-
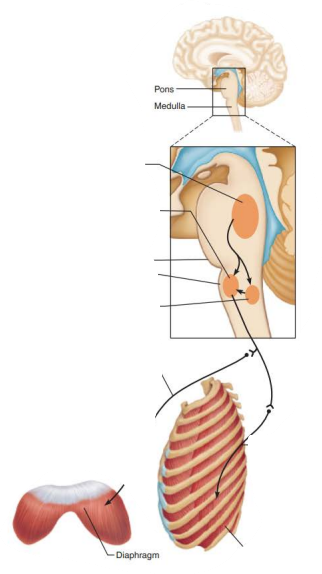
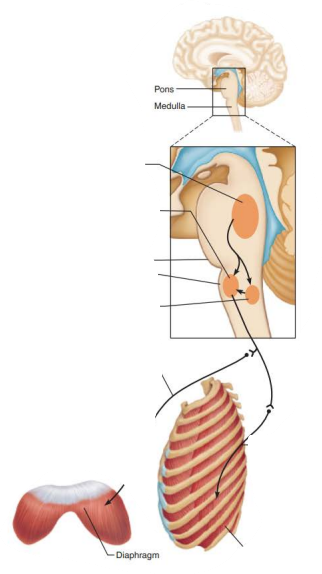
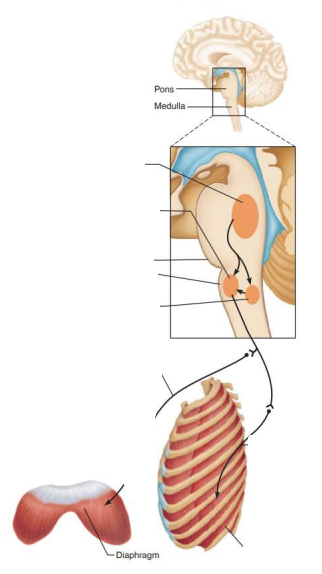
Role of CNS in respiration
Network of neurons that extends in the ventral brain stem from the spinal cord to the pons medulla junction
Ventral respiratory group
-
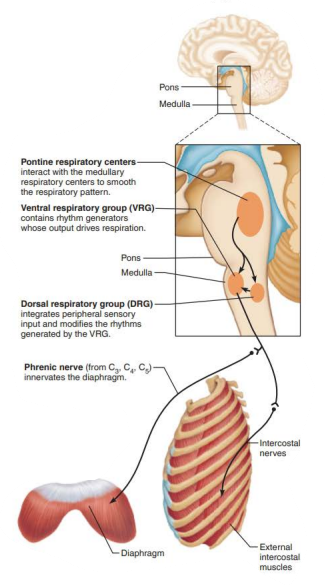
Role of CNS in respiration
Rhythm generating and integrative center
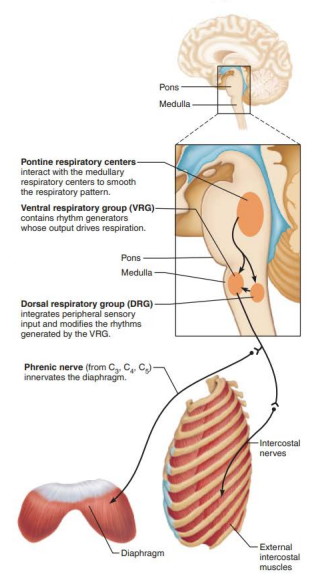
ventral respiratory group
-
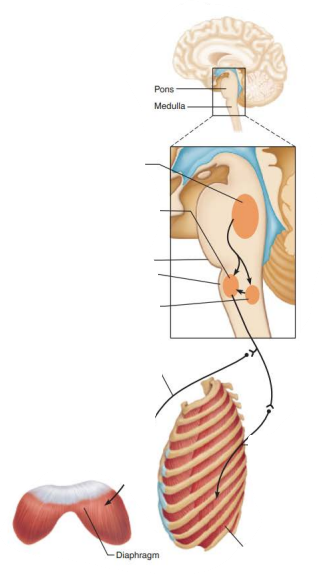
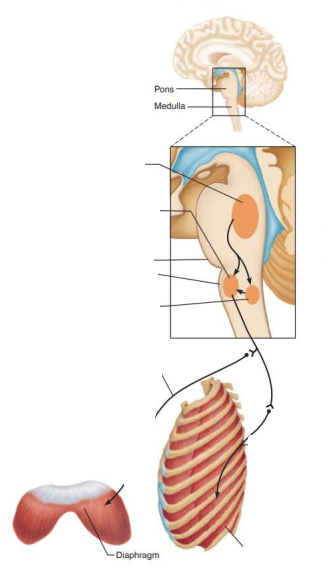
Role of CNS in respiration
____________ ____________ ____________
___________ __________
Impulses travel along ________ and _________ nerves to excite ________________ and ___________ ___________ muscles
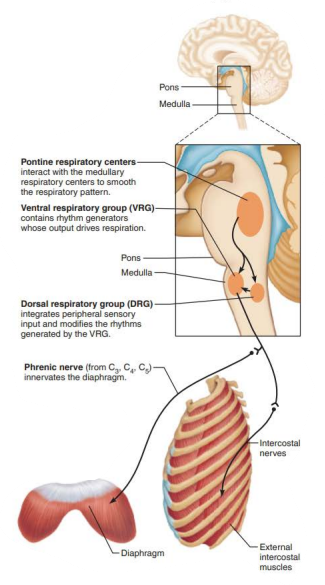
ventral respiratory group
inspiratory neurons
phrenic
intercostal
diaphragm
external intercostal
-
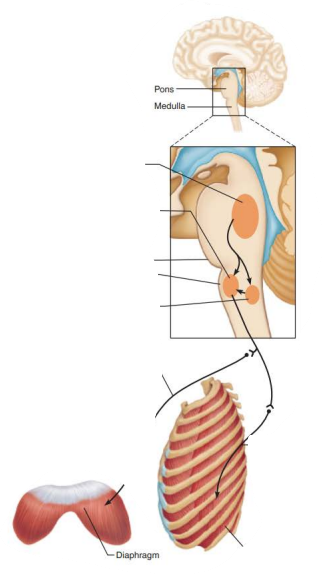
Role of CNS in respiration
_________________ _______________ ____________
__________ ____________
Impulses causes output to _______ and ___________ occurs as ________________ muscles _______ and lungs _______
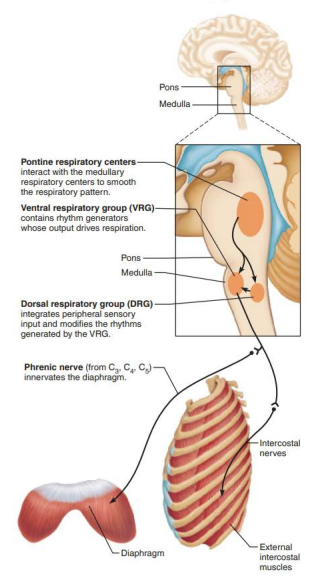
ventral respiratory group
expiratory neurons
stop
expiration
inspiratory
relax
recoil
-
Role of CNS in respiration
what generates gasping during severe hypoxia to restore O2 to the brain?
ventral respiratory group
-
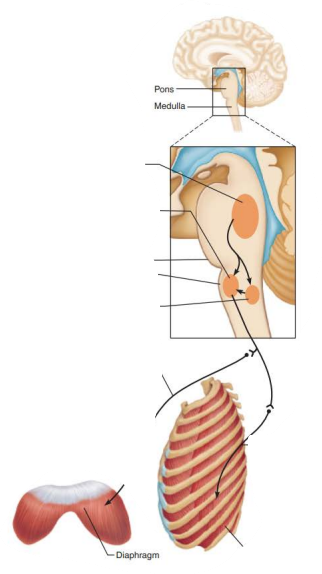
Role of CNS in respiration
when does respiration stop?
when a cluster of VRG neurons become suppressed from overdosing on morphine or alcohol
-
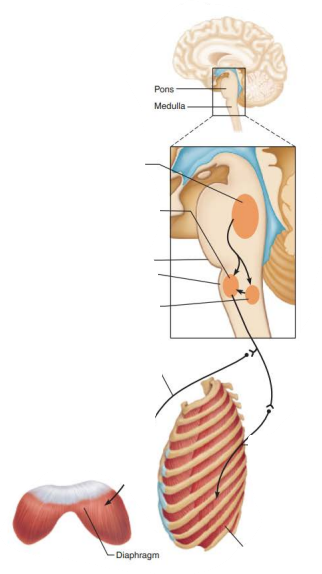
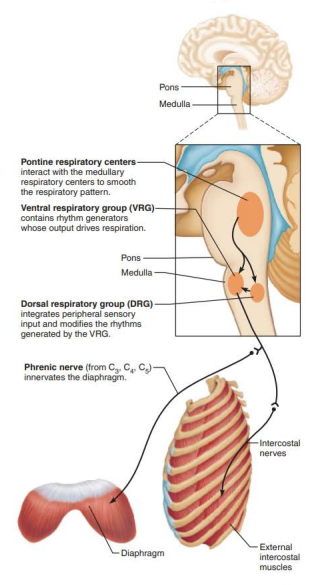
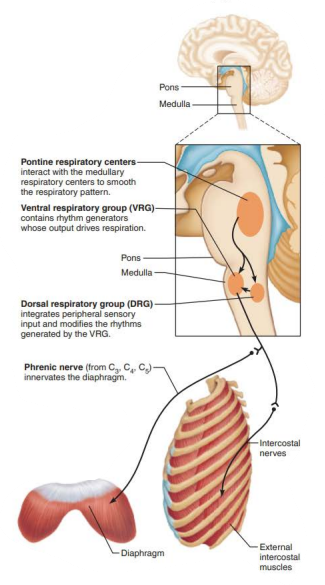
Role of CNS in respiration
_____________ ______________ _______________
Located dorsally near root of cranial nerve IX (______________)
dorsal respiratory group
glossopharyngeal
-
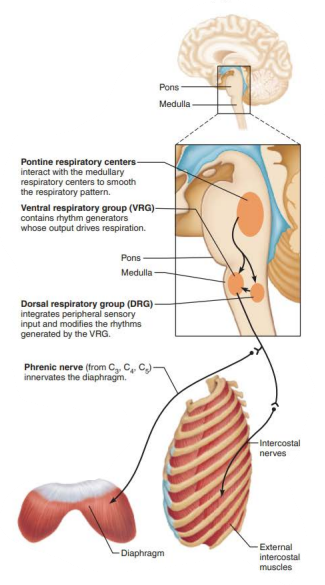
Role of CNS in respiration
_______________ _____________ ____________
________ input from __________ and _________ chemoreceptors
Communicates this with ____
dorsal respiratory group
integrates
peripheral
central
VRG
-
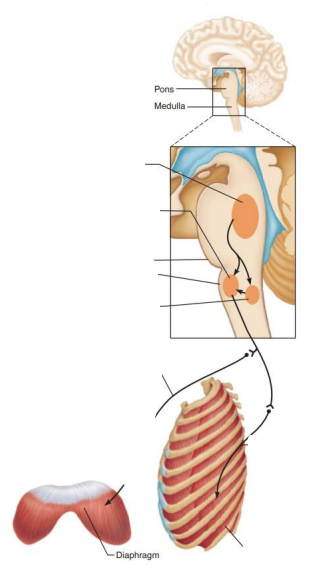
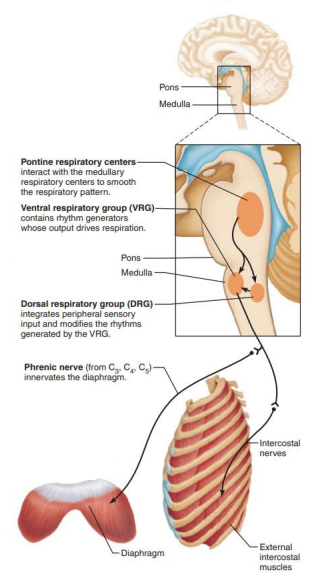
Role of CNS in respiration
___________ ___________ ______________
Receives input from higher brain centers and various sensory receptors
Influence and modify the activity of __________ _________
__________ out the transition from ___________ to __________ and vice versa
____________ impulses to ____ of medulla
Modifies and fine-tunes breathing rhythms during ____________ , ______, and _______
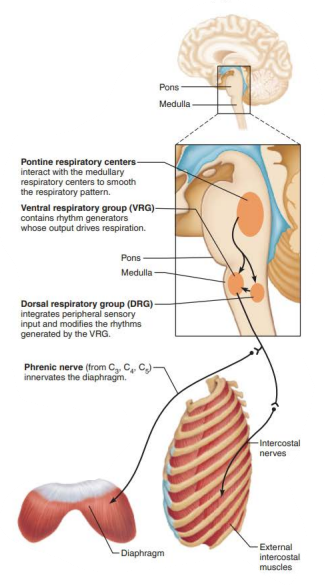
Pontine Respiratory Group
medullary neurons
smooth
inspiration
expiration
transmits
VRG
vocalization
sleep
exercise
-
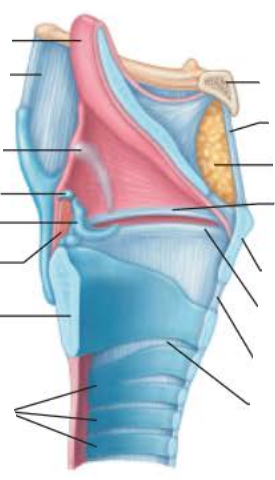
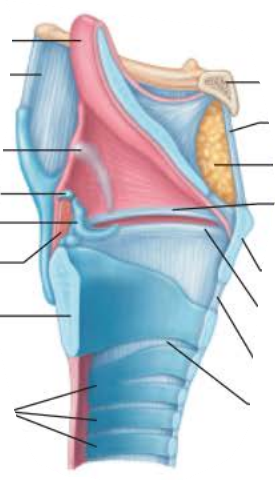
Role of the larynx in voice production 1/6
_______ _______ _______ and ________ ___ ________ changes with the action of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles
Most of these muscles move ___________ cartilages
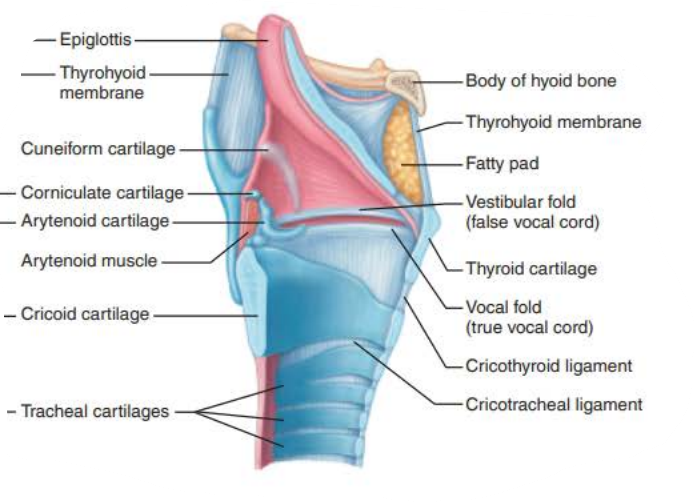
vocal fold length
size of glottis
arytenoid
-
Role of the larynx in voice production 2/6
As________ and __________ changes in ______ ________ change so does the sound
The _______ the vocal cords the faster they ______ and the higher the _______
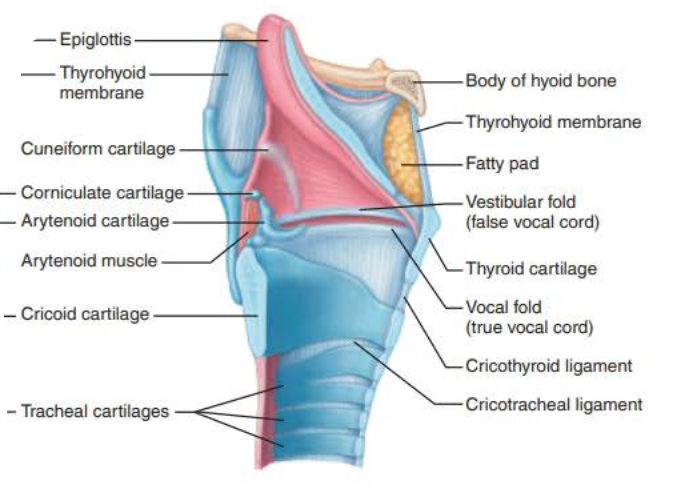
length
tension
vocal folds
tenser
vibrate
pitch
-
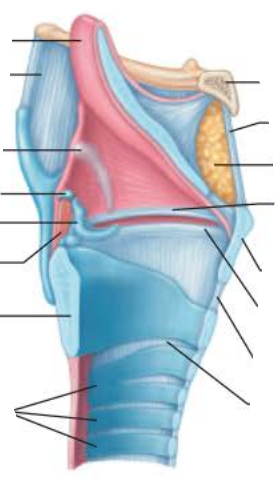
Role of the larynx in voice production 3/6
Loudness of voice depends on the force at which ___ _____ _____ ______ ______
The greater the _____, the stronger the _________, the ______ the sound
air rushes over vocal folds
force
vibration
louder
-
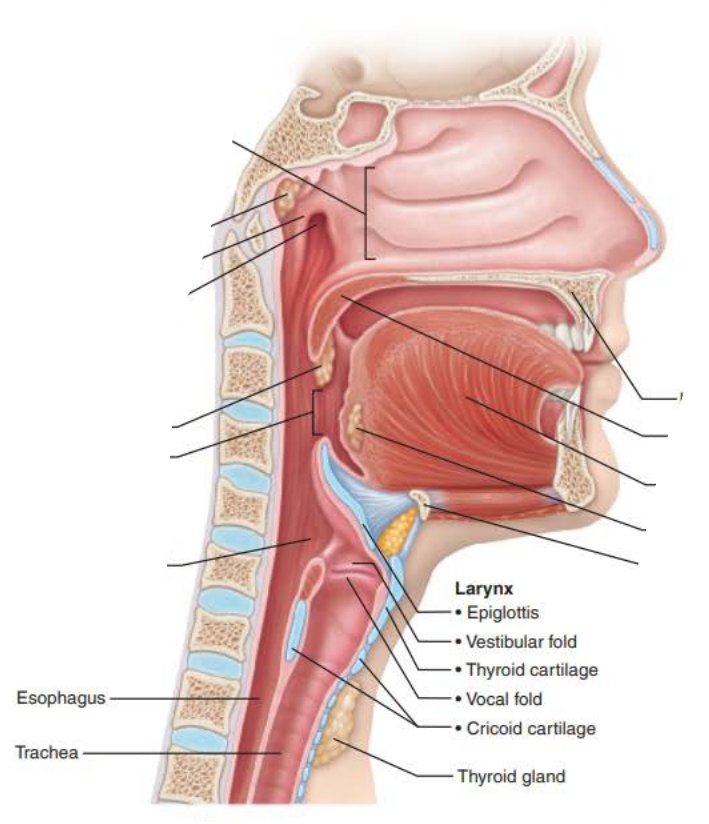
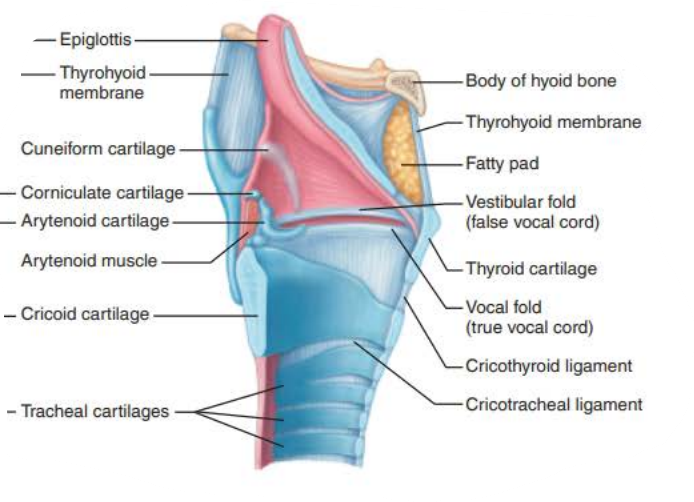
Role of the larynx in voice production 4/6
Perceived quality of voice depends on:
Length of ________
__________ _________ to __________ and _________ sound quality
pharynx
resonating chamber
amplify
enhance
-
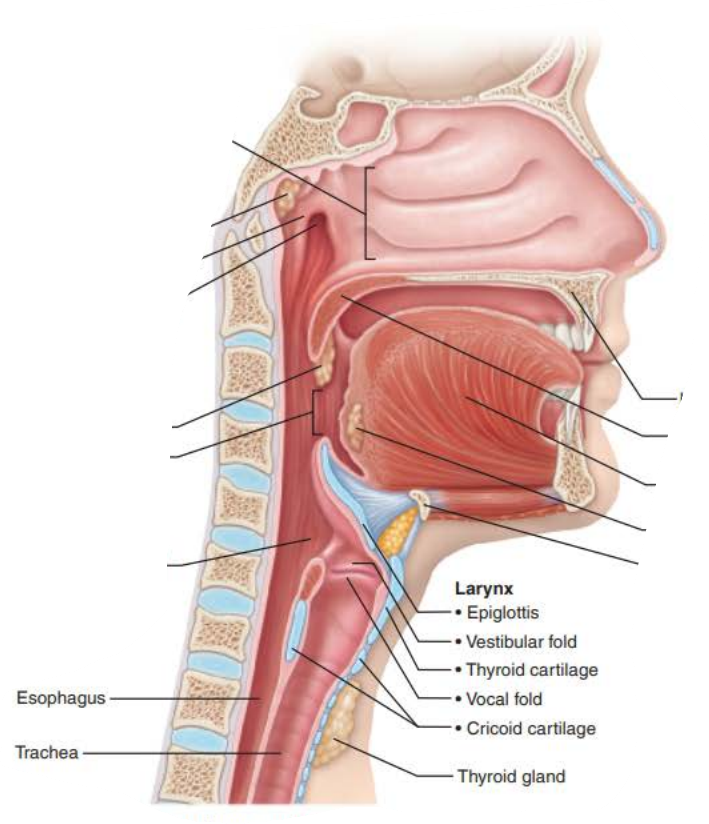
Role of the larynx in voice production 5/6
_____ , _____ , and _____ cavities
_______ ___________
oral
nasal
sinus
vocal resonance
-
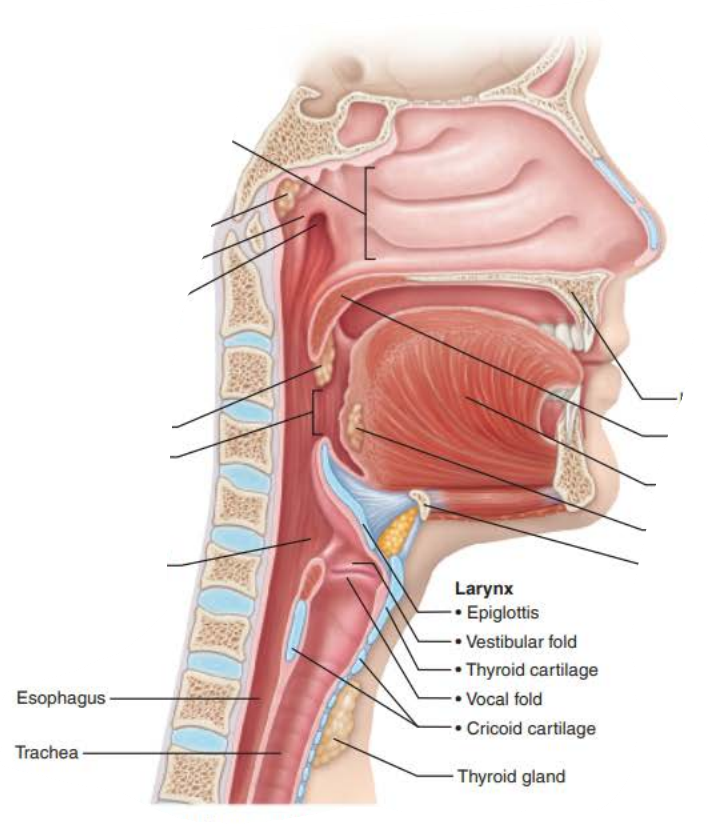
Role of the larynx in voice production 6/6
_________ in the __________ , _______ , _____ _______, and the ___ the shape the sound
_____________
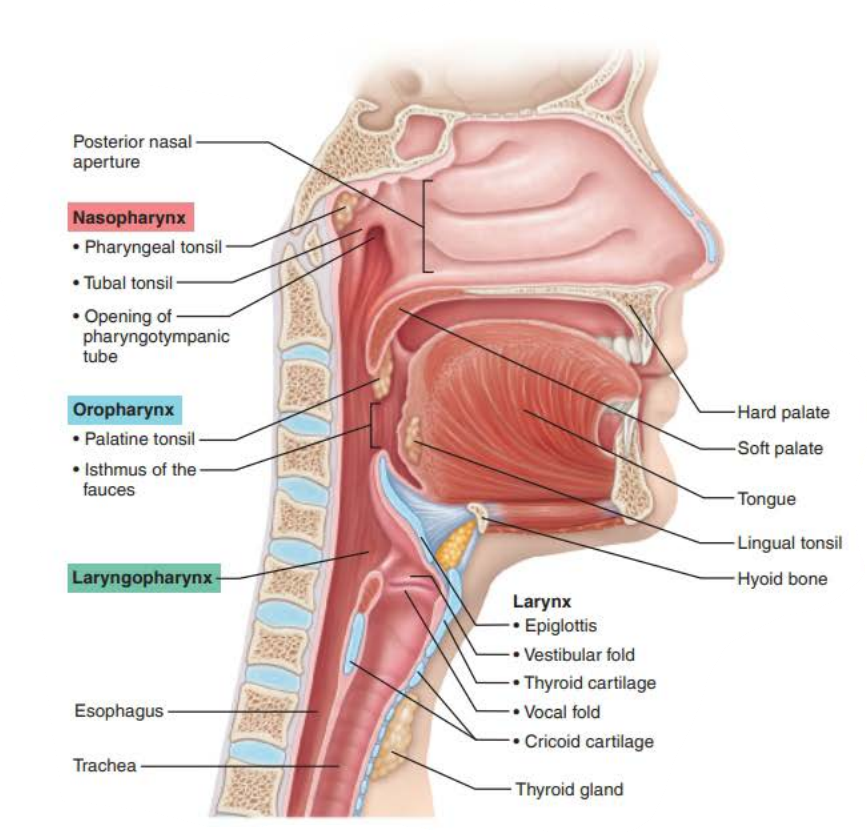
muscles
pharynx
tongue
soft palate
lips
enunciation
-
_________ _______
Function
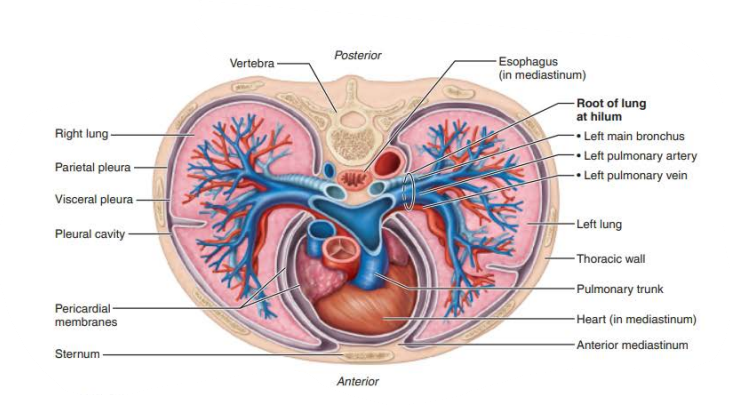
Produced by the pleura and fills the slit-like pleural cavity
____________ secretion that allows the ________ to glide easily over the _________ ________ during _____________ ____________
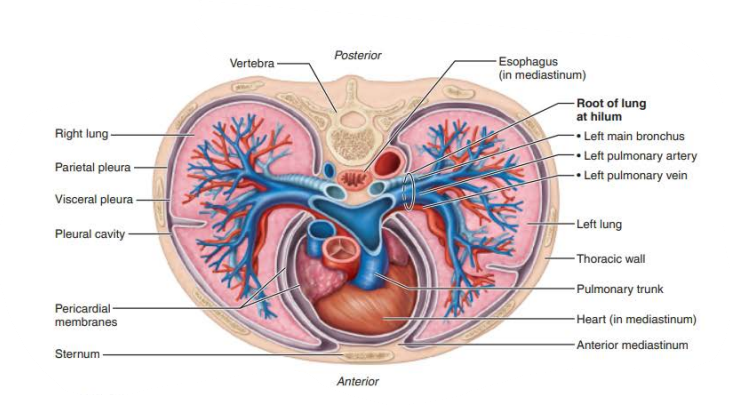
pleural fluid
lubricating
lungs
thorax wall
breathing movements
-
________ __________ of _________ _________ resists ____________ of the pleura
surface tension
pleural fluid
separation
-
______________ Stimulation
Dilates ____________
Decreased ________ ___________
Increases airflow to ________
sympathetic
bronchioles
airflow resistance
alveoli
-
______________ Stimulation
Constricts ______________
Increased __ _____ _________
Decreases airflow to ______
Parasympathetic
bronchioles
air flow resistance
alveoli
-
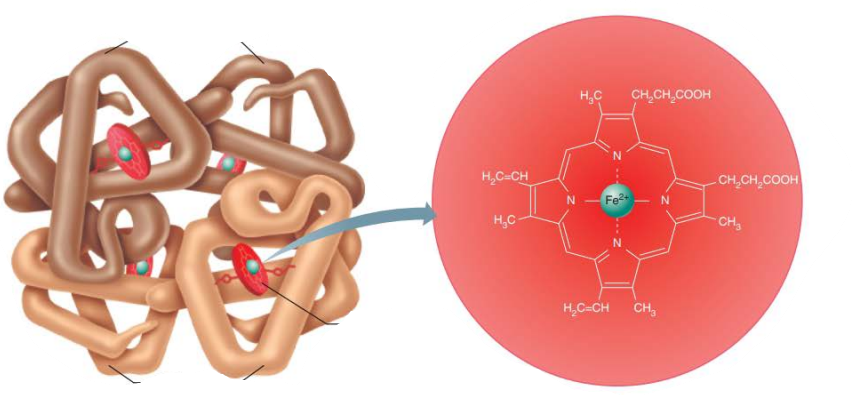
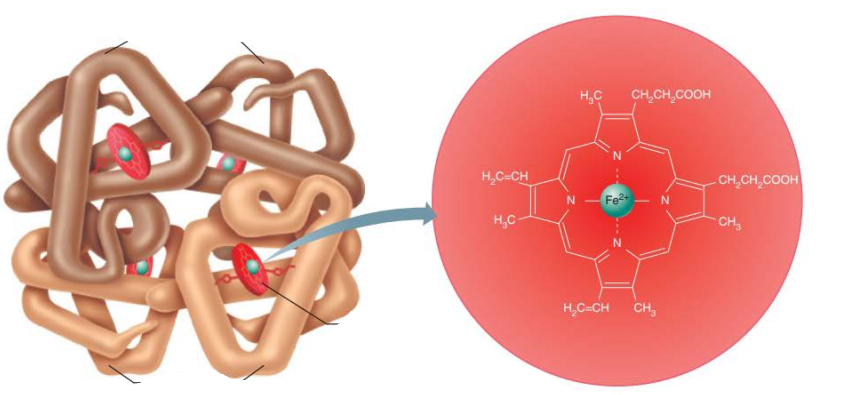
Hemoglobin
Structure
_____
___ pigment
Each Heme group contains an _____ ___ in the center
__ total
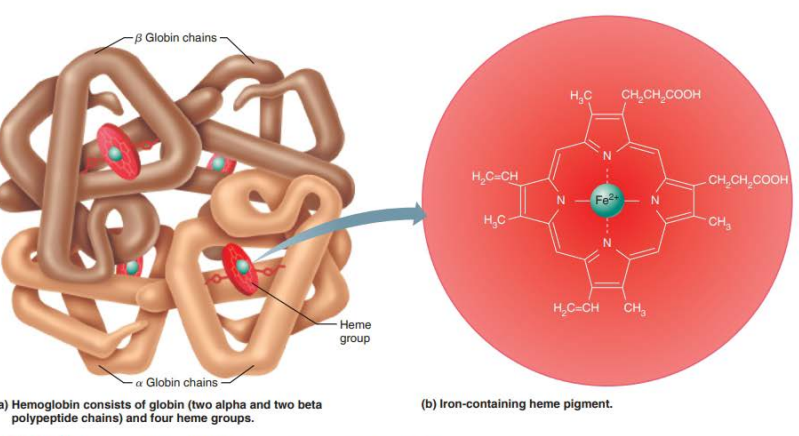
heme
red
iron ion
4
-
Hemoglobin
Structure
______
Four ____________ ______
Two _____ (α)
Two _____ (β)
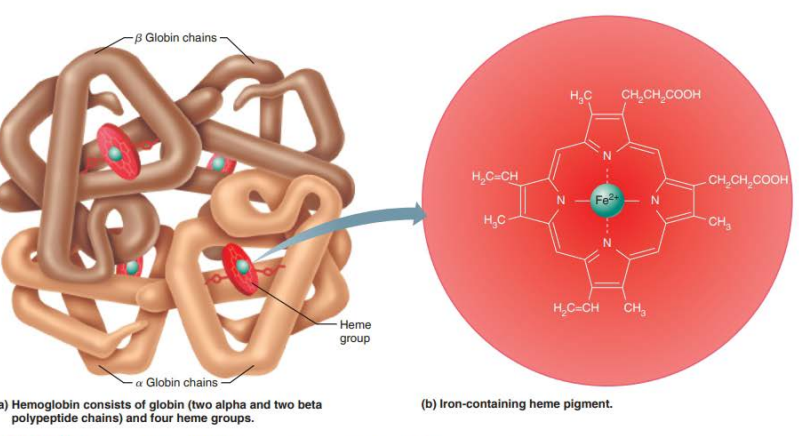
globin
polypeptide chains
alpha
beta
-
Surface Tension 1/5
___-______ _________
Molecules of the ______ are more strongly attracted to each other than ___ molecules
__________ _________ produces _________ at the ______ _______
Draws the liquid molecules closer and reduces contact with gas molecules
Resists any force that tends to increase the surface area of the liquid
gas-liquid boundary
liquid
gas
unequal attraction
tension
liquid surface
-
Surface Tension 2/5
_______ is a major component of what coats the __________ ____
Because of the ________ ______, water is always __________ the _______ to their _______ possible size
water
alveolar walls
surface tension
compressing
alveoli
smallest
-
Surface Tension 3/5
If the film coating the ________ were pure _____ it would __________ the _________ between breaths due to _________ __________
alveoli
water
collapse
surface tension
-
Surface Tension 4/5
__________ _____ contains ___________
Detergent-like complex of _______ and ________ produced by ____ ___ _______ ____
alveolar film
surfactant
lipids
proteins
type II alveolar cells
-
Surface Tension 5/5
_____________
__________ the ___________ of ______ molecules
Decreases the amount of _________ _________ in the alveolar fluid discouraging ________ _________
surfactant
decreases
cohesiveness
water
surface tension
alveolar collapse
-
Total pressure exerted by a mixture of gasses is the sum of the pressures exerted independently by each gas in a mixture
________ exerted by each ___ is a ________ __________
Dalton's law of partial pressures
pressure
gas
partial pressure
-
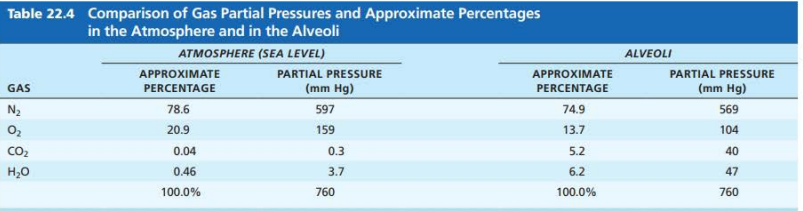
Atmospheric Pressure at sea level
__________ ___________ ___________ ________ ______________
( ____ ___ __ )
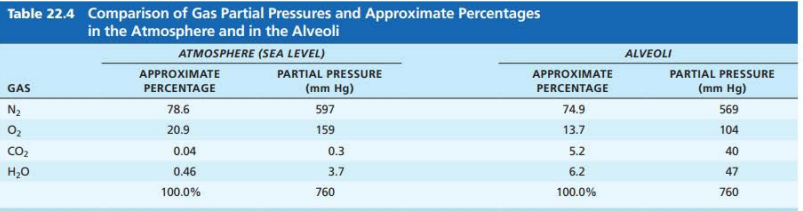
pressure exerted by the gasses surrounding the body
760 mm Hg
-
Atmosphere (Sea Level)
Gas: Nitrogen (N2)
Percentage: ____
Partial pressure _____
78.6%
597 mm Hg
-
Atmosphere (Sea Level)
Gas: Oxygen (O2)
Percentage: ____
Partial pressure _____
20.9%
159 mm Hg
-
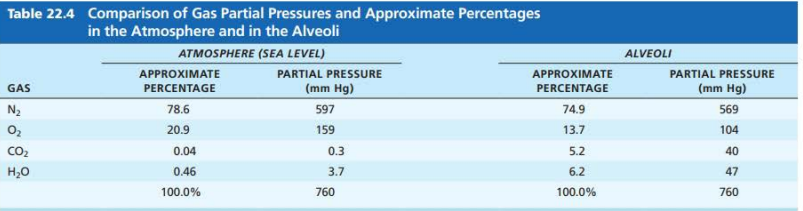
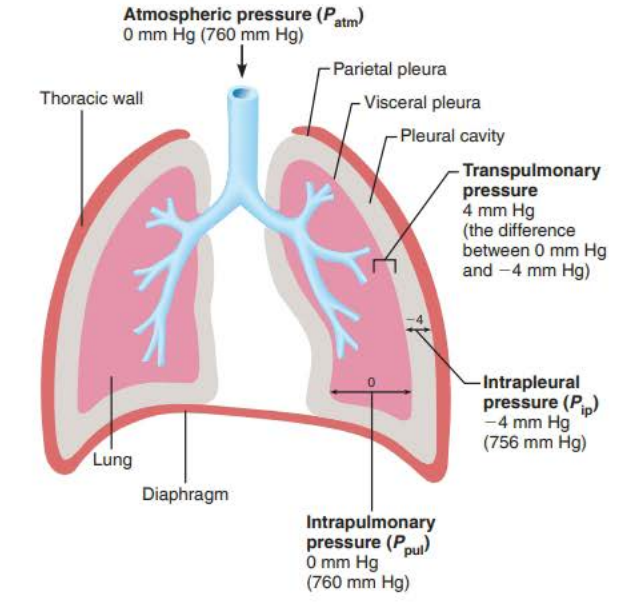
_______________ __________
Pressure in the alveoli
Always equalizes with the atmospheric pressure
760 mm Hg
intrapulmonary pressure
-
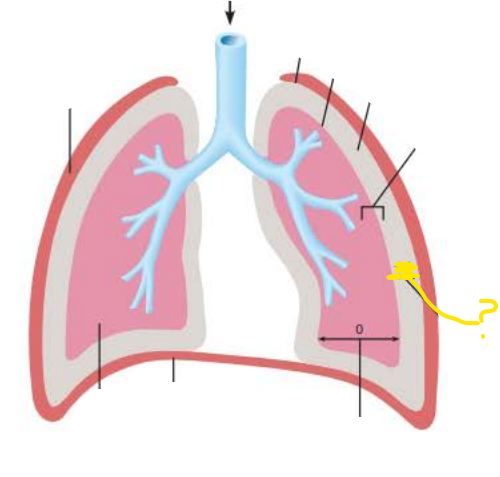
_____________ ____________
Pressure in the pleural cavity
Always 4mm Hg less than Ppul
(756 mm Hg)
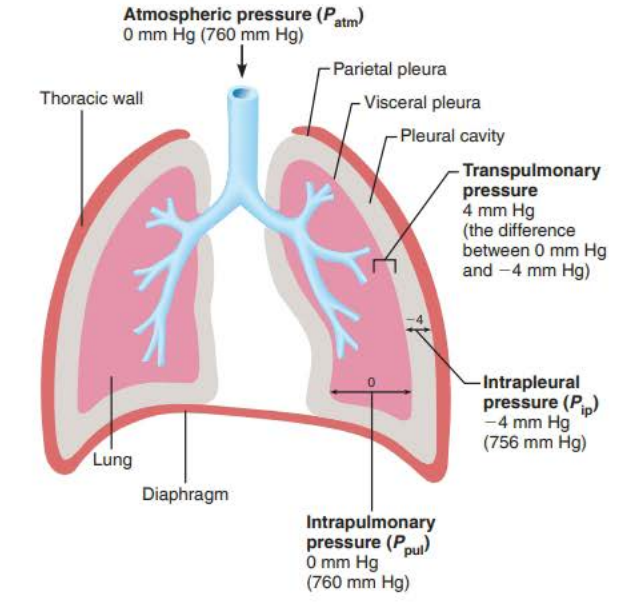
intrapleural pressure
-
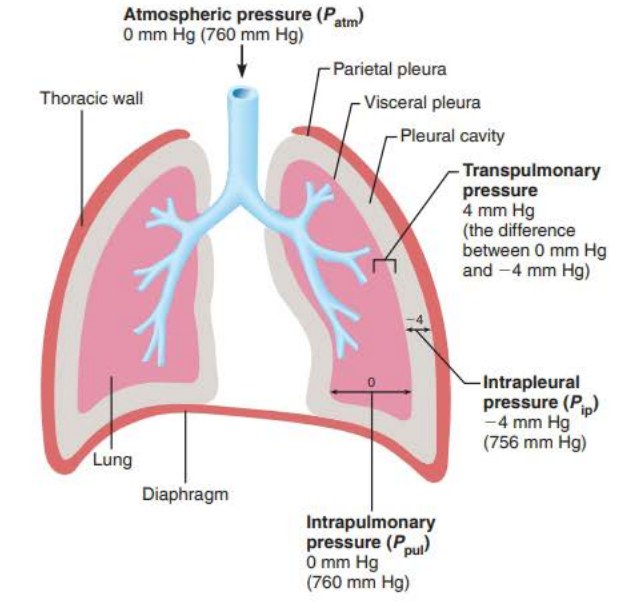
Why intrapleural pressure is lower (1/3)
Two forces act to pull the _________ _______ (lungs) away from the _______ _____ (parietal pleura) causing the lungs to collapse
1. Lungs’ natural tendency to ________ makes them assume the _________ size possible
2. _______ _________ of ________ ________ makes them assume the smallest size possible
visceral pleura
thorax wall
recoil
smallest
surface tension
alveolar fluid
-
Why intrapleural pressure is lower (2/3)
Two forces act to pull the visceral pleura (lungs) away from the thorax wall (parietal pleura) causing the lungs to collapse
1. Lungs’ natural tendency to recoil makes them assume the smallest size possible
2. Surface tension of alveolar fluid makes them assume the smallest size possible
These _____ __________ ______ are opposed by the natural _________ of the ______ ______
Force that tends to pull the thorax outward and enlarge the lungs
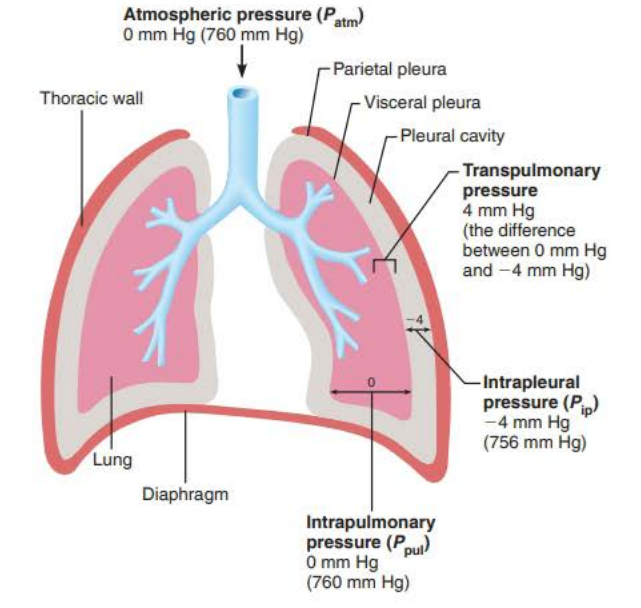
lung collapsing forces
opposed
elasticity
chest wall
-
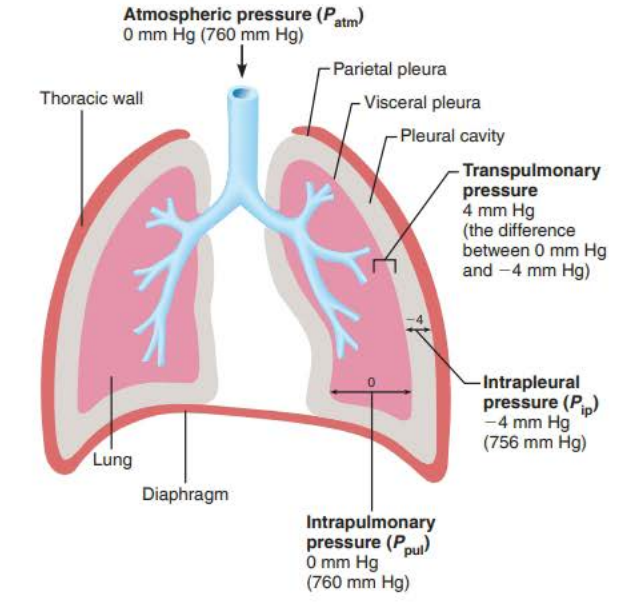
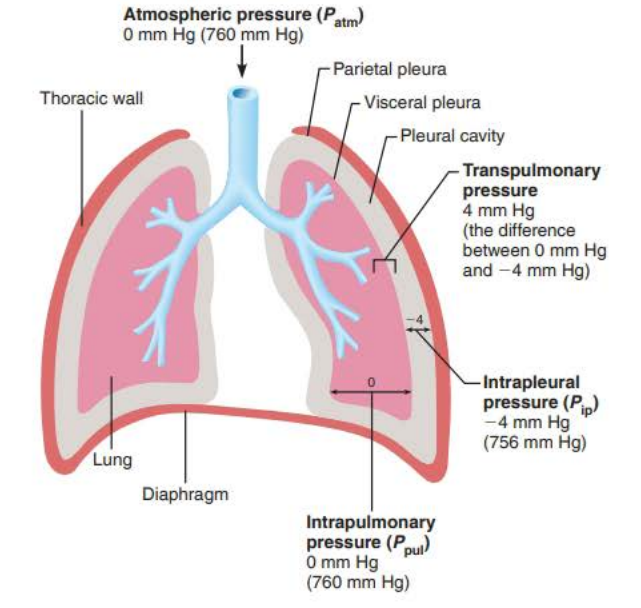
Why intrapleural pressure is lower (3/3)
______ _____ acts as an _________ force between the _____ and ________ ____
Allows _______ to slide but causes them to remain ______ together
Requires _________ ________ ___ __________
Net result of these forces is a _________ ______________
_ ___ __ less than _________________ __________ and the atmospheric pressure it is equal to
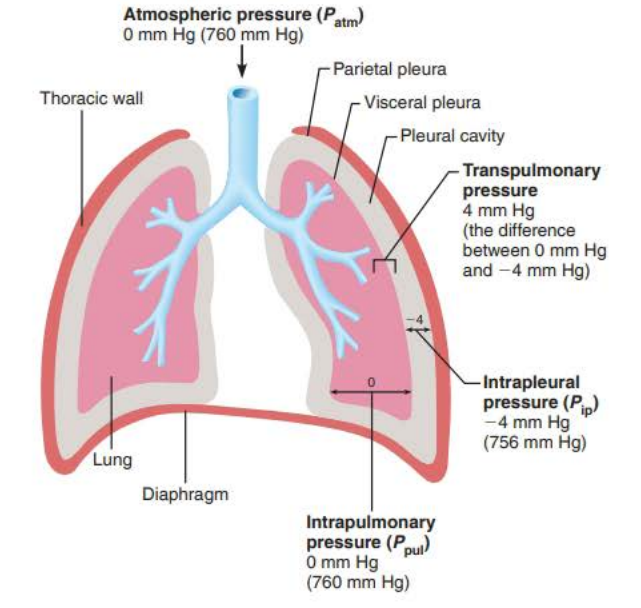
pleural fluid
adhesive
lungs
thorax wall
pleurae
stuck
extreme force to separate
negative intrapleural pressure
4mm Hg
intrapulmonary pressure
-
Pulmonary Circulation
_____________ _______
transports ___-poor and ___-laden blood to the ______ for oxygenation and carbon dioxide _________
pulmonary arteries
O2
CO2
lungs
unloading
-
Bronchial Circulation
___________ __________
Arise from _____
Enter lungs at _____
Run along ___________ _____
Provide ___________ _________ _______ to all _____ ______ except ________
bronchial arteries
aorta
hilum
branching bronchi
oxygenated systemic blood
lung tissue
alveoli
-
Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
The amount of ________ carried by ________ depends on the amount of ________ _________ _________ (PO2)
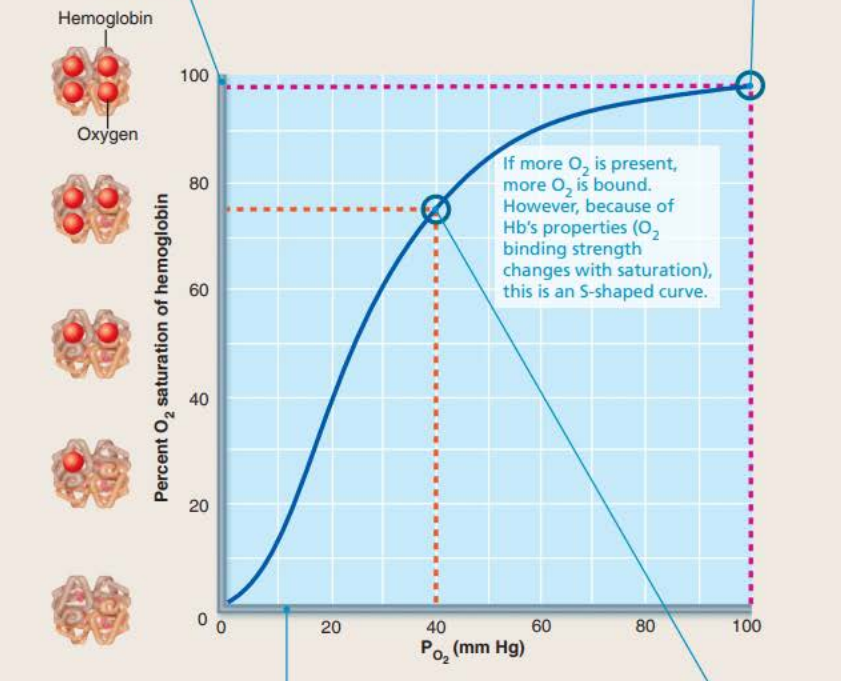
oxygen
hemoglobin
oxygen available locally
-
Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
If more _______ is ______
More _______ is _______
In the lungs PO2 is at 100 mm Hg
Causes hemoglobin to be almost fully saturated with O2 at 98%
4 bound oxygen molecules
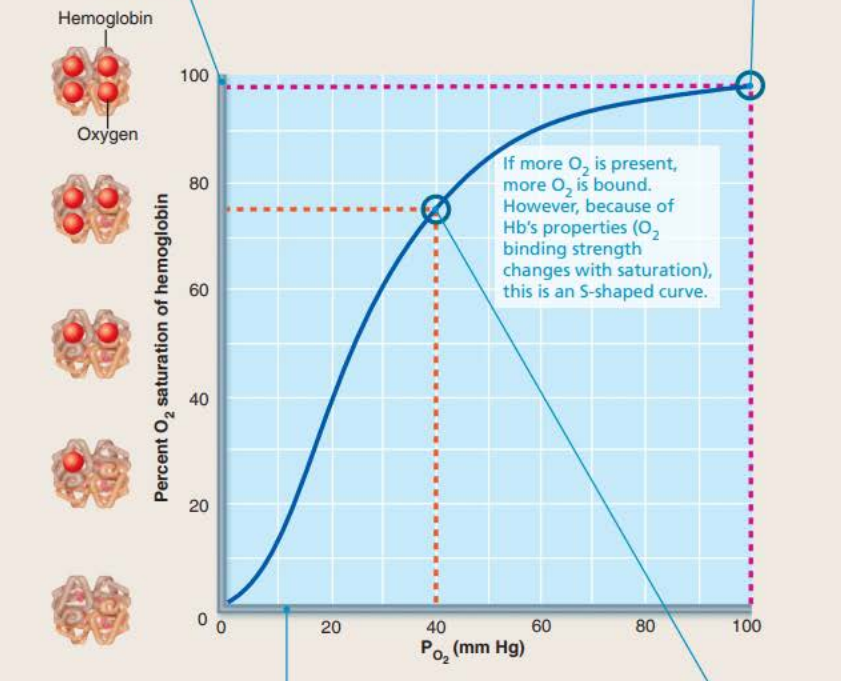
oxygen
present
oxygen
bound
-
Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
In the lungs PO2 is at ___ __ __
Causes _____________ to be almost fully saturated with O2 at ____
_ ______ ________ ____________
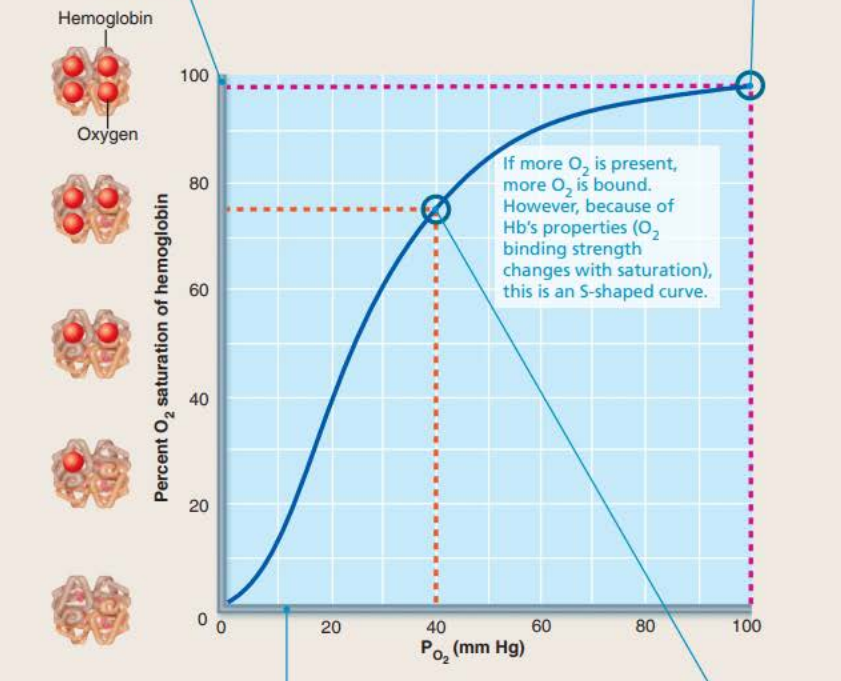
100 mm Hg
hemoglobin
98%
4 bound oxygen molecules
-
Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
In the tissues of other organs PO2 is lower at __ __ __
Causes ___________ to be less saturated with O2 at ___
_ ______ _______ ___________
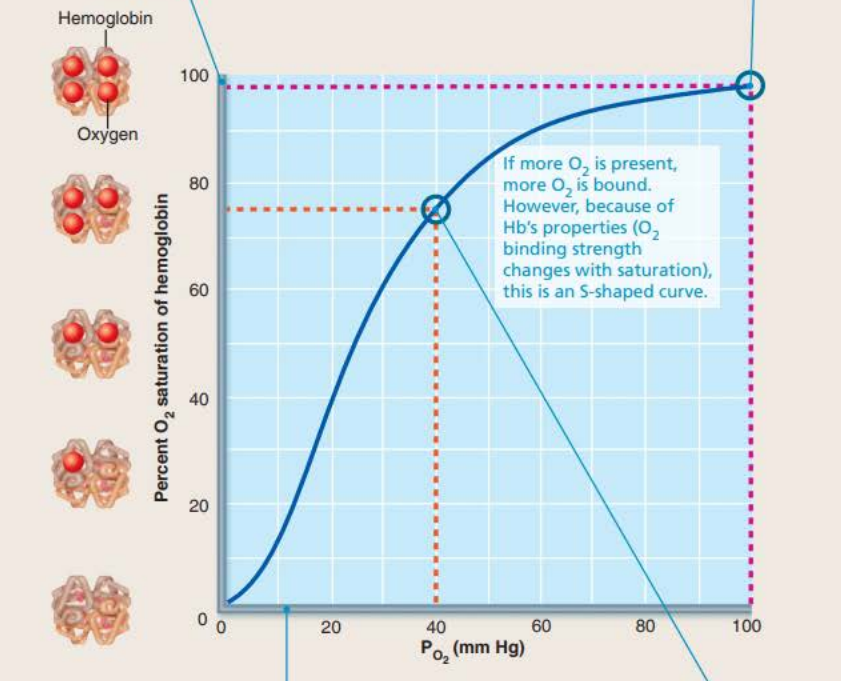
40 mm Hg
hemoglobin
75%
3 bound oxygen molecules
-
____________ __________ ____________ ________________(COPD)
Irreversible ___________ in the ability to _______ ___ ____ of the _____
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
decrease
force air out
lungs
-

Devices that prevent alveolar collapse and maintain positive airway pressure throughout the respiratory cycle

