-
Define phase
a set of related activities that occur around the same time
-
Define lifecycle
a set of phases and rules for changing between them
-
Define ethnography
observation of people involved in the business process the system is meant to integrate with
-
Define use case
a description of some piece of system functionality as a series of steps (a story), as understood/observed by a user of the system
-
Define plan
a description of how limited resources (money, time, people) are to be deployed in order to accomplish a goal
-
Define design
the process of breaking a problem into pieces and defining those pieces and the interfaces between them, with the aim of enabling software development
-
Define scenario
shows how a use case can be implemented, given the architecture
-
Define Test Driven Development
a development process in which the test is written before the code
-
Define lifecycle families/models
Groups of lifecycles that are very similar
-
Waterfall model phases
RDI TDM
Requirements
(Analysis)
Design
Implementation
Testing
Deployment
Maintenance
-
In the waterfall model, can the phases be done out of order?
No
-
True or false: In the waterfall model, several phases can be worked on at once
False
-
True or false: In the waterfall model, the project cannot go back to a previous phase
True
-
Difference between waterfall model and iterative waterfall model
In iterative models, you can go back and forth between phases
-
Circular iterative model diagram
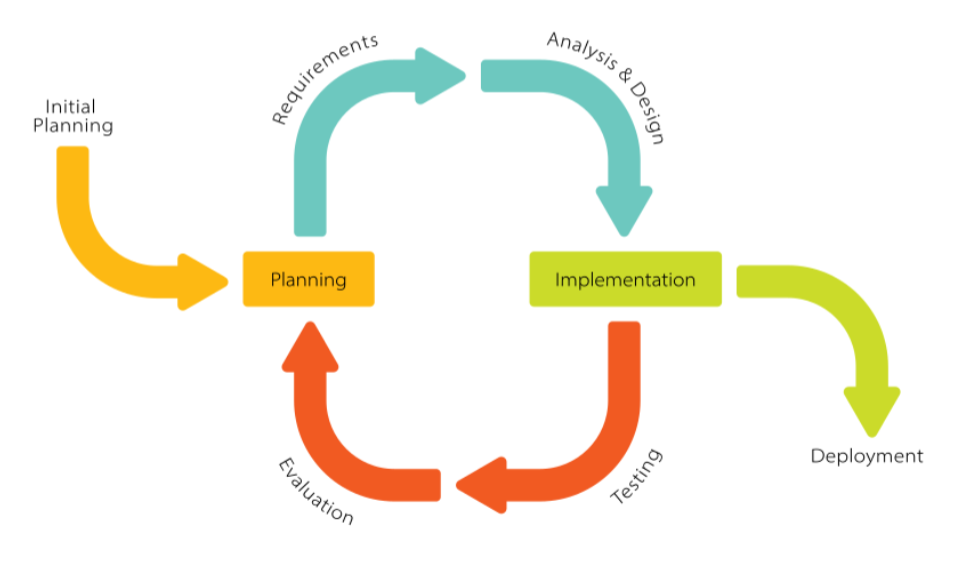
-
Agile models: general features
The number and names of the phases can differ, but the common features are:
- Spend a minimal amount of time understanding the end goal
- Instead, build something based on what is known now
- Get feedback based on what has been built in order to understand problem
better
- Use feedback to improve system
- Until the user is happy (or out of money)
-Coding and testing intermingled
- You can change to whatever phase allows you to make progress
-
Functional requirements definition
• Statements of services the system should provide, how the system should reactto particular inputs and how the system should behave in particular situations
• May also state what the system should not do
-
Non-functional requirements definition
• Constraints on the services or functions offered by the system such as timingconstraints, constraints on the development process, standards, etc.
• Often apply to the system as a whole rather than individual features or services
•Eg. response time must be under 0.5 seconds; System must not crash when user cancels order
-
Trick to tell apart functional from non-functional requirements
If you can point to a piece of code that makes something happen, that somethingis probably a functional requirement• If something is a limitation on how something can be implemented, or is theresults of many parts of the system interacting, that something is probably a non-functional requirement
-
Technical and legal issues that might prevent what the customer wants frombeing implemented fall into what category of the requirements?
Specifications
-
Requirements phase: specifications definition
TLDR: How exactly the system must achieve the requirements
Specifications are the detailed descriptions of both functional and non-functional requirements. They translate high-level requirements into precise, actionable guidelines for developers and testers. Specifications clarify the behavior of the system and how to achieve desired performance or standards.
For functional requirements: A specification might describe exact input formats, error handling, and expected outputs. For example, a specification for the login feature could specify that the system must validate user credentials against a database and display an error message for incorrect logins.
For non-functional requirements: A specification might define measurable goals such as "the application must process 100 transactions per second" or "encryption must be AES-256."
-
Spiral model phases/diagram
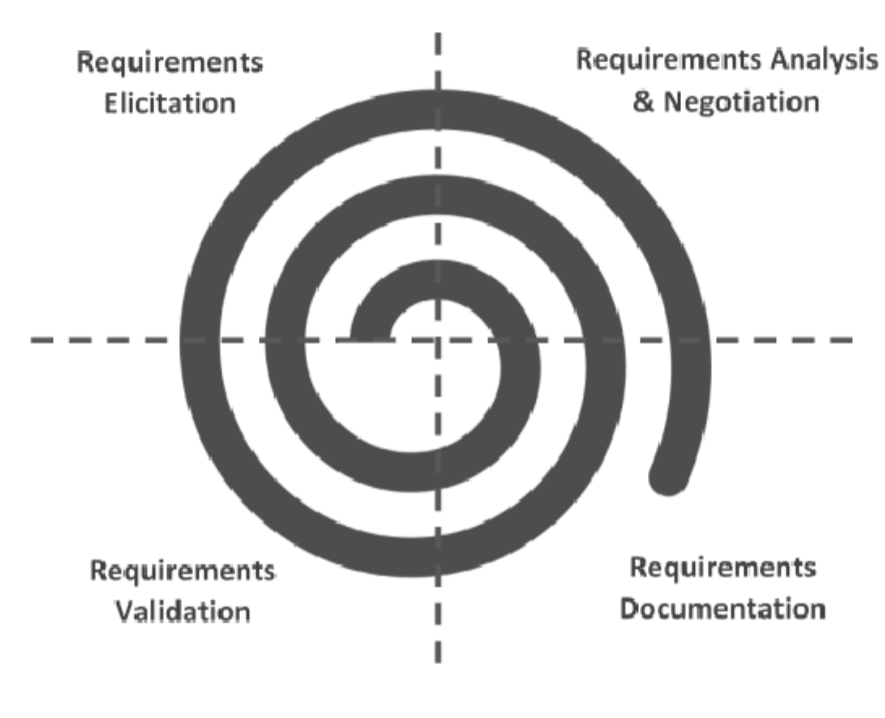
-
User story definition/example
A user story is an informal, general explanation of a software feature written fromthe perspective of the end user or customer
Eg. As a customer, I want to order a Big Mac because I am hungry
-
3 main uses of the requirements document
- Basis of contract
- Basis of planning
- Basis for testing
-
Internal/External plans definition
Internal: planning for the developers External: planning for the client/customer
-
logical and physical views in software architecture + meanings
- Logical
-shows the system's functionality and how it is organized into components-the view most people think of when they think of a software architecture-typically represented using class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and
activity diagrams
- Physical
-shows the system's physical components and how they are interconnected-often minimal for software-only systems-can be useful for systems where part of the processing or storage
happens in the cloud-Or for an embedded system, like a kiosk
-typically represented using deployment diagrams and network diagrams
-
Architectural scenario definition
shows how a use case can be implemented, given the architecture
-
Provess and development views in software architecture + meanings
- Process
-shows the system's dynamic behavior, including how its componentsinteract with each other and with the environment-Useful for systems that engage in a lot of parallel processing-Or distributed systems where otherwise isolated components must
interact periodically-typically represented using state diagrams and sequence diagrams
- Development
-depicts a system from the standpoint of a programmer and is concerned
with software organization and administration-typically includes:-Architectural layers-Communications paths-Packages-Starts to look like the logical view as details are added-Or on smaller systems
-
4 qualities of a good design
CorrectnessUnderstandabilityEfficiencyMaintainability
-
Meaning of reuse in implementation phase
Using code/software that someone else wrote
-
Define coupling
a measure of how much one piece of software depends on another
-
6 types of coupling from best to worst, + definitions
-Data
-Same parameters/arguments used in different modules
-Stamp
- Modules share a composite data structure (eg. an Object), but not all the
elements are used by each module
-Control
-One module controls the behavior of another module
-External
-The degree to which the system relies on external entities
-Common
-two or more modules in the system share (access/manipulate) global
data
- Content
-one module directly accesses or modifies the content of another module
-
6 types of cohesion (of elements within a module) from best to worst, + definitions
-Functional
-elements perform a single, well-defined task or function
-Sequential
-elements are arranged in a specific sequence, with the output of one
element serving as the input for the next element
-Communicational
-elements operate on the same input data or share data through
parameters, but the data itself is external to the module
-Procedural
-elements are grouped because they must happen in a particular order to
achieve a singular goal but otherwise have nothing to do with each other
-Temporal
-elements are executed at the same time or within the
same timeframe in order to fulfill some purpose, but don't have to
happen in any particular order
-Coincidental
-Elements are not related to each other
-
Define software measurement
Attempting to assign a numeric value to an attribute of asoftware project/process
-
3 areas for software measurement
Planning, Development, Testing/QA
-
Software measurement: factors/constraints that make make development harder can be distilled into ______ _______. These are usually used in planning.
function points
-
Notes software measurement
One way to measure code complexity is to use cyclomatic complexity, which usually involves creating a control graph of the program's logic and computing an equation that uses the number of nodes and edges
-
Software measurement: brief definition of Planning, Monitoring and Managing
- Planning (how do we think it might go?)
- Monitoring (how is it going?)
- Managing (how can it be controlled?)
-
Software measurement brings us from the idea of ________ to _________
Planning, Monitoring
-
Cyclomatic complexity (M) formula with edges (E) and nodes (N)
M = E – N + 2
-
Reasons why software monitoring is so hard
- Every project is new
- Many managers have never coded
- So much money is on the line
- Difficult to change course
- Time pressure
- Programmer misjudgment due to optimism
- History of failure in software projects
-
Why is it so hard to measure progress in software projects?
- Setbacks are inevitable
- Change affects reqs and goals
-
Bitterman’s First Law of Software Metrics
Any measure of coding productivity will punish better coders
-
Goodhart's Law
When a measure becomes a target, it ceases to be a good measure
-
Bitterman's Law of Measurement
Never be measured
-
Testing: verification vs validation
- Verification: defects in construction
- Validation: defects in functionality
-
Code inspections are part of (verification/validation?) testing
verification
-
Functional testing, non-functional testing, sanity testing are part of (verification/validation?) testing
validation
-
What does the scribe do during code inspection
Records results
-
Who in the company should never be a part of code inspection?
Managers
-
Test doubles definition
programming constructs used in testing to simulate the behavior of real objects or components
-
Test doubles examples
Dummy, Stub, Mock, Fake
-
4 types of maintenance + definitions
Perfective
-Aims to add new features over time
Corrective
-Aims to fix bugs
Adaptive
-Modifying the software system to adapt to changes in the environment
Preventive
-Modifying the software to prevent future problems
-
Regression Tests definition
• The single most important thing a fix can do is not break anything that previouslyworked• The best way to ensure this is to run every test against each new fix to see whathappens• The best way to do that is to automate running all tests• When tests are used this way they are called regression tests, and the process ofrunning them automatically is called automated regression testing
-
TDD definition
Test Driven Development
- A way of building software where the tests are written first- TDD checks units one by one
- Both tests and units should be small
-
Design degradation definition
Degradation of software design- Caused by changing requirements- This results in changes to software that violate the original design philosophy (i.e.hacks)- Also known as design rot
• It is not that the design has gotten worse• It is that the problem has changed, and the original design is no longer such a good fit
-
What is used to counteract design degradation and too much dependency management
SOLID
-
Dependency management/maintenance definition
The process of minimizing dependencies, and understanding the remainingones
-
_________ ________ should be created to manage dependencies between modules in an application
dependency firewalls
-
SOLID acronym
Simple responsibility principle
Open/Closed principle
Liskov Substitution
Interface Segregation
Dependency Inversion
-
Open/Closed principle definition
software entities should be open for extension, but closed for modification (extension does not require modification)
-
Liskov Substitution definition
Derived classes must be substitutable for their base classes
-
Interface segregation definition
Clients should not be forced to depend upon interfaces that they do not use
-
What SOLID principle is being violated here?
Interface segregation
-
What SOLID principle is being violated here?
Liskov Substitution
-
What SOLID principle is being violated here?
Open/Closed
-
Dependency Inversion definition
A Class should depend on Abstraction, not Implementation
-
Waterfall model: The work product for each phase is a typically a __________
document
-
4 main ideals of agile
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Working software over comprehensive documentation
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following a plan
-
5 Xp values
Communication
Simplicity
Feedback
Courage
Respect
-
What lifecycle does the planning game belong to
Xp
-
3 Xp practices
Pair Programming, Test-Driven Development, and Continuous Integration
-
Xp: define continuous integration
Check in code early, check in code often.
-
What lifecycle does collective code ownership (anyone can refactor code) belong to
Xp
-
Xp: An iteration is the time during which a team will work on a ....
set of cards
-
Parts of an iteration (Xp)
planning (The planning game), coding (sitting together, with an on-site customer), testing, and delivering a working increment of the product. Meetings at the beginning and end of an iteration.

