-
Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia are able to:
Produce type III secretion systems
•Introduce proteins into host cells
•Inhibit phagocytosis
•Rearrange the cytoskeletons of eukaryotic cells
•Induce apoptosis
-
Eggs and poultry are common sources of salmonella and lead to:
Salmonellosis and typhoid fever
-
The process of salmonellosis 1-3
- Salmonella attaches via adhesion
- To cells lining the small intestine.
- Salmonella triggers endocytosis.
once in the GI tract, they multiply w/in endocytic vesicle.
-
in step 4 After Salmonella kills the host in the GI tract the effect that occur are:
induces fever, cramps, and diarrhea
-
Step 5 what happens when salmonella enters the bloodstream?
it can infect tissues throughout your body causing meningitis and endocarditis
-
Characteristics of salmonella
Bacilli are rod-shaped and have flagella all around.
uses a needle-like structure to inject bacteria in the host cell
-
Infected cells release pro-inflammatory cytokines causing an inflammatory response.
When salmonella travels through the GI tract.
-
Life-threatening fever that can lead to death.
Typhoid
-
Typhoid fever is caused by
Salmonella typhi member of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
-
Pathogenesis of Shigella
- Using a type III secretion system (TSS),
- injects several bacterial effectors ultimately leading to bacterial internalization within a vacuole.
- It escapes rapidly from the vacuole, replicates within the cytosol, and spreads from cell to cell.
-
Salmonella Typhoid
•Caused by Salmonella enterica
•Humans are the only host
•Carriers are often asymptomatic
•Bacteria ingested in contaminated food or water.
-
Salmonella Typhoid fever
•Bacteria pass through intestines to various organs replicates in the macrophage
•Causes gastroenteritis, bacteremia, and peritonitis
-
Shigella
-Enterotoxin
-Non-motile
-Part of the Enterobacteriaceae family,
- gram-negative rod-shaped pathogenic bacteria
- They are non-motile, non-encapsulated, and facultative anaerobes that do not ferment lactose, or do so slowly
-
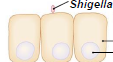
Process Shigella 1
Shigella attaches to the epithelial cells of the colon.
-
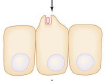
Process Shigella 2
Shigella triggers endocytosis.
Nucleus
Epithelial cell
-
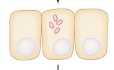
Process Shigella 3
Shigella multiplies in the cytosol.
-
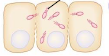
Process Shigella 4
Shigella invades neighboring epithelial cells, thus avoiding immune defenses. (Actin fibers)
-
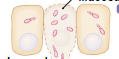
Process Shigella 5
An Abscess forms as epithelial cells are killed by the infection. (Mucosal abscess)
-
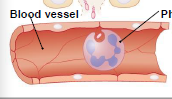
Process Shigella 6
Blood vessel
Shigella that enters the blood is quickly phagocytized and destroyed. No bacteremia. Phagocyte

