The Chemical Level of Organization
Organization of atoms, molecules, ions and more. Chapter 2 of A&P
-
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass
-
Mass
The amount of matter a substance contains; weight is the force of gravity acting on mass
-
What are the three forms of matter?
solid, liquid, gas
-
What are the four Major Elements?
Oxygen (O), Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Nitrogen (N)
-
Function of (O)?
Used to generate ATP (Adenosine Triphospate)
-
Function of (C)?
Forms chains and rings of all organic molecules; proteins and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
-
Function of (H)?
Ionized form (H+) makes fluids more acidic
-
Function of (N)?
Component of all proteins and nucleic acids
-
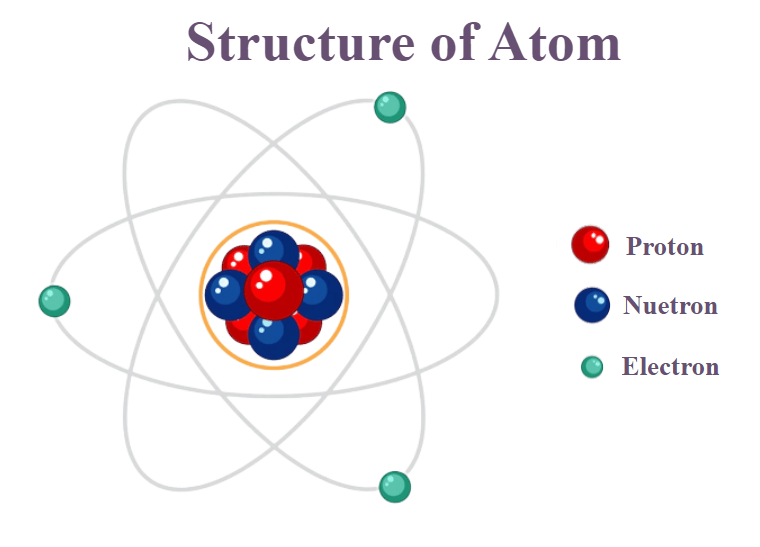
___ are positively charged atoms, and are located in the nucleus
Protons
-
___ are atoms that have no charge, in the nucleus.
Neutrons
-
___ are negatively charged atoms, that forms a cloud outside the nucleus.
Electrons
-
Only ___ electrons can be in the first shell.
2
-
How many electrons can be in the second shell?
8
-
How many electrons can be in the third shell?
18
-
The ___ is the number of protons in an atom.
Atomic number
-
The atomic number is also the ___.
number of electrons
-
What is the mass number?
The number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
-
What are isotopes?
Different atoms of the same element with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons, thus different mass number.
-
Why are radioactive isotopes unstable?
Their nuclei decay to make a simpler form and as they decay they emit radiation.
-
___ of an element is the average mass of all its various isotopes of the various types.
The atomic mass/weight
-
What is an ion?
An atom that has a positive or negative charge after giving or gaining an electron.
-
What is a free radical?
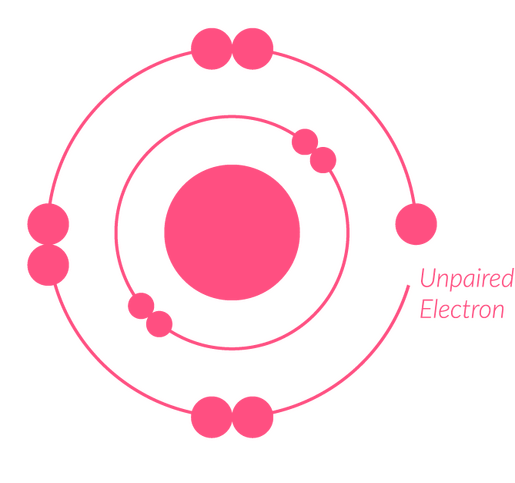
An atom or group of atoms with an unpaired electron in the outermost valence shell.
-
How do free radicals become stable?
By giving or taking another electron.
-
What is a compound?
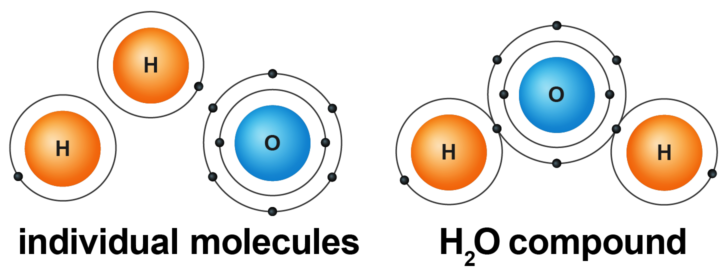
Molecules that contain two or more different kinds of elements.
-
Chemical bonds are when ___.
the atoms of a molecule are held together by forces of attraction.
-
What determines the likelihood of an atom forming a chemical bond with another atom?
The number of electrons in its valence shell.
-
Describe the Octet Rule
Atoms that have incomplete outer shells tend to combine with each other in chemical reactions to make a chemically stable arrangement of eight valence electrons.
-
What are ionic bonds?
When atoms lose or gain one or more electrons and holds ions of opposite charge (opposites attract).
-
___ and negatively charged ions are attracted to one another.
Positively
-
___ are positively charged ions that gave away one or more electrons (donors).
Cations
-
Who are the receivers in a bond?
Anions; negatively charged ions that receive one or more electrons from another atom.
-
What kind of bond is formed when the electrons are being shared between two or more atoms?
Covalent bond
-
What is a triple covalent bond?
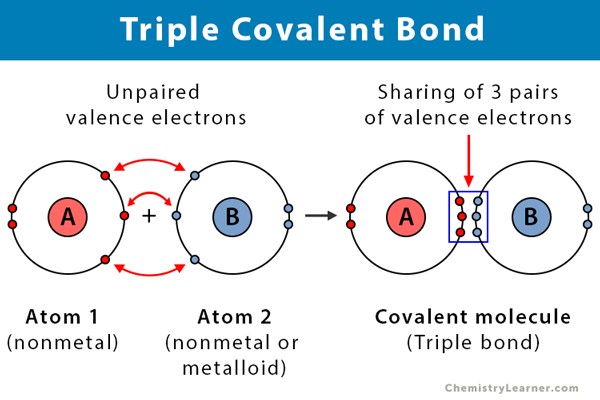
When three pairs of electrons are being shared.
-
What is a nonpolar covalent bond?
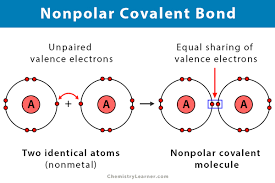
The equal sharing of electrons, one doesn't attract more strongly than the other and the number shared is the same.
-
Polar covalent bonds are ___.
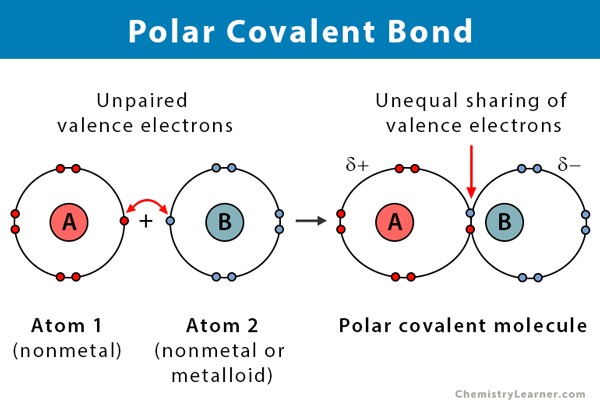
when atoms are sharing electrons unequally, one atom attracts more strongly than the other.
-
Hydrogen bonds are when ___.
two other atoms associate with a (H) atom.
-
What kind of bond gives water considerable surface tension?
Hydrogen bond
-
Why can't hydrogen bonds bind atoms together?
They only serve as links between molecules.
-
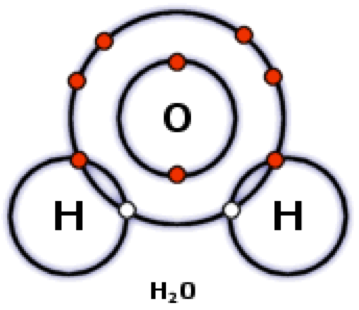
What kind of bond is this?
Polar covalent bond.
-
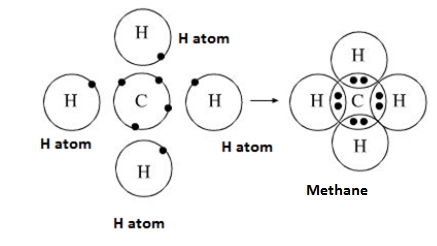
What kind of bond is this?
Nonpolar covalent bond
-
When do chemical reactions occur?
When new bonds are formed and old bonds break.
-
Reactants are the
starting substances of a chemical reaction.
-
Products are the
ending substances.
-
___ is when the total mass of the reactants and the products stay the same before and after a reaction. They only have different chemical properties because they've been rearranged.
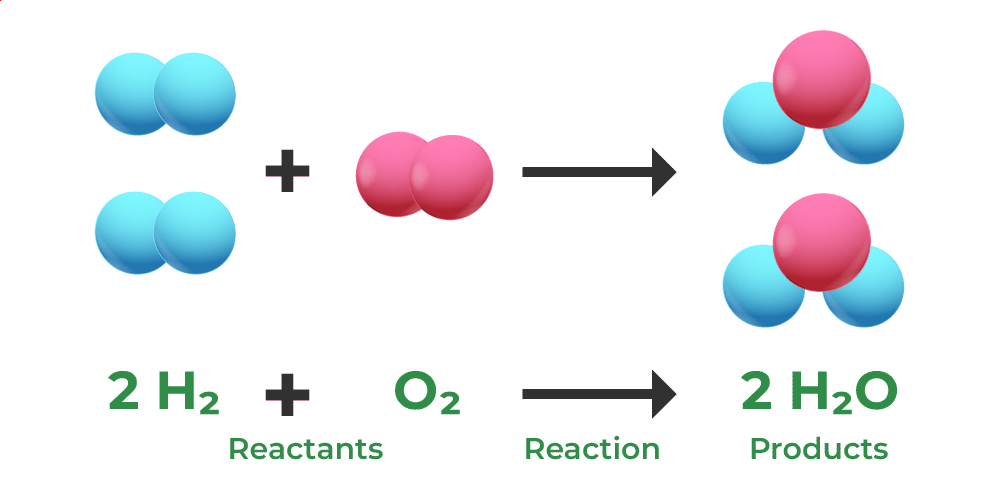
Law of conservation of mass
-
___ is energy stored in matter due to its position.
Potential energy
-
A person ready to jump down some steps is an example of?
Potential energy
-
What is kinetic energy?
Energy in motion
-
A person jumping down some steps is an example of?
Kinetic energy
-
What is chemical energy?
It is a form of potential energy that is stored in the bonds of molecules and compounds.
-
The law of conservation of energy is when?
The amount of energy at the beginning and end of a chemical reaction is the same.
-
Energy can't be...?
created or destroyed, but it can be altered to be something else.
-
Describe exergonic reactions
When a product has more energy before it was broken.
-
When do exergonic reaction occur?
Catabolism
-
Describe endergonic reactions
When a product absorbs more energy than they release.
-
Activation energy is the ___.
collision energy needed to break chemical bonds.
-
What are some factors that can influence the chance of a collision?
Temperature and concentration
-
What are catalysts?
Chemical compounds that speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for one to occur.
-
Does a catalyst alter the potential energy of the reactants and products?
No, it only lowers the amount of energy needed for a reaction.
-
What is a synthesis reaction?
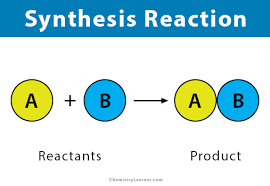
Reactions that combine to form new and larger molecules; they are anabolic.
-
A catabolic/decomposition reaction occurs when ___.
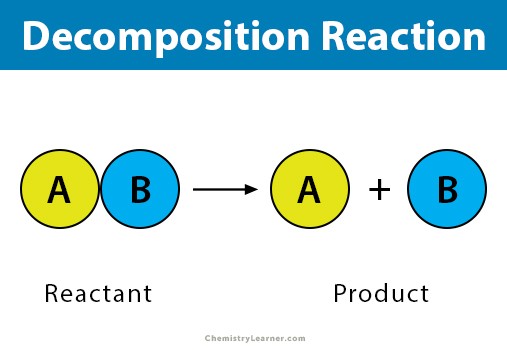
a molecule is broken down into smaller parts.
-
What is an exchange reaction?
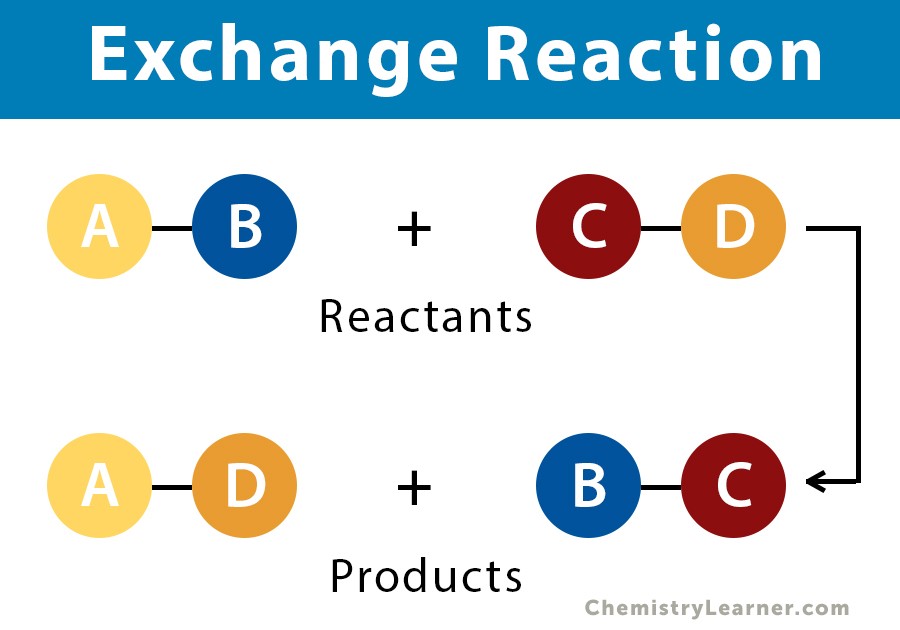
It is when an atom(s) is replaced by another atom.
-
What is a reversible reaction?
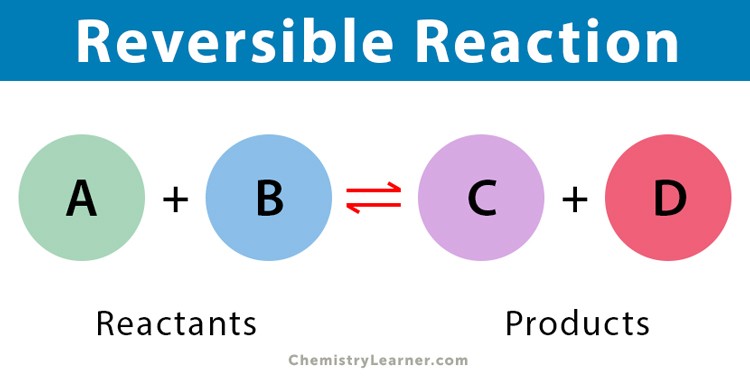
When products can revert back to the reactants.
-
What do inorganic compounds lack?
Carbon
-
Organic compounds always have ___.
Carbon and hydrogen, and usually have oxygen.
-
What type of bond do organic compounds always have?
Covalent
-
Water is an ___.
inorganic compound
-
Substances with polarity ___.
dissolve in water because they are hydrophilic
-
Nonpolar substances are ___.
hydrophobic
-
What does hydrolysis do?
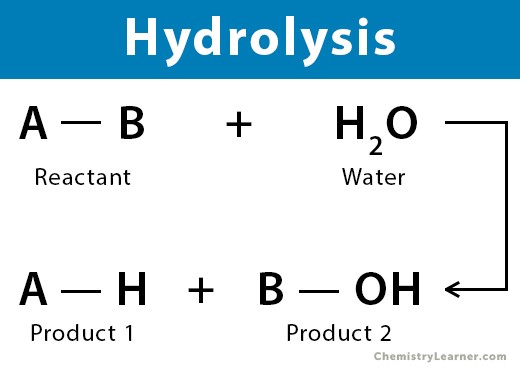
It breaks larger molecules into simpler ones by adding a water molecule.
-
What type of reaction is hydrolysis?
Decomposition
-
What does dehydration synthesis do?
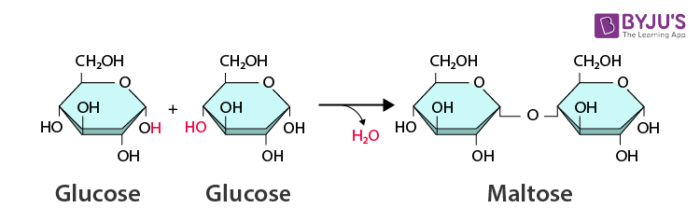
It makes new bonds by removing a molecule of water.
-
Where is water found in the body?
Wherever friction needs to be reduced or eliminated (joints, bones).
-
A ___ is a combo of elements or compounds that are physically blended together but not chemically bound.
mixture
-
A solution is ___.
a solute being dissolved in the solvent
-
What is a colloid?
A mixture that has large enough particles in it to scatter light. Usually transparent.
-
What is an example of a colloid?
Milk
-
Suspensions are ___.
heterogeneous mixtures that will have one material suspended, but will eventually settle at the bottom.
-
Oxidation-Reduction is the ___.
transfer of electrons between atoms and molecules.
-
Acids
Ionize into one or more (H+) ions and one or more anions. (H+ and Cl-)
-
Bases
Dissociates into one more hydroxide ions (OH-) and one or more cations. (K+ and OH-)
-
Salts
Dissociates into cations or anions, neither (H+) or (OH-). Formed when acids and bases react with each other. (K+ and Cl-)
-
What does the pH scale measure?
The acidity and alkalinity of a solution.
-
>7 on the pH scale indicate what?
The acidity of a solution
-
<7 on the pH scale indicate what?
The alkalinity of a solution
-
What does a buffer system do?
To convert strong acids into weaker acids or bases.
-
The carbonic and acid-bicarbonate is ___.
an important buffer system in our body.
-
___ is a chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule.
Carbon skeleton
-
What are monomers?
Identical or similar small building-block molecules (macromolecules).
-
When many monomers are covalently bonded to each other, what does it form?
Polymer
-
What is an isomer?
They are molecules that have the same molecular formula but have different structures.
-
Carbohydrates can be divided into three major groups (based on their sizes):
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
-
How are disaccharides formed?
Formed from two monosaccharides by dehydration synthesis.
-
Sucrose = glucose + fructose, is an example of what?
Hydrolysis of a disaccharide
-
How do lipids become soluble?
By combining with proteins and forming lipoproteins.
-
What are the functions of proteins? (Name at least one)
They give structure to the body, regulate processes, provide protection, help muscle contractions, transport substances and serve as enzymes.
-
What creates proteins?
Amino acids
-
Enzymes are ___.
catalysts of a living cell
-
___ forms the genetic code inside each cell and regulates most of the activity that takes place in out cells.
DNA
-
___ relays info from the genes in the cell's nucleus to guide each cell's assembly from amino acids into proteins.
RNA
-
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Uracil (U) are called ___.
Nitrogenous bases

