-

Name this
Lamp
-
Electrical current
Flow of electrical charge around the circuit
-
Unit for current
Amp (A)
-
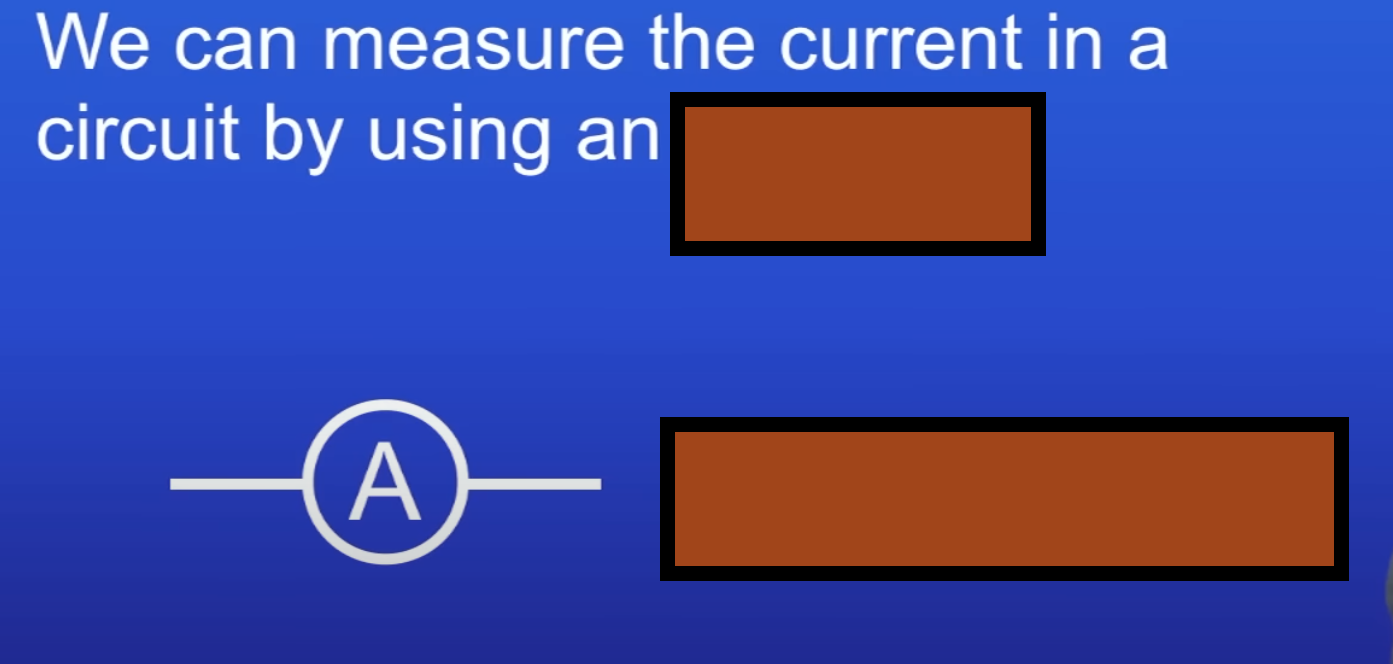
What's missing?
Ammeter
-
Current is the _____ all around the circuit
same
-
The current in the branches adds up to ???
The current in the branches adds up to the total current leaving the cell
-
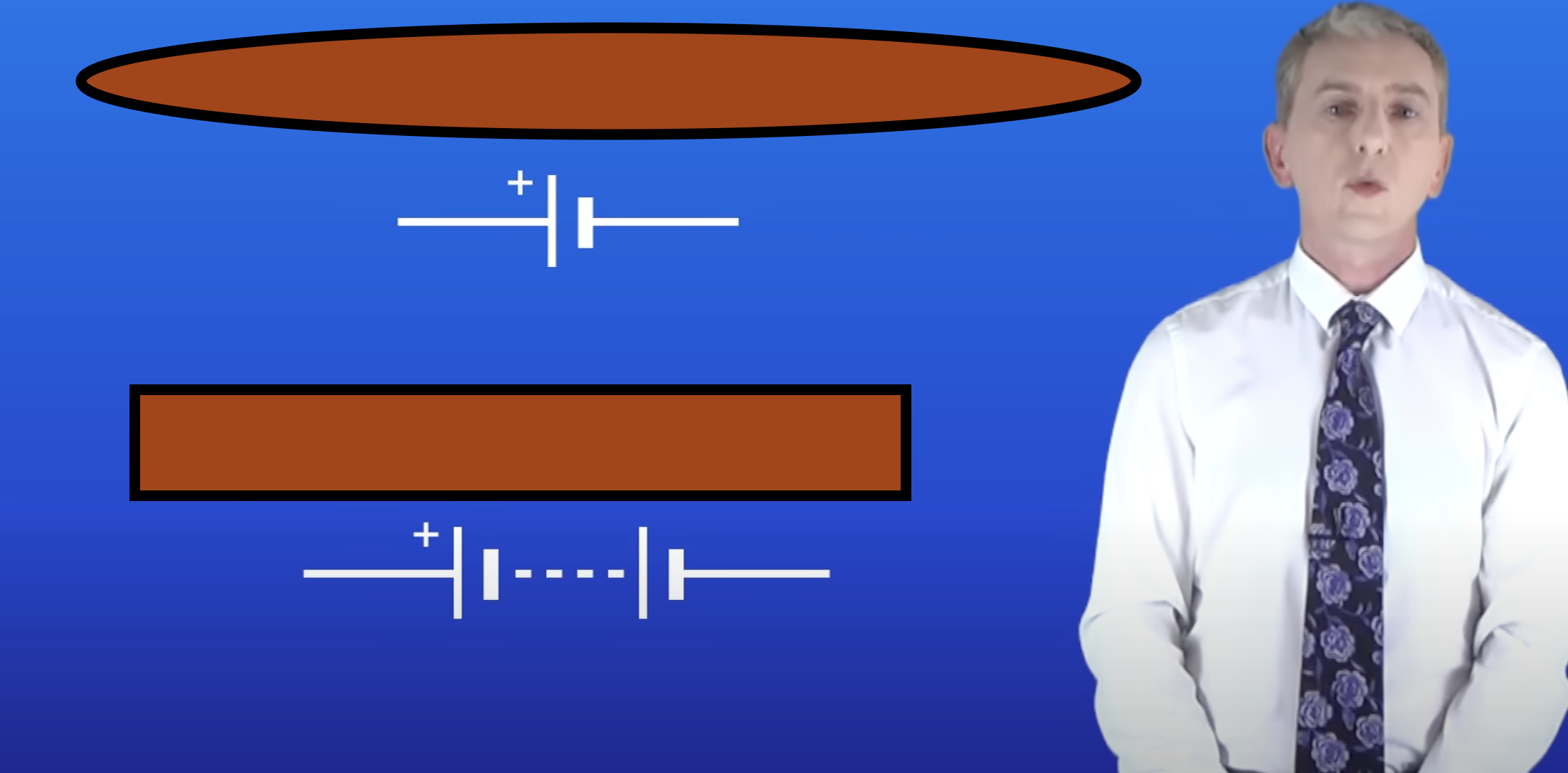
What's missing
Cell and Battery
-
What measures potential difference
Voltmeter
-
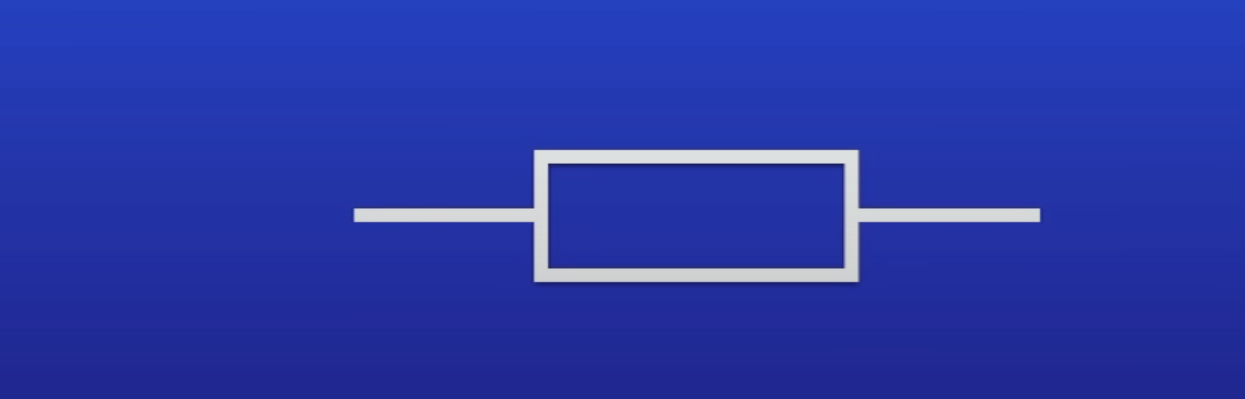
What's this
Resistor
-
Ohmic conductor
Resistance is constant
-
Diode function
allows current to flow in one direction but not in the reverse direction
-
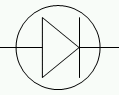
what's this
Diode
-
Light dependent resistor resistance in different conditions
High resistance in dark conditions
Low resistance in light conditions
-
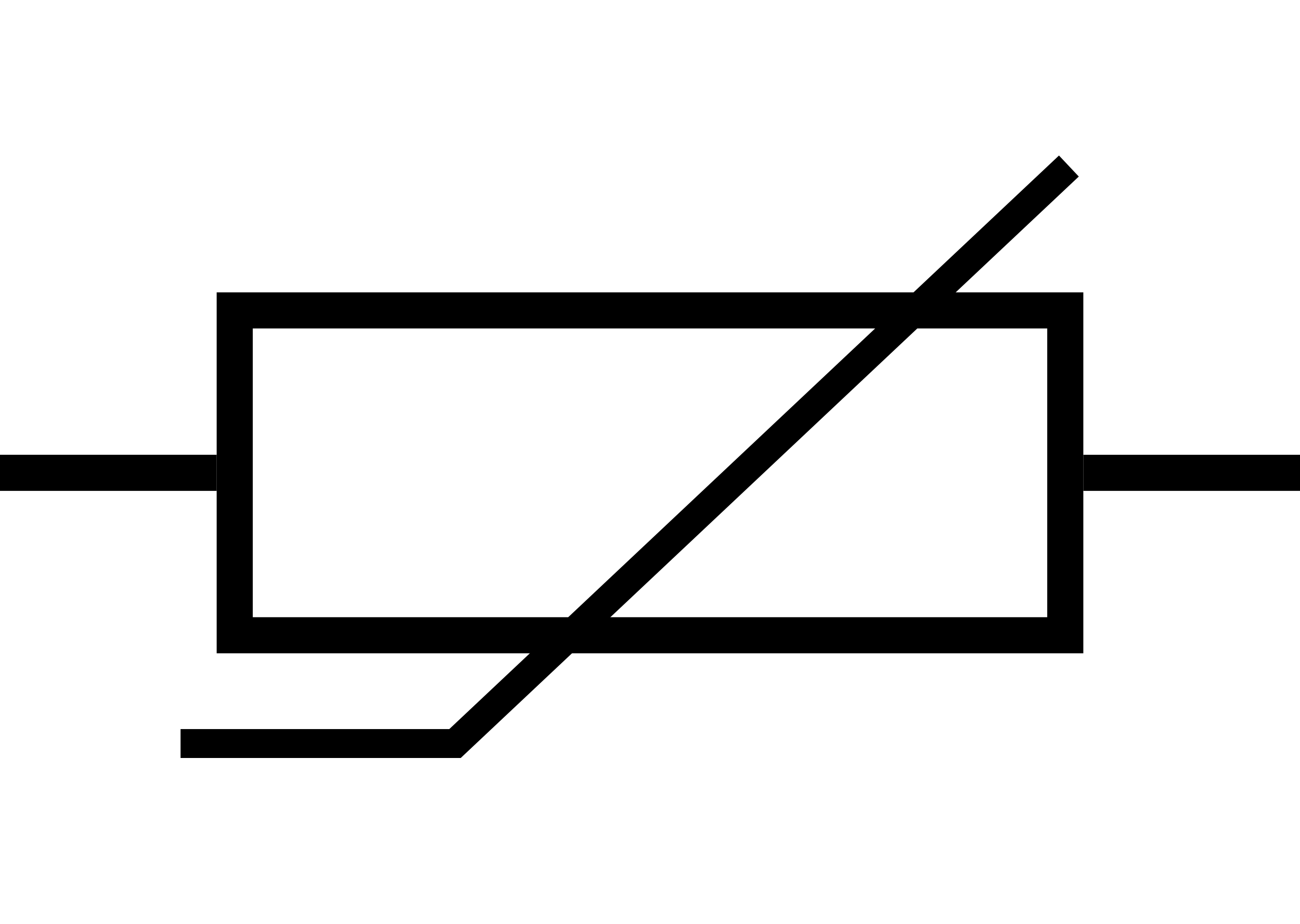
what this
Thermistor
-
Thermistor : resistances link to temperature
Resistance decreases if temperature increases
-
RESISTANCE PRACTICAL
Connect the circuit with voltmeter ammeter and battery
Connect the crocodile clips to the resistance wire, 100 centimetres (cm) apart.
Record the reading on the ammeter and on the voltmeter.
Move one of the crocodile clips closer until they are 90 cm apart.
Record the new readings on the ammeter and the voltmeter.
Repeat the previous steps reducing the length of the wire by 10 cm each time down to a minimum length of 10 cm.
Use the results to calculate the resistance of each length of wire by using R = V/I
-
RESISTANCE CURRENT
Connect the circuit voltmeter ammeter and variable resistor
Ensure that the power supply is set to zero at the start.
Record the reading on the voltmeter and ammeter.
Use the variable resistor to alter the potential difference.
Record the new readings on the voltmeter and ammeter.
Repeat steps three to four, each time increasing the potential difference slightly.
Reverse the power supply connections and repeat steps two to six.
Plot a graph of current against potential difference for each component.
Repeat the experiment but replace the fixed resistor with a bulb.
-
Alternative current
Constantly changing direction
BENEFIT: very easy to use transformers
-
Direct current
Moving one direction
-
Alternating current frequency and potential difference in uK
50hz
230 volts
-
Transformers
An electrical device that increases, or decreases, the potential difference of an alternating current
-
Step up transformers
increase potential difference massively
-
high voltage cables use
less energy is lost due to the high potential difference difference
-
Step down transformers
decrease potential difference massively before it passes to homes


