-
what glands are present in the external acoustic meatus?
ceruminous glands
-
what composes the outer ear?
auricle
external acoustic meatus
tympanic membrane
-
what does the tympanic membrane do?
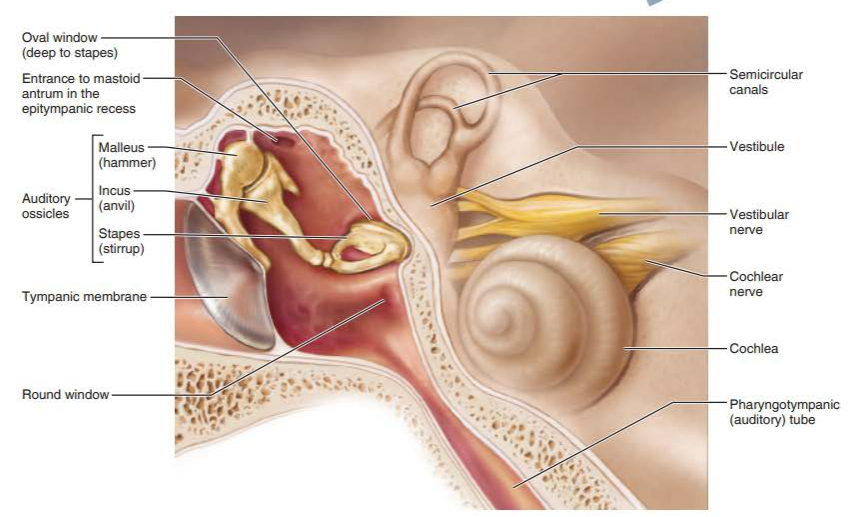
transfers sound energy to the middle ear
-
what is the roof of the middle ear cavity?
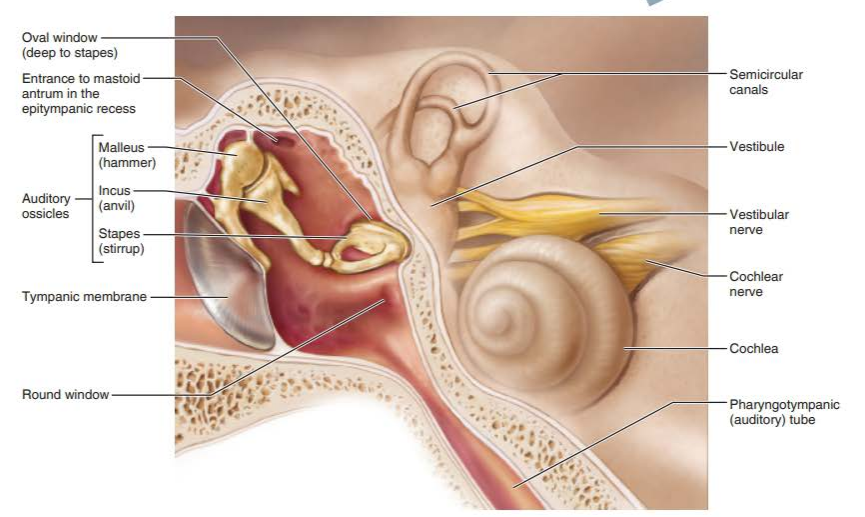
epitympanic access
-
what allows for communication with mastoid air cells housed in the mastoid process?
mastoid antrum in middle ear
-
what is the importance of the eustachian tube?
equalizes pressure in middle ear cavity with external air pressure allowing the eardrum to vibrate freely
-
where are the auditory ossicles located?
what are they?
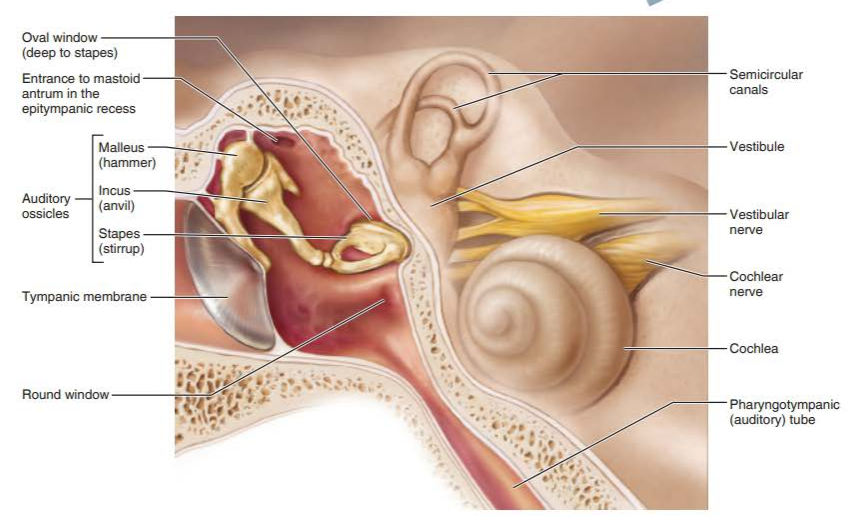
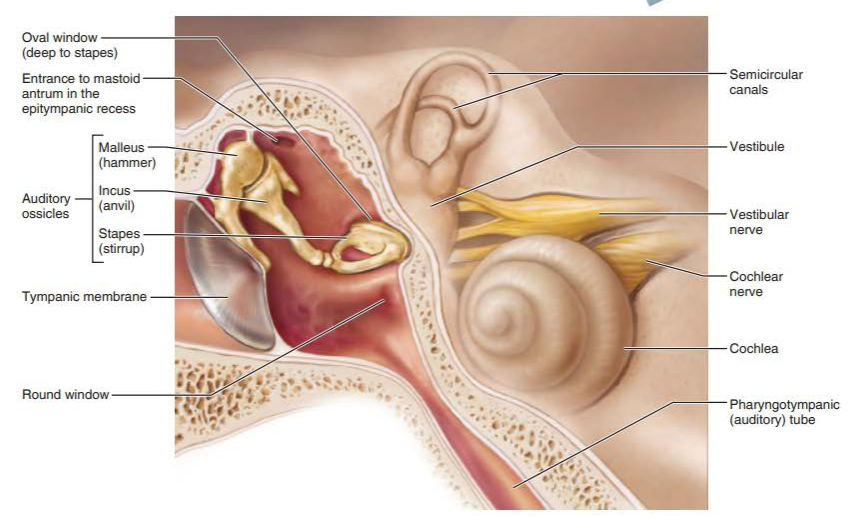
middle ear
malleus
incus
stapes
-
what transmits the vibratory motion of the tympanic membrane to the oval window?
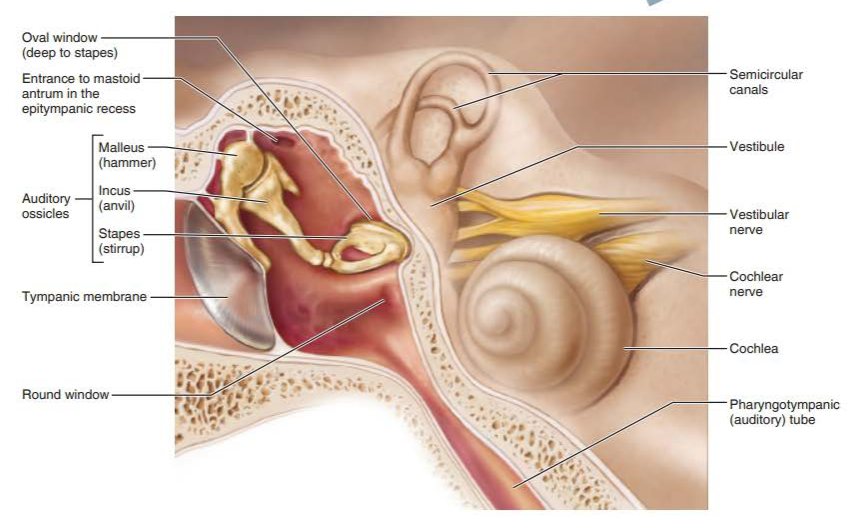
stapes
-
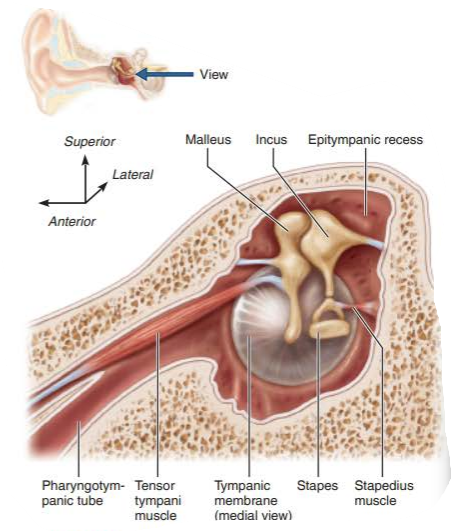
what two muscles minimize damage to hearing receptors?
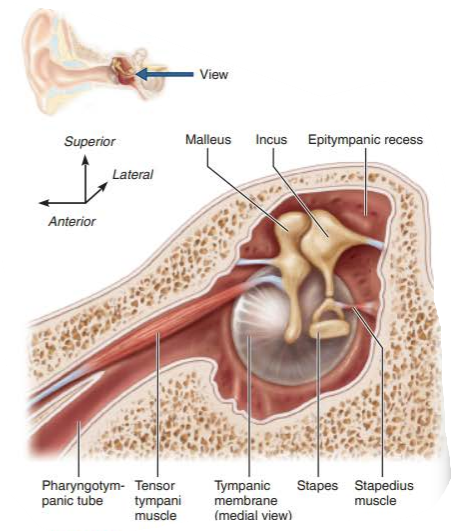
tensor tympani
stapedius
-
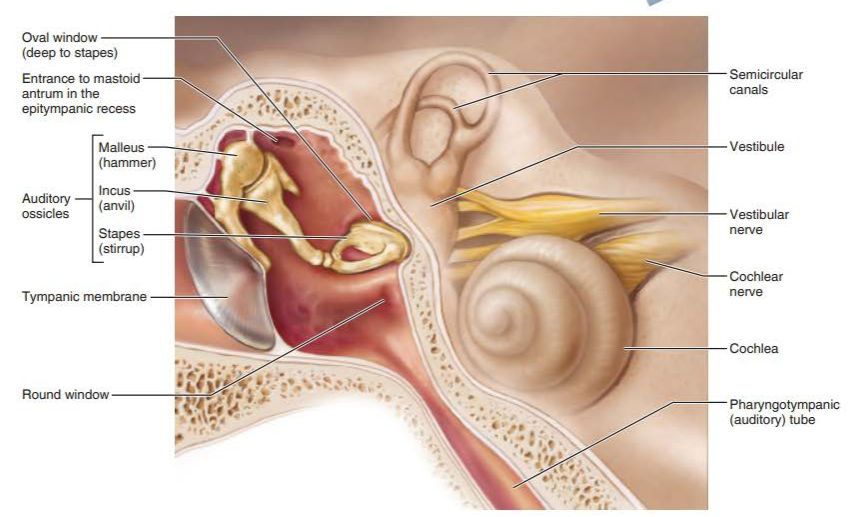
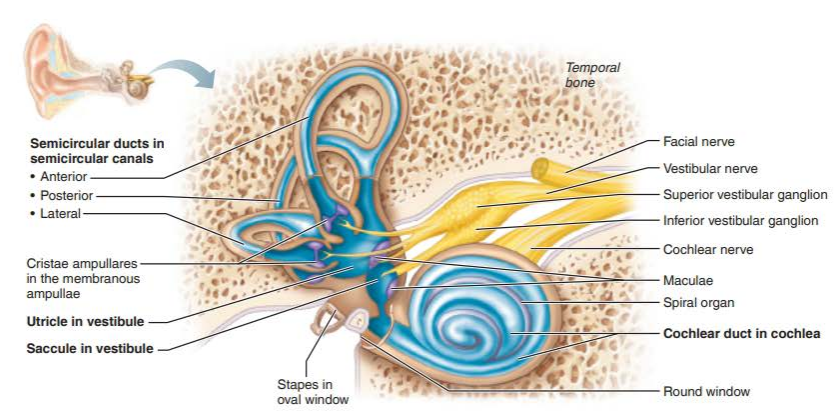
what are the two divisions of the internal ear?
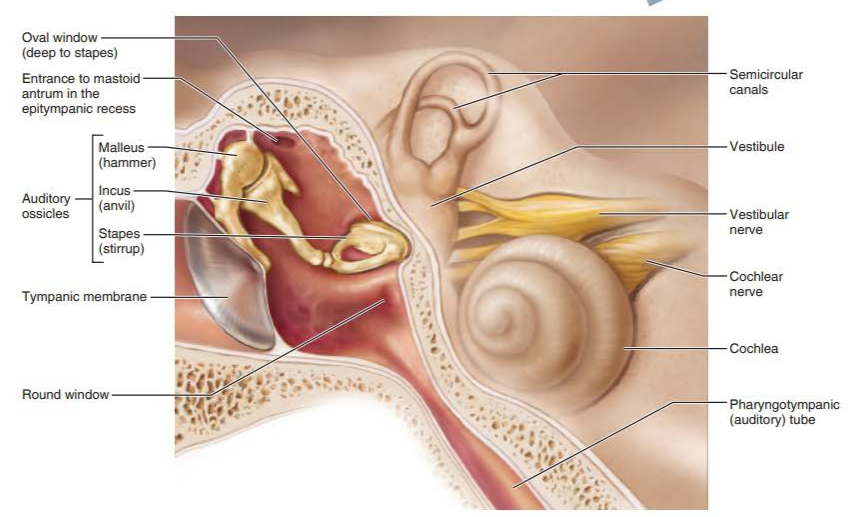
bony labyrinth
membranous labyrinth
-
what fills the bony labyrinth?
perilymph
-
what fills the membranous labyrinth?
endolymph
-
state two functions of perilymph and endolymph
conduct sound vibrations
respond to mechanical forces occurring during changes in body position and acceleration
-
what are the three regions of the bony labyrinth?
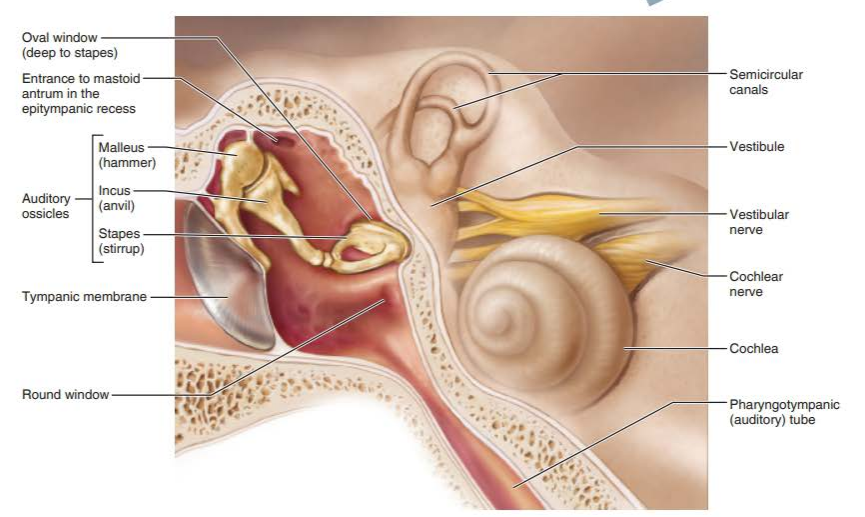
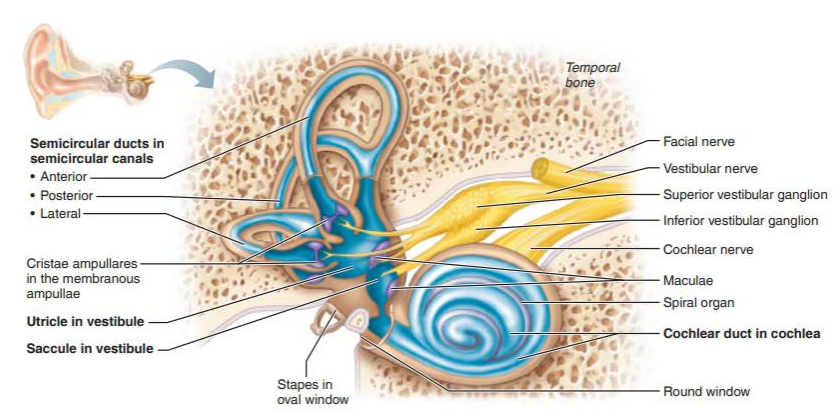
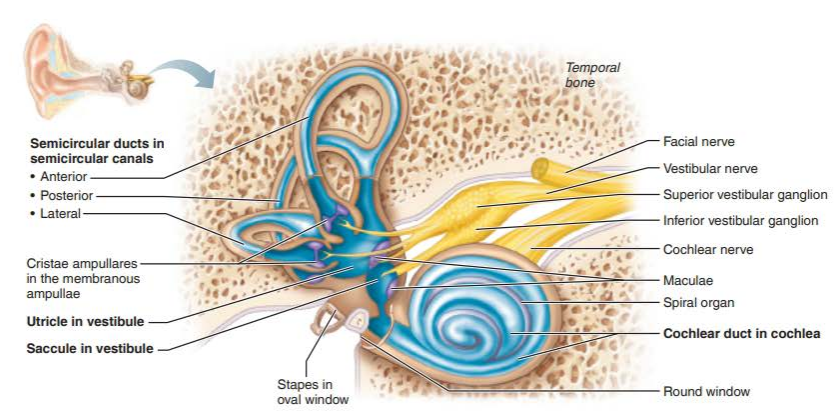
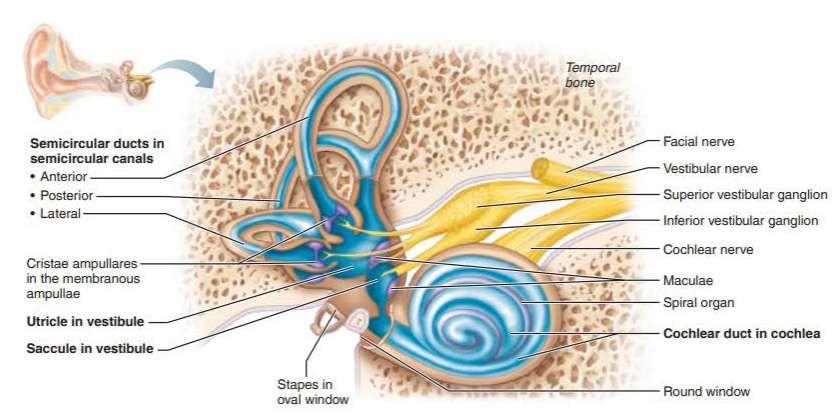
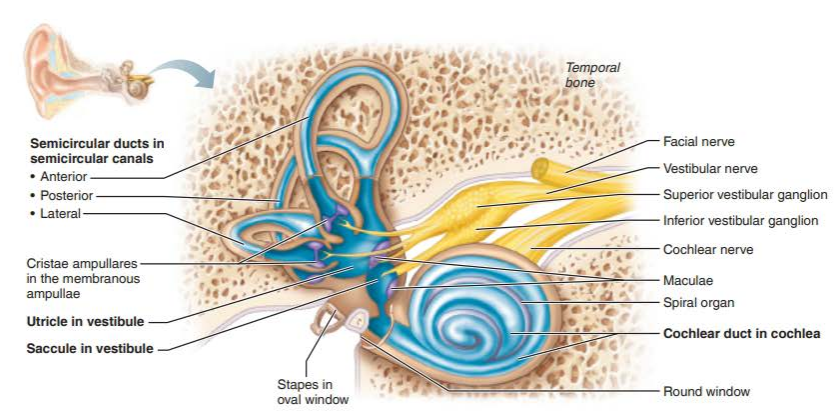
vestibule
semicircular canals
cochlea
-
what are the two membranous labyrinth sacs suspended in the vestibular perilymph?
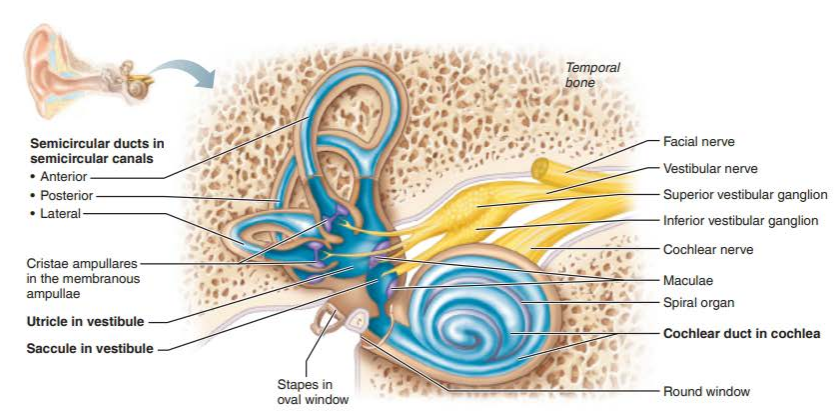
saccule
utricle
-
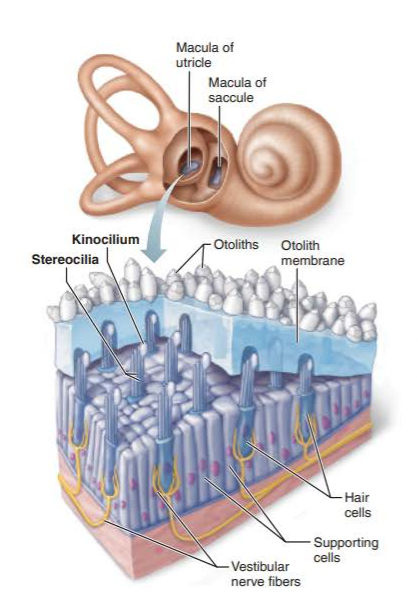
what is housed within the saccule and utricle?
maculae
-
what structure responds to the pull of gravity and reports to changes in head position?
maculae
-
what are the three semicircular canals?
lateral semicircular canal
anterior semicircular canal
posterior semicircular canal
-
what is found within each semicircular duct of the semicircular canals?
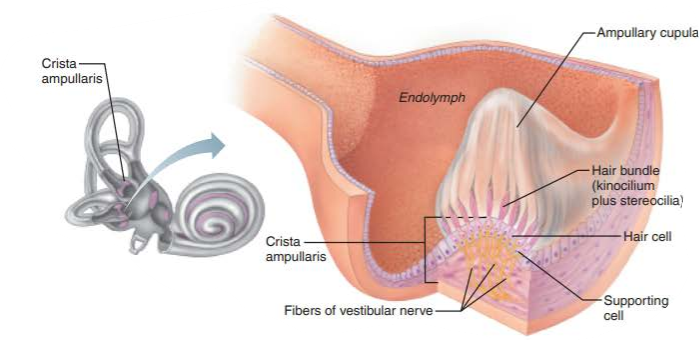
crista ampullaris
-
what is the function of the crista ampullaris?
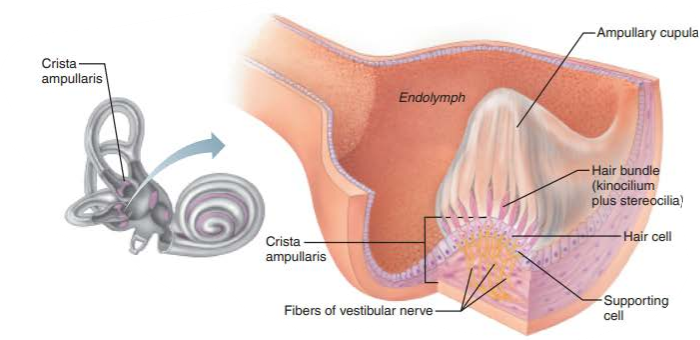
responds to rotational movements of the head
-
what is the membranous structure within the cochlea?
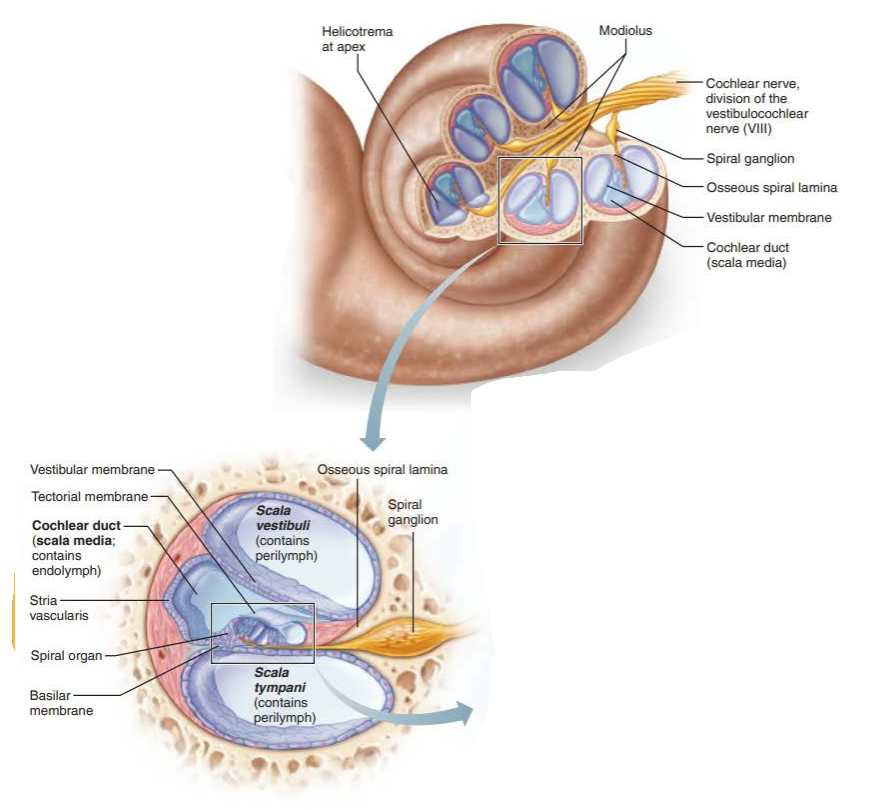
cochlear duct
-
what is housed within the scala media of the cochlear duct?
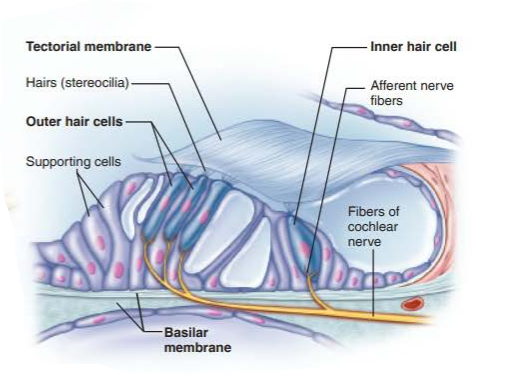
spiral organ
-
what are the cells of the spiral organ?
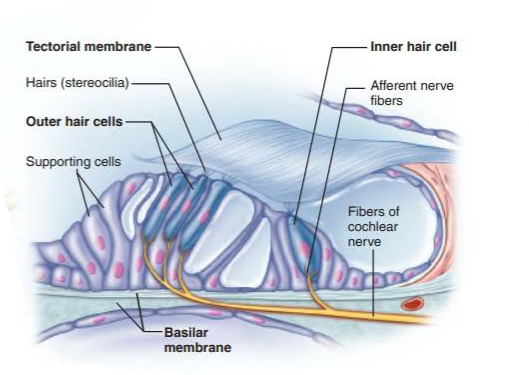
cochlear hair cells
-
Afferent fibers of the __________ coil around the bases of the hair cells and runs from the __________ through the modiolus of the brain
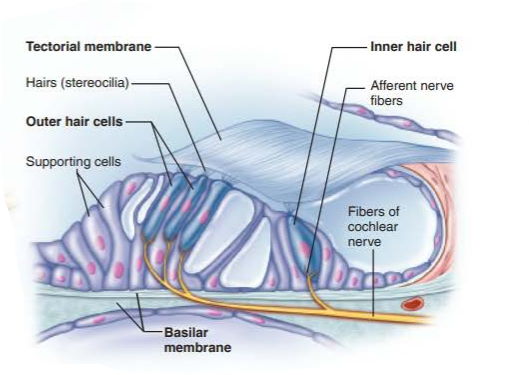
cochlear nerve
spiral organ
-
what three chambers composes the cavity of the cochlea?
scala vestibuli
scala media
scala tympani
-
what liquid is found in the scala vestibuli?
perilymph
-
what liquid is found within the scala media?
endolymph
-
what liquid is found within the scala tympani?
perilymph
-
scala tympani and scala vestibuli are continuous with each other at the cochlear apex region called the ______________
helicotrema
-
what is the roof of the cochlear duct?
what does it contain?
what does this structure secrete?
vestibular membrane
stria vascularis
endolymph
-
what is the floor of the scala media of the cochlear duct?
what is its function
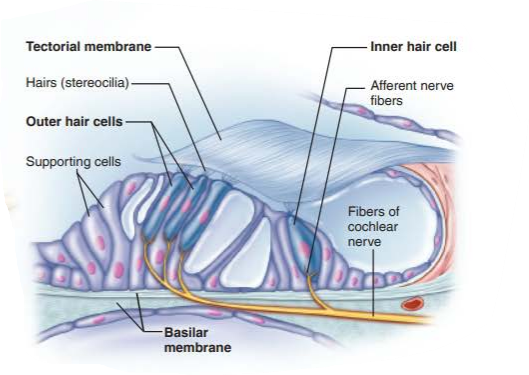
basilar membrane
supports the spiral organ in sound reception
-
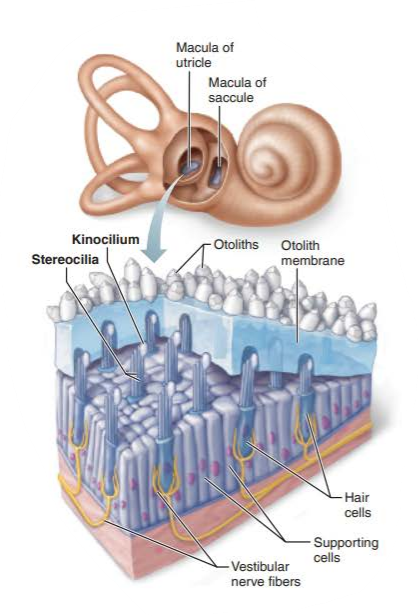
what are the hair cells of the macula?
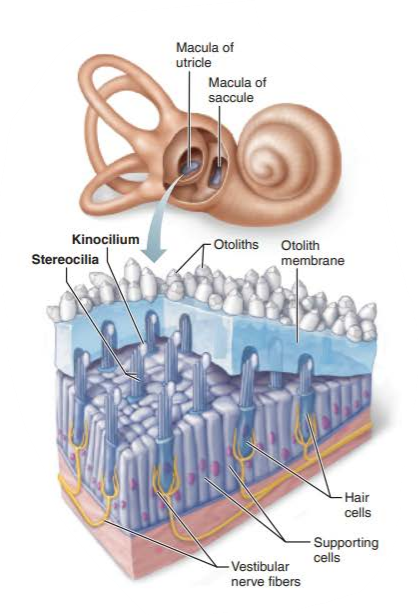
stereocilia
kinocilium
-
where are the hairs of the macula embedded in?
what does this jelly-like mass structure contain?
what are their function?
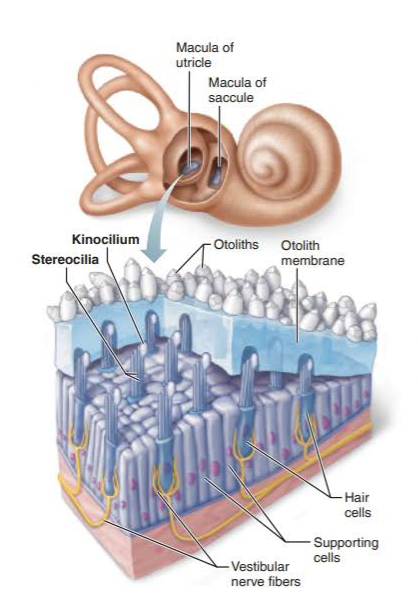
otolith membrane
otoliths
increase the membrane's weight and its resistance to changes in motion or inertia
-
in the utricle the macula is ________
this allows the utricular macula to respond best to acceleration in the _____________________________
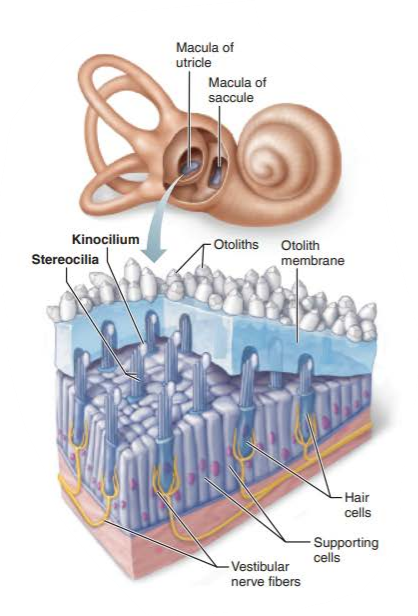
horizontal
horizontal plane and tilting the head
-
in the saccule the macula is nearly _______
this allows the saccular maculae to respond best to _______________________________________
vertical
vertical movements
-
when hairs bend toward kinocilium the:
hair cells ________
increases the _____________
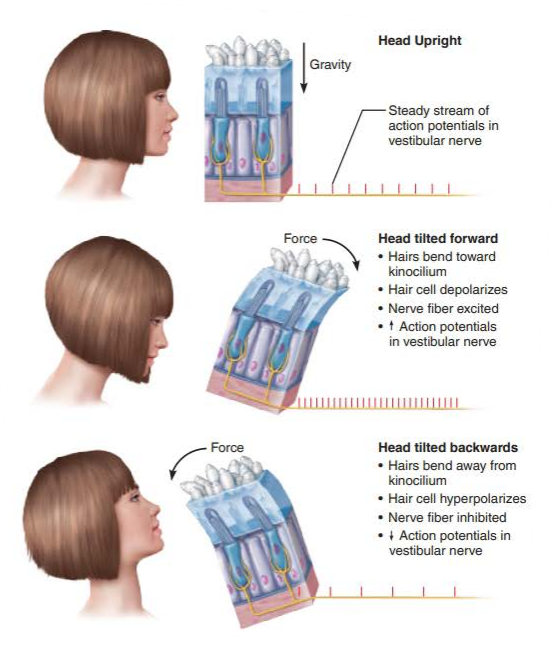
depolarize
amount of neurotransmitters released
-
when hairs bend away kinocilium
receptors ___________
release less _____________
hyperpolarize
neurotransmitters
-
instead of an otolith membrane, the crista ampullares has a pointed cap structure called the _______________
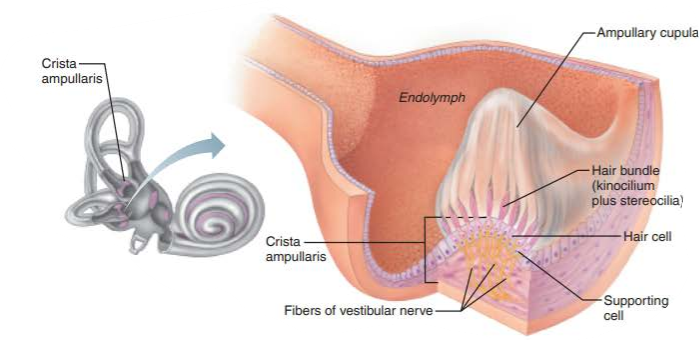
ampullary cupula
-
how are receptors of the crista ampullares activated?
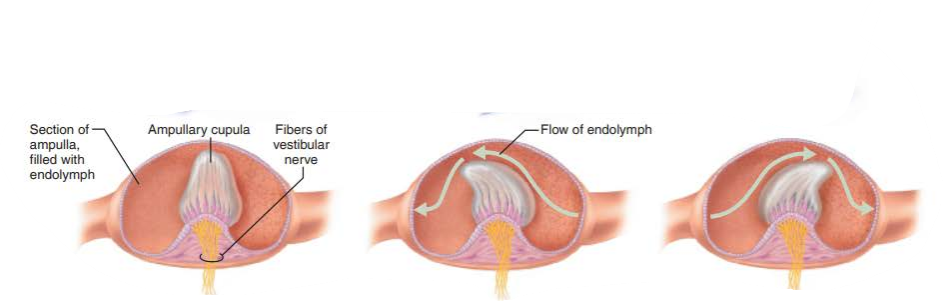
flowing endolymph bending the ampullary cupula and exciting the hair cells

