-
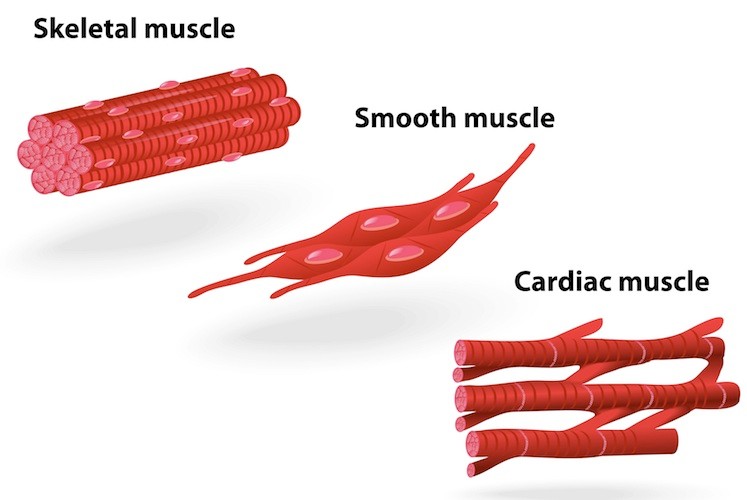
What are the three types of muscle?
-Skeletal
-Smooth
-Cardiac
-
What do skeletal muscles do?
Attach to and move the skeleton. Voluntary muscles contract and pull but cannot push so must work in pairs to extend.
-
What do smooth muscles do?
Involuntary muscles that carry out unconscious routine tasks of the body such as moving food down the digestive system, keeping the eyes in focus and adjusting the diameter of blood vessels.
-
What are cardiac muscles?
Muscles that are only found in the wall of the heart. Composed of branching fibres that form a three-dimensional network.
-
What do extensor muscles do?
Straighten the limbs attached to the bone, the bone acts as a lever, can contract to bring the limb back down (EXTEND, relax)
-
What do flexor muscles do?
Bend the joints and act to “pick up” the limb (FLEX, contract)
-
What do abductor muscles do?
Move the limb away from the body (abduct your limbs)
-
What do adductor muscles do?
Move limbs towards the midline (add to your body)
-
What are muscle fibres made up of?
Sarcomeres
-
What are sarcomeres made up of?
Microfilaments named myosin and actin
-
What causes motion?
Actin and myosin
-
How is movement created?
Muscles turn chemical energy into mechanical energy (movement). This is done by the muscles contracting and relaxing
-
What system is responsible for voluntary movement?
Somatic nervous system
-
What does each muscle have?
A personal nerve
-
What is the process of muscles creating movement called?
The sliding filament model