroses do for the muscle system?
- extensions of epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium
- anchors muscle to bone (periosteum), cartilage, or fascia
-
What is a tendon?
a rope like bundle of dense regular connective tissue
-
What is aponeurosis?
a flat sheet of dense regular connective tissue
-
What is the makeup of the skeletal muscle fiber structure?
- its a large cylindrical and multinucleate cell, with parts:
- sarcolemma (cell membrane)
- T-tubules
- sarcoplasm (cytoplasm)
- myofibrils (intracellular structures)
- sarcoplasmic reticulum
-
What are T-tubules?
- continuations of sarcolemma that extend deep into fiber (cell)
- wrap around myofibrils
- goes through, not up and down
-
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
- smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- criss crosses over myofribril bunches
- has terminal cisternae along every T-tubules on both sides of it, this area of 3 things is called a triad
-
What are myofibrils?
- intracellular strcutures
- witnin each fiber there are hundreds to thousands
- composed of sarcomeres
- help with muscle contraction
-
What are sarcomeres?
- composed of proteins
- have two types of myofilaments (thin and thick)
- have a specific banding pattern
- sarcomeres join end to end at Z discs to from myofibril
-
What is the banding pattern of sarcomere?
- I band at edges by the Z disc, just think myofilaments
- A band goes from right after I band to right before the next, has thick and thin in it (covers length of thick one)
- H band is the center, thats just a thick myofilament
- M line is in the center of sarcomere, where thick filaments attach
-
What is the thin myofilament formed of?
3 proteins:
- actin
- tropomyosin
- troponin
-
What are thick filaments made of? What do they do?
- formed by protein called myosin
- attached to Z-discs by titin
- myosin has 2 globular leads and rod like tail
- at rest the heads extend towards actin, when contracting they attach to it and shorten the sarcomere
-
What's the lever system for muscle movement?
- bone/muscle interaction at a joint
- levers: bone
- fulcrum: joint
- effort: contraction of agonist
- resistance: opposes movement
-
How does pulling bones when they contract work?
- origin: attachment on a tendon to stationary bone
- insertion: attachment of a tendon to a moveable bone
-
How does using a group action work?
- agonists: major muscle producing movement
- synergists: help the agonist action and prevent undesirable outcomes caused by agonist movement
- antagonist: produces opposite action of agonist (contraction inhibited when agonist contracts)

