-
Any traffic coming to or from the ___ of the Arista is visible when running the tcpdump utility on the Arista.
control plane
-
tcpdump allows users to instantly analyze important traffic such as ___, as well as any other traffic that is destined for the switch itself.
spanning tree and routing protocols
-
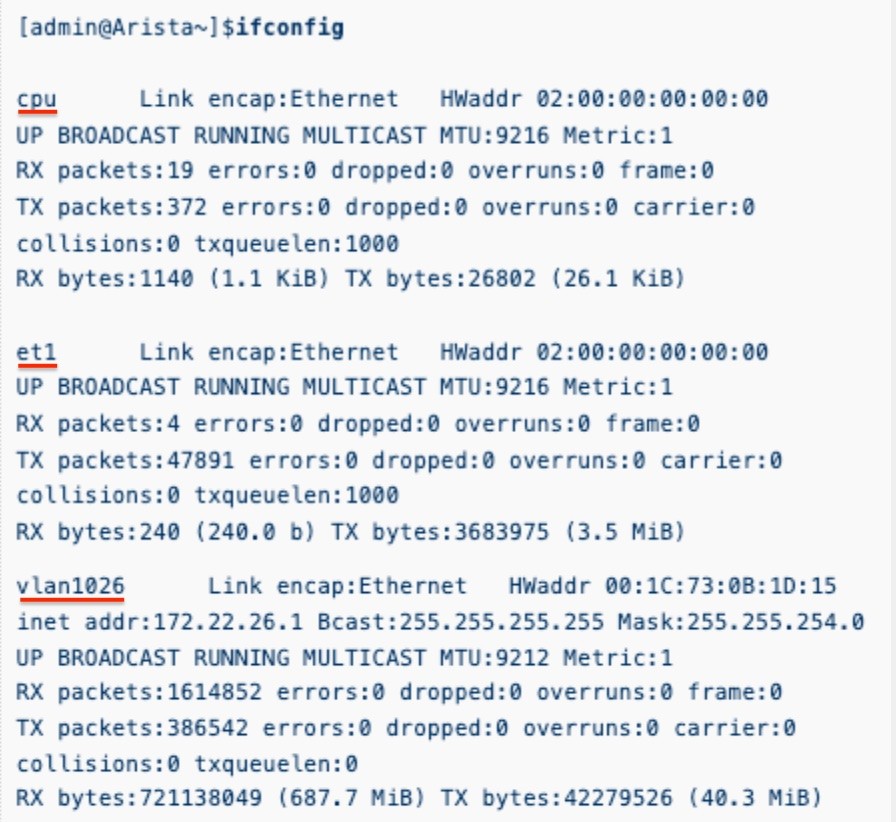
The Linux ___ command can be used to see the available interfaces in the Linux kernel.
ifconfig
-
ifconfig: The list of interfaces will reflect each of the physical interfaces on the Arista switch as well as any ___ interfaces.
virtual
-
Any VLAN which has been assigned an ___ will show up as a VLAN interface.
IP address (SVI)
-
Filter by VLAN interface
bash tcpdump -i vlan1026
-
The ‘-v’ and ‘-vv’ flags can be used to provide ___ output.
more detailed
-
Filter traffic on a specific destination port number
bash tcpdump dst port 22
-
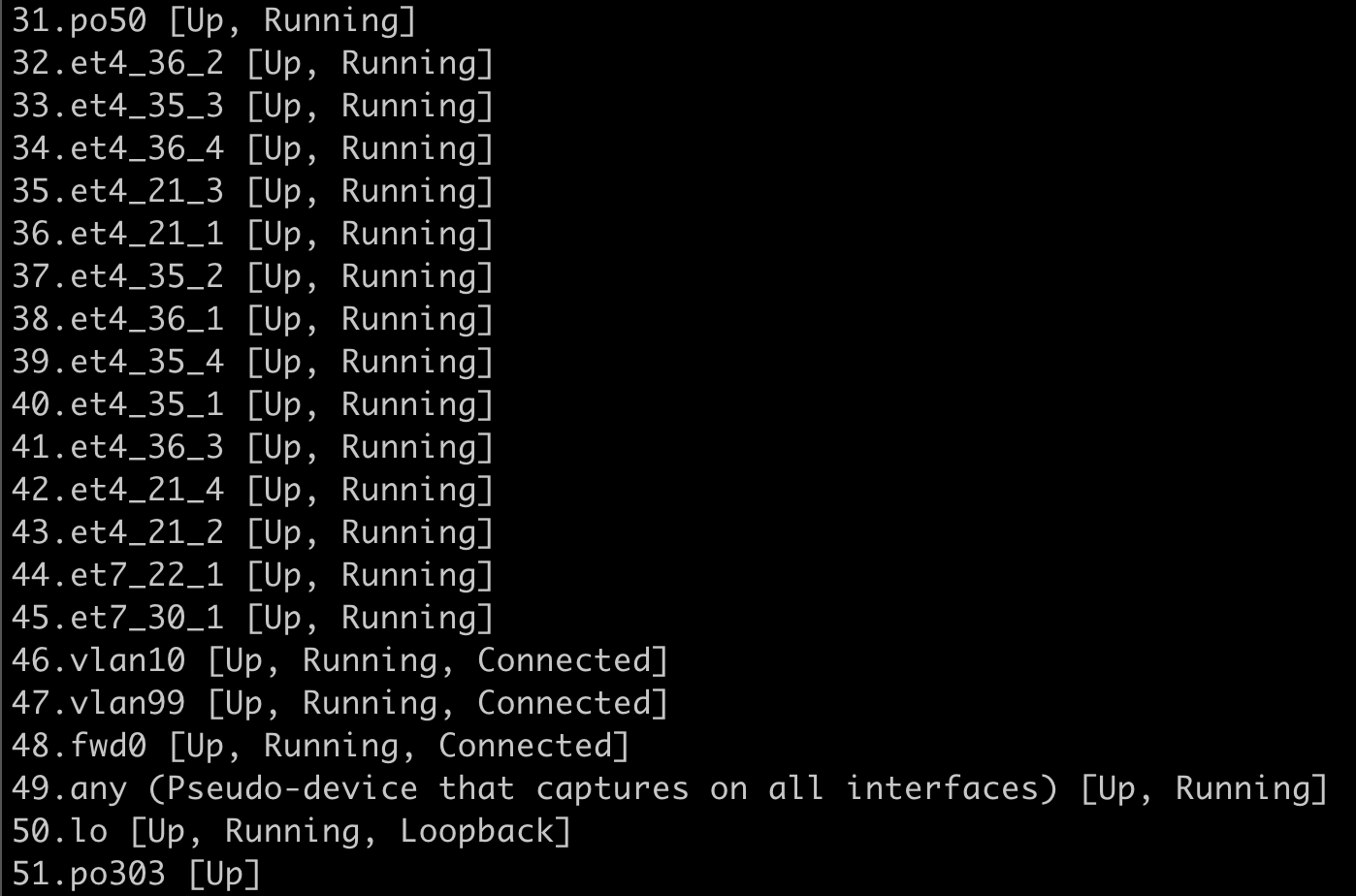
List all network interfaces available for capture
bash tcpdump -D
-
By default, tcpdump attempts to resolve IP addresses and port numbers into ___
names
-
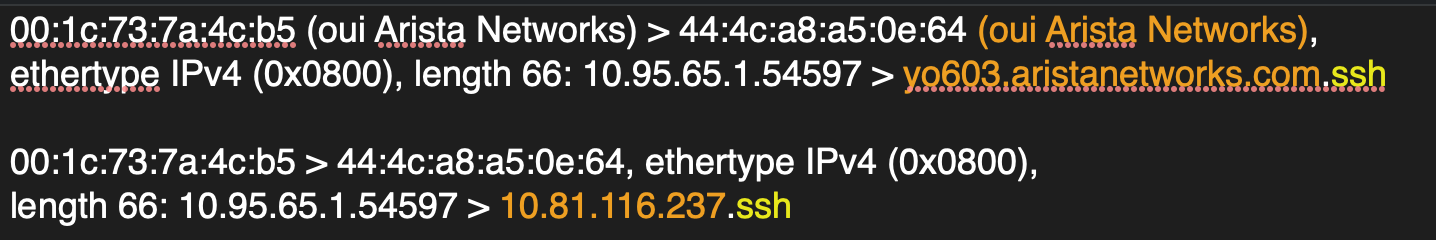
Disable hostname resolution using the __ flag.
-n
-
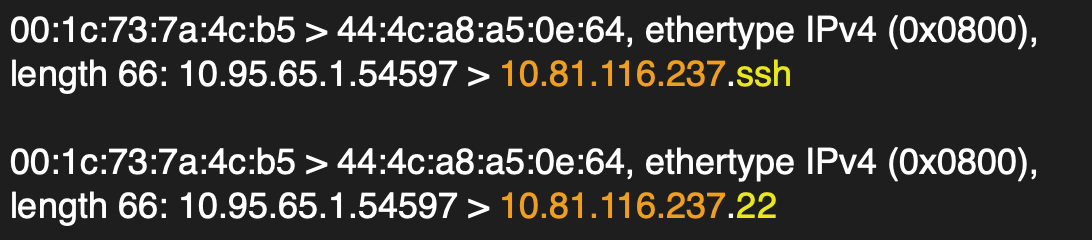
Disable hostname AND port name resolution using the __ flag.
-nn
-
Stop capturing after 10 packets
bash tcpdump -c 10
-
Filter by IP address (source or destination) using 10.95.65.1
bash tcpdump host 10.95.65.1
-
Filter traffic by interface po50
bash tcpdump -i po50
-
Filter traffic by source IP address, using 10.95.65.1
bash tcpdump src 10.95.65.1
-
Filter traffic by destination IP address, using 10.95.65.1
bash tcpdump dst 10.95.65.1
-
Filter traffic by protocol (ICMP)
bash tcpdump icmp
-
Filter traffic to or from host 10.95.65.1 of type ICMP. Disable name/port resolution and limit capture to 5 packets.
bash tcpdump -nnc5 host 10.95.65.1 and icmp
-
Filter SSH traffic destined to host 10.95.65.1
bash tcpdump dst 10.95.65.1 and port 22
-
How do I see LLDP packets coming from an interface?
bash tcpdump -i et1 ether dst host 01:80:c2:00:00:0e
-
My server is port-channeled to my Arista switch, and it is not coming up. How do I capture LACP packets coming to and from the server to form the port-channel?
bash tcpdump -nevvi et1 ether host 01:80:c2:00:00:02
-
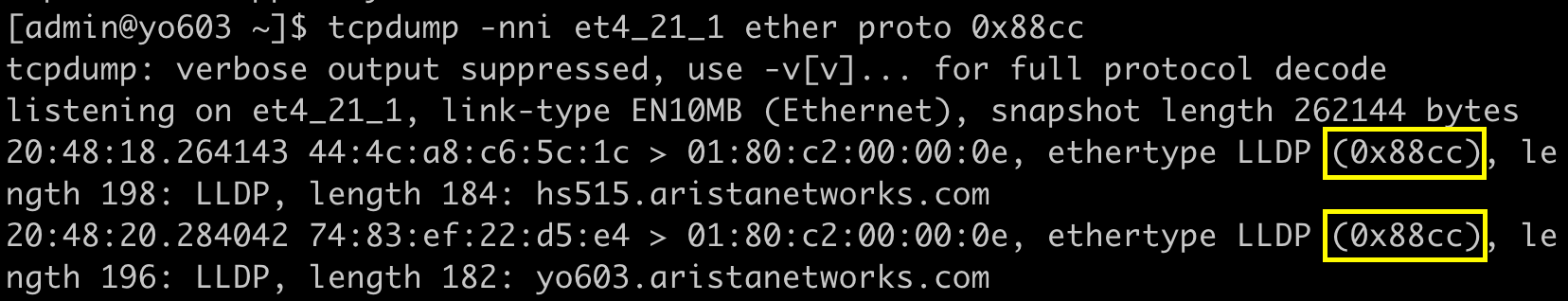 Filter LLDP traffic on interface Ethernet4/22/1
Filter LLDP traffic on interface Ethernet4/22/1bash tcpdump -i et4_22_1 ether host 01:80:c2:00:00:0e ... or bash tcpdump -i et4_22_1 ether proto 0x88cc
-
LLDP well-known multicast MAC address
01:80:c2:00:00:0e -
LACP well-known multicast MAC address
01:80:c2:00:00:02
-
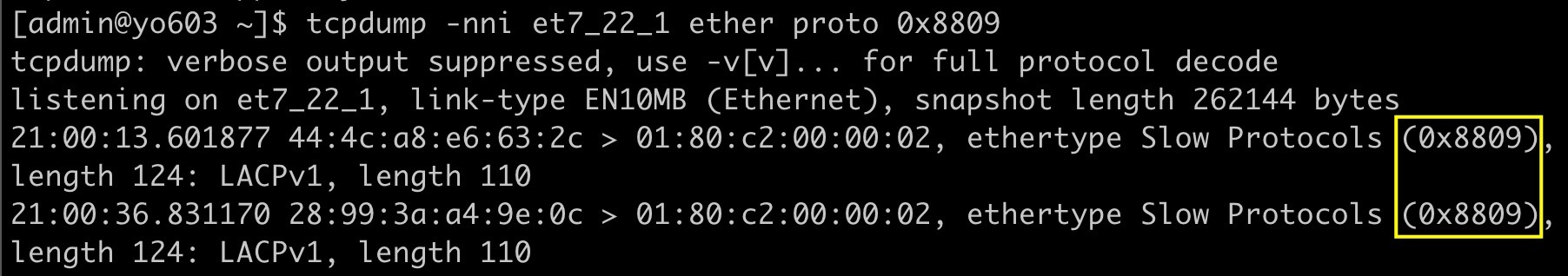 Filter LACP traffic on interface Ethernet4/22/1
Filter LACP traffic on interface Ethernet4/22/1bash tcpdump -i et4_22_1 ether host 01:80:c2:00:00:02 ... or bash tcpdump -i et4_22_1 ether proto 0x8809)
-
Filter SSL traffic to/from IP 10.95.65.1 on Management0. Write the capture to test.pcap on flash.
bash tcpdump -nni ma0 host 10.95.65.1 and port 22 -w flash:test.pcap
-
Read the first packet from test.pcap in Flash. Disable IP and port name resolution.
bash tcpdump -nnc1 -r flash:test.pcap
-
How do I capture OSPF packets between neighbors?
bash tcpdump -nnevi po50 proto ospf
-
Listen on all interfaces just to see if you're seeing any traffic.
-i any
-
Increase the amount of packet information you get back.
-v, -vv, -vvv
-
Show the packet’s contents in both hex and ASCII.
-X
-
Same as -X, but also shows the ethernet header.
-XX
-
Only get x number of packets and then stop.
-c
-
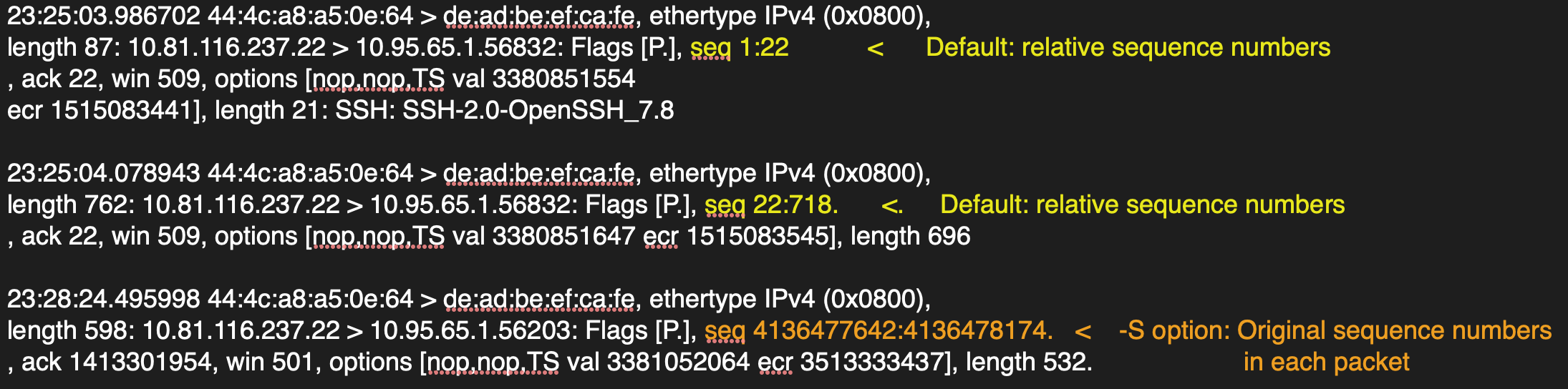
Print absolute sequence numbers.
-S
-
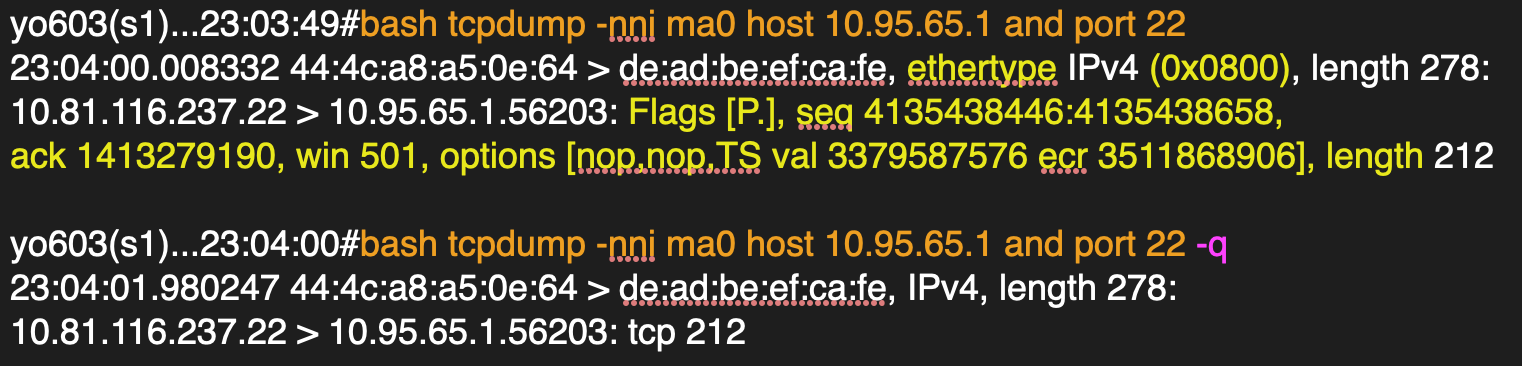
Show minimal protocol information.
-q
-
Filtering for a specific host with VLAN tags
bash tcpdump -i ma0 vlan and host 10.95.65.1
-
Filtering for either arp or icmp without VLAN tags
bash tcpdump -i ma0 arp or icmp
-
Filtering for either arp or icmp with VLAN tags
bash tcpdump -i ma0 vlan and '(arp or icmp)'
-
Filtering for either arp or icmp with or without VLAN tags
bash tcpdump -i ma0 '(arp or icmp) or (vlan and (arp or icmp))'
-
The ‘vlan’ keyword in a tcpdump filter changes the lookup offsets for all other keywords ___ the keyword. This behavior is irrespective of parentheses.
following
-
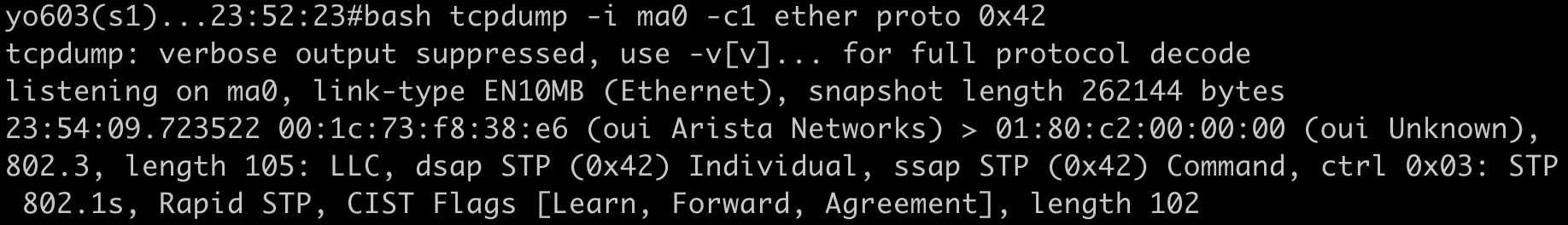
Filter for BPDUs Without VLAN tags i.e. RSTP/MSTP/untagged native VLAN in Rapid PVST
bash tcpdump -i ma0 stp ... or bash tcpdump -i ma0 ether proto 0x42)
-
Filter for BPDUs With VLAN tags i.e. tagged VLAN BPDUs in Rapid PVST
bash tcpdump -i ma0 vlan and ether dst 01:00:0c:cc:cc:cd -
Print all packets but NOT those from host 00:25:90:32:ec:2a
bash tcpdump -i ma0 not ether src 00:25:90:32:ec:2a
-
Filter for VXLAN VNI 200
bash tcpdump -i ma0 'port 4789 and udp[8:2] = 0x0800 and udp[11:4] = 200'
-
Filter for a VXLAN inner destination of MAC 28:99:3a:8f:b1:41
bash tcpdump -i ma0 'port 4789 and udp[8:2] = 0x0800 and udp[16:4] = 0x28993a8f and udp[20:2] = 0xb141'
-
Filter for a VXLAN inner source MAC of 28:99:3a:8f:ae:a7
bash tcpdump -i ma0 'port 4789 and udp[8:2] = 0x0800 and udp[22:4] = 0x28993a8f and udp[26:2] = 0xaea7'
-
Filter for a VXLAN iinner source IP of 20.20.20.10
bash tcpdump -i ma0 'port 4789 and udp[8:2] = 0x0800 and udp[42:4] = 0x1414140a'
-
Filter for a VXLAN inner destination IP of 20.20.20.5
bash tcpdump -i ma0 'port 4789 and udp[8:2] = 0x0800 and udp[46:4] = 0x14141405'
-
we can punt traffic to CPU to take captures. It will ___ the CPU as policies rate limiting traffic to CPU are in place (about 1Gb/s)
not overwhelm
-
LACP packets must be viewed on ___, not the port-channel!
physical interfaces
-
Filtered Mirroring ___: Configure an ACL with entries that match traffic we are interested in (TX, RX, or both) ending with "mirror session <session name>"
Step 1
-
Filtered Mirroring ___: Set the last ACL rule as permit ip any any (If the interface doesn’t already have an ACL)
Step 2
-
Filtered Mirroring ___: Assign the ACL to the interface we would like to capture traffic on
Step 3
-
Filtered Mirroring ___: Add a destination monitor session port Ethernet, Port-channel, CPU or Tunnel
Step 4
-

Filtered Mirroring: Associate ACL entries with a monitor session using the key words ___
mirror session
-
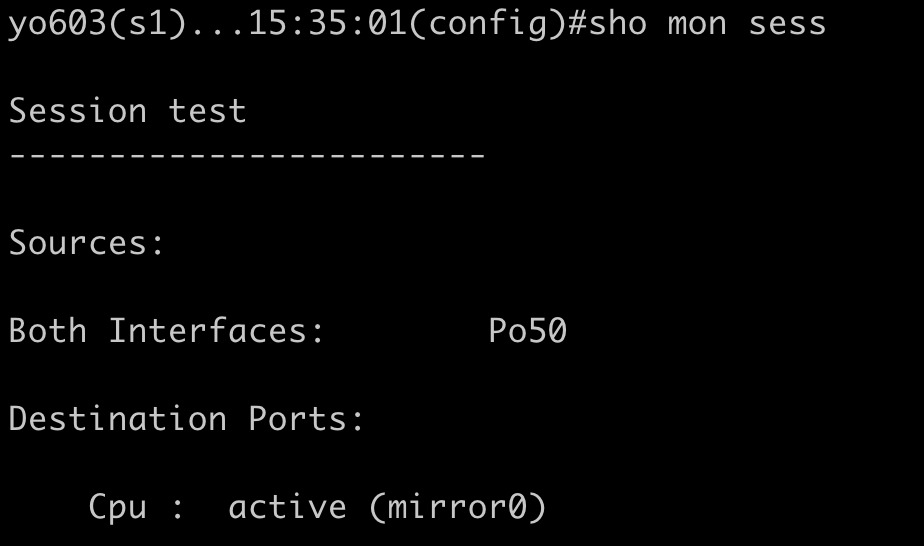
Print traffic from the monitor session pictured. Filter traffic to/from host 10.95.65.1. Disable host name and port name resolutions.
bash tcpdump -nni mirror0 host 10.95.65.1
-
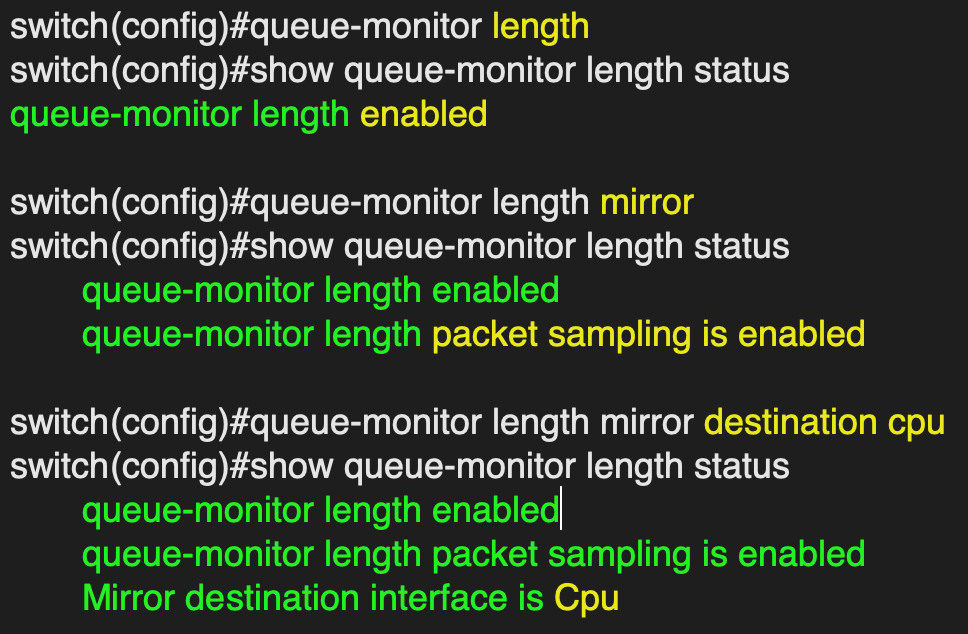
Configure the switch to automatically send sampled LANZ traffic to the CPU
queue-monitor length mirror destination cpu
-
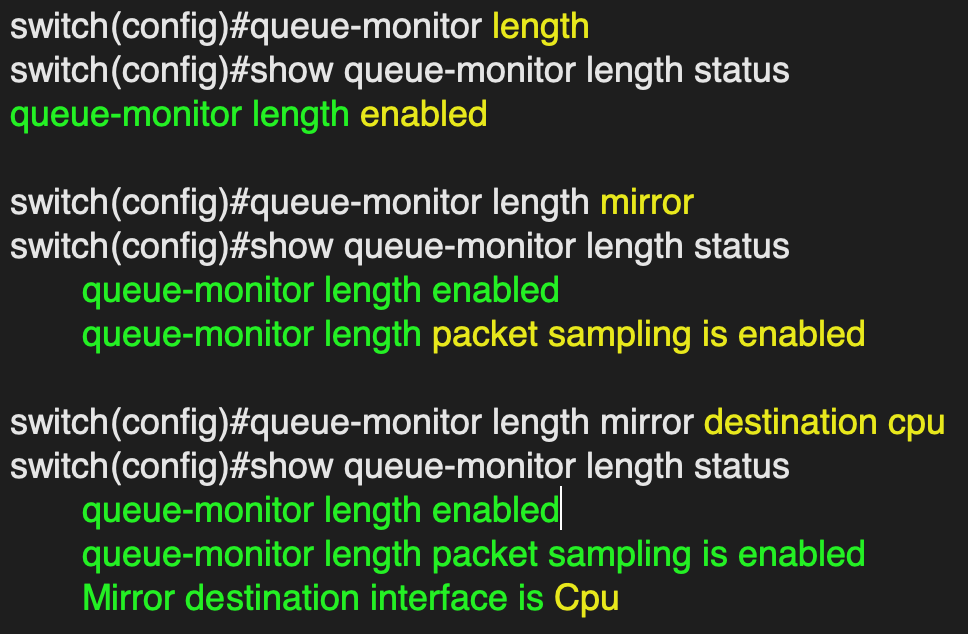
Enable LANZ
queue-monitor length
-
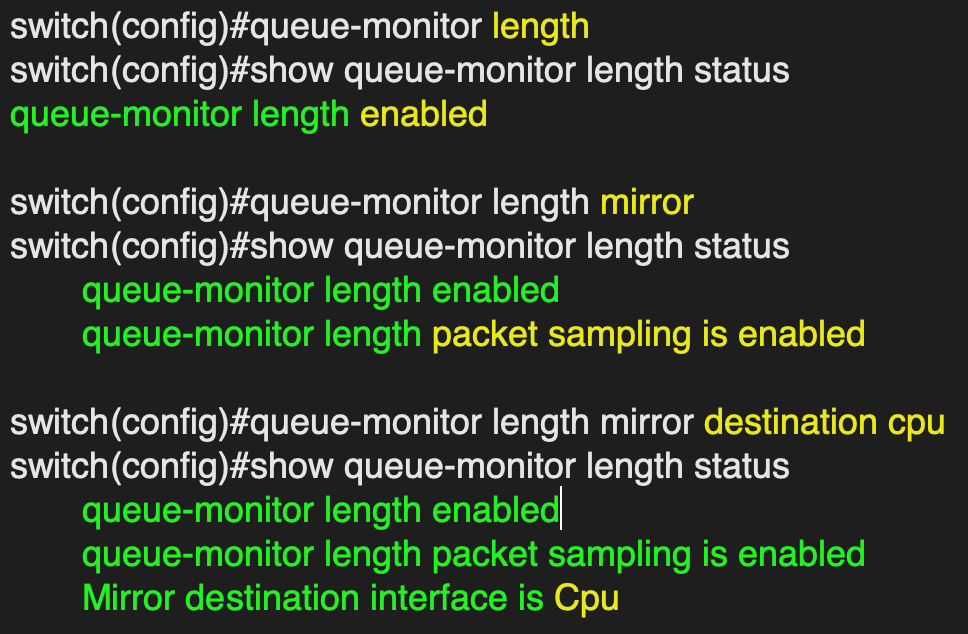
Configure the switch to enable packet sampling of LANZ traffic
queue-monitor length mirror
-
This command configures a port mirroring session to truncate mirrored packets, retaining only the first 128-192 bytes.
monitor session truncate
-
Packet truncation can be used to prevent ___ of a monitor session’s destination port. It helps control the utilization of the Mirror CoPP.
oversubscription
-
packet ___ applies to the mirroring session as a whole, and cannot be applied to individual source ports.
truncation
-

On Sand, the size of truncated packets can be set to either ___ or ___ bytes.
128, 192
-
On Strata/Alta, the number of bytes to be retained when truncating packets is fixed at ___
160

