-
Histamine
1. Released from mast cells: allergies, anaphylactic reactions, injury/trauma, snake/insect bites.
2. Bind to histamine receptors = tissue response
3. H1: peripheral sensory neurons, intestinal smooth muscle, secretory mucosa, pulmonary smooth muscle
4. H2: Gastric effects
5. Both: Cardiovascular, dermatologic
-
Antihistamines
1. First gen: sedative effect
2. Second gen: non-sedating
-
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
1. Antihistamine
2. Indication: Allergic, anaphylactic reactions, sleep aid.
3. TE: blocks H1 receptor
4. SE: sedation, dry mouth, constipation, urinary hesitancy
5. NC: safety/don't mix w/ sedating meds or alcohol; increase fiber and fluids; take at bedtime.
-
cetirizine (Zyrtec)
1. Antihistamine
2. Second-gen non-sedating / high dose can cause fatigue
3. Indication: allergy (rhinitis drainage of nose, urticaria)
4. TE: blocks H1 receptors
5. NC: once daily; fluids/hard candy for dry mouth.
-
phenylephrine (Neo-synephrine)
and Pseudoephedrine (sudafed)
1. Decongestant
2. Indication: nasal congestion
3. TE: stimulate alpha1, adrenergic receptors
4. SE: CNS stimulation, increased BP, tachycardia/palpations
5. Prolonged / overuse = rebound congestion. Use only as needed.
6. Nursing: sleep aid if needed. Use prn, teach proper use, short term use, be aware of misuse.
-
Epinephrine (Adrenaline, Epi-pen)
1. Dilates bronchioles, reduce bronchospasm, increase BP
2. Indications: Cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis, hypotension due to septic shock, asthma and mydriasis during intraocular surgery.
3. Rapid onset and duration.
4. SE: restlessness, angina, anxiety, restlessness, tachycardia, dizziness, shakiness, tingling/numbness to hands and feet, arrhythmias.
5. NC: drug of choice in emergency situations, monitor VS, monitor respiratory status, patient teaching epi-pen
-
Antitussives / Cough Suppressants
1. Nonproductive / dry cough
2. Suppress the cough reflex in the brain.
3. Useful: painful coughs, coughing at night, decrease vomiting/gagging
4. Prescription or OTC
5. Opioid and nonopioids
-
Codeine (antitussive)
1. opioid
2. sedation
3. potential for abuse, use only prn
4. take with food or milk
5. caution in chronic respiratory conditions
6. caution in children and older adult.
-
Dextromethorphan (Delsym) (antitussive)
1. nonopioid
2. Drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, nausea
3. OTC
-
guaifenesin (Mucinex)
1. Expectorant
2. Indication: productive cough to loosen mucus
3. TE: stimulate respiratory tract fluid to reduce viscosity of secretions
4. SE: dizziness, drowsiness, headache, gi upset
5. Increase fluid intake
6. Change positions slowly
7. Caution in coughs that last more than one week.
-
acetylcysteine (Mucomyst)
1. Mucolytic (thin mucous)
1. Indication: Decrease viscosity of mucous
2. TE: Break protein links to thin mucus to expectorate
3. SE: bronchospasm, GI distress
4. Inhaled via nebulizer
5. Monitor respiratory status
6. Have suction available
7. Give 5 minutes after bronchodilator.
8. Reversal agent for acetaminophen overdoses.
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd)
1. pulmonary diseases
2. blocks airflow and other breathing related problems
3. Emphysema
4. Chronic bronchitis
5. Symptoms: frequent coughing or wheezing, excess phlegm, mucus and sputum, difficulty taking a deep breath.
6. Medications treat cough and wheezing.
-
albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin)
1. Beta2 Adrenergic Agonist
2. Indication: treats bronchospasms, acute asthma attacks
3. SE: tachycardia, palpitations, tremors, chest pain, insomnia
4. Antidiabetic drugs may require increased dosing
5. NC: do not take at or near bed time; use before glucocorticoid inhaler; avoid caffeine; short acting vs. long acting; monitor for tachycardia.
-
ipratropium (Atrovent)
1. Anticholinergic
2. Not a rescue drug; long term therapy
3. Indication: bronchospasm associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (chronic bronchitis and emphysema)
4. SE: dry mouth, headaches, blurred vision, hypotension
5. Maintenance therapy
6. Not rapid rescue
7. NC: unpleasant taste; rinse mouth afterwards; hard candy, sip water; screen allergy to soy or peanuts.
-
Theophylline
1. Methylxanthines
2. Indication: acute asthma exacerbations and other chronic lung disease (emphysema and chronic bronchitis)
3. Few side effects at therapeutic range (5-15 mcg/mL)
4. Adverse effects > 20 mcg/mL N/V, restlessness, insomnia, seizures, diarrhea.
-
Gluccorticoids
1. Indication: asthma
2. TE: decrease inflammation and suppress the immune system.
3. Inhaled: maintenance treatment
4. Oral: smallest dose for the shortest amount of time
5. Routes: inhaled: beclomethasone dipropionate (qvar); Nasal Fluticasone (flonase); Oral: prednisone / dexamethasone (decadron); IV dexamethasone (decadron)
-
Glucocorticoids Side Effects
1. Inhaled SE: throat irritation, hoarseness, dry mouth, coughing, oral candidiasis.
2. Oral and IV SE: adrenal suppression, headache, hyperglycemia, insomnia, menstrual irregularities, fluid retention, thin skin, increased infection risk
-
Inhaled Glucocorticoids NC
1. Inhaled glucocorticoids use a spacer
2. Scheduled use not as needed
3. Shake inhaler
4. Wait 1-5 minutes between doses
5. Rinse mouth after use
6. Screen for allergy peanuts and soy.
-
Inhaler sequence
1. Order of administration:
1. Bronchodilator first (beta 2 adrenergic agonist) = dilate
2. Long acting or combined inhalers. Anticholinergic - Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent)
3. Glucocorticoid /steroid inhalers.
-
montelukast (Singulair)
1. Leukotriene (Anti-inflammatory)
2. Indication: asthma, relief of symptoms of allergic rhinitis
3. TE: suppress leukotrienes
4. SE: upper respiratory infection, headache, cough, abdominal pain, diarrhea, rhinorrhea, neuropsychiatric events (black box warning)
5. Report behavioral changes / thoughts of suicide.
-
Asthma Peak Flow Meter
1. Personal best
2. Daily and more frequently if drops below 80% of normal.
-
Hypothyroid
1. Underactive thyroid
2. Signs and Symptoms develop slowly overtime.
3. More obvious side effects as it continues.
4. Elevated thyroid stimulated hormone (TSH)
5. Common causes: autoimmune, surgery, radiation, medications
6. Fatigue, weight gain, depression, brittle hair and nails, cold intolerance.
-
levothyroxine (Synthroid)
1. Indications: thyroid replacement therapy for hypothyroid
2. SE: hyperthyroid
3. Interactions: decrease digoxin effect, enhance oral anticoagulants, decrease insulin/ antidiabetic drugs.
4. NC: take daily, lifelong treatment; 3-4 weeks for effects; teach signs of hyperthyroid; dosed in mcg; take 30-60 mins before breakfast; brands cannot be interchanged.
-
Hyperthyroid
1. Overactive thyroid
2. Mimics other health problems, may be difficult to diagnose.
3. Causes: Grave's disease, Plummer's disease, thyroiditis.
4. Diarrhea/frequent bowel movements, increased appetite, muscle weakness, heat intolerance, exophthalmos, sleep disorders, palpitations, tachycardia, nervous/irritable, goiter.
-
propylthiouracil (PTU)
1. Antithyroid drug / suppresses thyroid hormone production
2. Used prior to surgery to remove the thyroid.
3. SE: agranulocytosis, hypothyroid, liver toxicity.
4. Nursing: monitor for hypothyroid; teach to report signs of infection.
-
Glucocorticoids
1. Solu-Medrol, Hydrocortisone, prednisone, dexamethasone
2. Indications: Trauma, surgery, inflammation, allergic reactions, organ transplant.
3. PO, IM, IV, topical, aerosol, eye drops
4. Lower the activity of the immune system.
5. Long-term - secondary adrenal insufficiency.
-
Prednisone
1. glucocorticoid
2. take with food
3. MUST taper off
4. avoid during pregnancy
5. SE: increase blood sugar, abnormal fat deposits, muscle wasting, sodium/water retention, thin skin, glaucoma, psychosis/irritability, hypertension, increased risk of infection.
-
Diabetes overview
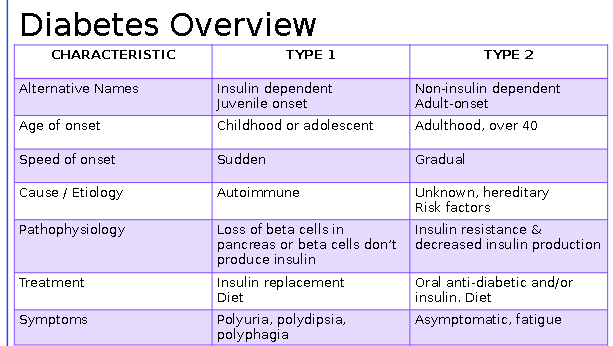
-
Hypoglycemia
1. Symptoms: shaking, sweating, anxious, dizziness, fast heartbeat, impaired vision, weakness fatigue, headache
2. Treatment: glucagon, immediate onset of action. IM/IV/SC
3. Indication: severe hypoglycemia
4. Side effects: N/v
-
Insulin
1. Indication: Diabetes mellitus type 1 and type 2
2. Four types: rapid, short, immediate, long
3. Different onset, peak and durations (sylabus pg. 8)
4. Adverse effect: hypoglycemia
5. Monitor potassium
-
Insulin nursing interventions
1. Want to avoid hypoglycemia
2. Check blood glucose level
3. Timing for meals
4. Rotate sites
5. May need extra doses in times of illness and stress
6. Hypoglycemia (conscious vs unconscious)
7. Teach pt and family signs of hypoglycemia.
8. Medication interactions.
-
Mixing Insulin
1. Draw clear before cloudy
-
glipizide (glucotrol)
1. Sulfonylurea (treat type 2 dm)
2. TE: simulates the release of insulin
3. SE: hypoglycemia, nausea, diarrhea
4. Contraindications: pregnancy, lactation.
5. Adminsitration: take 30 minutes before breakfast
6. Interactions
7. No alcohol.
-
Metformin (glucophage)
1. Biguanide
2. TE: decrease hepatic glucose production, decreased intestinal absorption of glucose, improved insulin sensitivity.
3. SE: diarrhea, n/v, metallic taste, flatulence, asthenia, GI upset, b12/folate deficiency, lactic acidosis.
4. Contraindications: renal impairment.
5. NC: discontinue prior to contrast dye for imaging; monitor for vitamin b12 and folic acid deficicines; teach about lactic acidosis symptoms; gi effects improve over time. Take with a meal
-
pioglitazone (actos)
1. Thiazolidinedione
2. TE: decrease insulin resistance in tissues
3. SE: fluid retention, increase lipid levels, respiratory infections, myalgia, headaches, increased incidence of heart failure.
4. Contraindications: cardiovascular disease
5. Interactions
-
sitagliptin (Januvia)
1. Gliptins
2. TE: slow the actin of incretin hormones
3. SE: respiratory infection, pancreatitis, GI upset, rash, headache
4. Contraindications: oral tablet only, with or without food, teach signs of respiratory infection and pancreatitis.
-
exenatide (Byetta)
1. Incretin Mimetic
2. SC injection
3. Indication: type 2 diabetes
4. TE: increase incretin
5. SE: hypoglycemia, GI upset, pancreatitis
6. Contraindications
7. Inject 60 mins prior to am and pm meals
8. Take with sulfonylureas increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
9. NC: many drug interactions; complete list of medications; include lifestyle modifications (diet and exercise); teaching; follow recommendations for blood sugar monitoring; teach signs of hypoglycemia.
-
Vaccines
1. Antigen that stimulates immune response
2. traditional vaccines, attenuated vaccines, toxoids, conjugate vaccines, recombinant subunit vaccines, adjuvant.
-
Vaccine Safety
1. Mild reactions are common
2. Contraindications: moderate to severe illness or anaphylaxis to vaccine or component of the vaccine.
3. International travel
4. Report cases of vaccine preventable diseases.
5. Report cases of adverse reactions after immunizations.
-
Vaccine Nursing Considerations
1. Teaching
2. Screen for sensitivities: eggs for flu vaccine
3. Vaccine information statement (VIS) from the CDC
4. Obtain a vaccination history
5. Monitor for 30 minutes for adverse reactions.
-
Vitamin Categories
1. Water-soluble: B complex and C; not stored in the body; consistent supplement required; readily excreted in urine.
2. Fat-soluble: A, D, E, K; stored in fatty tissue, liver and muscle; excreted in the urine at a slow rate.
-
Vitamin B12 / Cyanocobalamin
1. Function purpose: helps with dna synth/ converts folic acid to active form, promotes cell division, aids in production of red blood cells, nervous system integrity.. mylein sheath.
2. Foods: enriched cereals, fish, dairy products, egg yolks.
3. TE uses: pernicious anemia, strict vegans at risk for b12 deficiency.
4. Deficiency: Beefy red tongue, pallor, neuropathy, pernicious anemia, GI disorders, poor growth, neurologic damage
5. Overdose / excess
6. Adverse drug effects rare.
-
Vitamin B12 / Cyanocoblamin cont.
1. PO, SC, IM, intranasal
2. SE: erythema (red skin), hypertension, hypokalmia.
3. Nursing: take with food to enhance absorption, drugs that affect absorption, monitor K+ and symptoms of hypokalemia.
-
Folic Acid (Folate, B9)
1. Function/purpose: help with dna production, rbc,wbc,platelet productions.
2 Foods: legumes, citrus fruits, nuts, leafy greens, yeast, organ meats.
3. Therapeutic uses: Prevent neural tube defects developing fetus, Megalobastic anemia (big rbcs) , alcohol related folate deficiency.
4. Deficiency: Anorexia, Nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, anemia, neural tube defects/spina bifida.
5. Overdose / Excess: temporarily mask a b12 deficiency
6. PO, SC, IM, IV
7. SE: increased yellowing of urine, masks B12 deficiency.
8. Nursing: CDC recommends women of reproductive age get 400 mcg daily, pregnancy.
-
Iron / Ferrous Sulfate
1. Function / purpose: needed to attach oxygen to rbcs.
2. Foods: liver, egg yolks, dried beans, green vegetables and fruit
3. TE: pregnancy induced needs / iron deficiency anemia. gastric bypass
4. deficiency: fatigue, sob, pale
5. Overdose / excess: iron toxicity can be FATAL (liver toxic). ONLY IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
6. PO, IM, IV
7. SE: gi side effects, metallic taste, dark stools, teeth staining with exilir
8. Nursing: foods and antacids decrease absorption of iron; vitamin C increases absorption (orange juice), take with food to minimize gi side effects, candy or gum for metallic taste, teaching on dark stools and teeth staining. (use straw)
-
Vitamin K
1. Function / purpose: blood clotting
2. Sources: leafy greens, brocoli, cheese, egg yolks
3. TE: warfarin (coumadin) reversal
4. Deficiency: increases clotting time, bleeding, hemorrhage.
5. Overdose / excess: excessive blood clotting = mi/stroke
6. Nursing considerations: newborns are born vit. k deficient.
7. patient teaching: focused on pts taking warfarin or mothers giving birth to their newborns.
-
Classification of Pain
1. acute - less than 3 months, surgery, tissue injury
2. chronic - lasting longer than 3 months,
3. intractable - pain not relieve by standard measures (epidurals)
-
Feelings of pain
1. Nociceptive - aches/throbbing
2. Neuropathic - nerve pain
3. Mixed - combination of nerve/aches
-
Nonopioid analgesics
1. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs)
2. Acetaminophen
3. Centrally acting nonopioids
-
Opioid analgesics
1. Opioid agonists (bind to mu receptors)
2. Opioid agonist-antagonists (bind to mu and kappa receptors)
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
1. Salicylates (aspirin) !
2. Phenylacetic Acid
3. Propionic acid
4. COX 2 Inhibitors !
-
Tissue Injury
1. Tissue injury
2. cell membrane releases arachidonic acid
3. stimulates inflammatory response
4. releases cox1 and cox2
5. Cox1: promotes kidney function, protects stomach lining, promotes platelet aggregation(sticking together).
6. Cox2: causes inflammation, increases body temperature, triggers pain.
-
Aspirin (ASA)
1. Salicylate (from willow tree)
2. Blocks Cox-1 and Cox-2
3. Mild to moderate pain
4. TE: anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet (mi/stroke prevention), antipyretic
5. SE: bleeding, GI distress.
6. Contra: children w/ viral infections, peptic ulcer, bleeding disorder, 7 days of surgery, pregnant, combination with NSAID of ANTICOGULANTS, food containing salicylates.
-
Salicylate (Aspirin) Nursing Interventions
1. Normal serum levels 15-30 mg/dL
2. monitor for signs of bleeding / platelets
3. Avoid alcohol.
4. Recommend acetaminophen for children.
5. Stops prior to surgery or dental procedures.
6. Pts with asthma (hypersens)
7. take with food.
-
Salicylate posioning
1. breathing too fast too much
2. pain/ vomitting
3. tinnitus
4. young kids mostly od
-
Ibuprofen (advil, motrin)
1. Propionic acid
2. Block COX1 and Cox2
3. Treats mild to moderate flame and inflammation
4. TE: anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antiplatelet
5. SE: gastric distress, fluid retention
6. Highly protein bound.
7. NC: Monitor for signs of bleeding, take with food, monitor liver/renal function, do not use with other NSAIDS or Anticoagulants, peptic ulcers signs, hold for surgery, no alcohol.
-
celecoxib (celebrex)
1. COX-2 inhibitor
2. Mild to moderate pain
3. TE: analgesic, antipyretic
4. SE: GI distress (less than COX1 inhibitors), renal dysfunction, cardiovascular thrombotic events, new or worsening HTN (CLOTS)
5. Contra: pregnancy, children, kidney and liver dysfunction, GI bleed.
6. Drug Interactions: Effects of furosemide decrease; Increase anticoagulants effects of warfarin (check INR 2-3); ACE inhibits / ace2 effects reduced.
7. Nursing Interventions: Take with food; monitor renal/hepatic function; educate patient on signs of GI bleed,mi,stroke; symptoms of fluid retention; PO 2 hrs before or after antacids.
-
Opioid vs. Nonopioid Analgesics
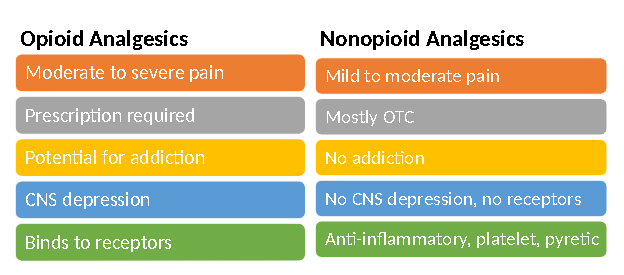
-
Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
1. nonopioid analgesic
2. analgesic for mild to moderatre pain
3. Fever reduction / antipyretic
4. SE: hepatotoxicity, acetaminophen toxicity, HTN w/ daily use
5. Contra: Liver failure, alcoholism, renal disease
6. Max daily dose: 4 grams for adults
7. Infants/children weight based per manufactures
-
Acetaminophen overdose
1. Early symptoms: sweating, n/v, diarrhea, and abdominal pain
2. Irreversible liver damage, hepatic necrosis, death
3. Overdose antidote: acetylcysteine (mucomyst) PO or IV.
4. caution with combination products.
-
tramadol (Ultram)
1. Non-opioid
2. Moderate to severe pain
3. SE: sedation, dizziness, headache, GI
4. Contraindications: seizure disorders, MAOI use in last 14 days, children, respiratory depression
5. NI: lowest dose, shortest amount of time, caution with ambulation, monitor respirations
6. Take with food
7. 1 hr to feel effects of medication
-
Opioid Analgesics / Opioid Agonists
1. Moderate to severe pain
2. Act mostly on the CNS on various receptors for pain signaling
3. Hard copy prescription or physician unique identifier for electronic rx.
4. High abuse potential
5. Caution in patients with head injuries, respiratory disorders, older adults, pregnant or breast feeding.
6. do not stop abruptly after long term use, withdrawal symptoms.
-
Schedule of Controlled Substances
1. Schedule I: No currently accepted medical use
2. Schedule II: high abuse potential leading to psychological or physical dependence.
3. Schedule III: moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence
4. Schedule IV: low potential for abuse and low risk of potential
5. Schedule V: lower potential with limited quantities of narcotics.
-
Morphine
1. Acts of mu receptors
2. Used for moderate to severe pain: acute MI symptoms.
3. IR versus ER
4. SE: respiratory depression, hypotension, dizziness, constipation, urinary retention, pruritis (itching) and sedation
5. Antidote: naloxone (narcan)
-
Oxycodone
1. Moderate to severe pain
2. IR vs ER
3. Oxycodone/acetaminophen (Percocet)
4. SE: sedation, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention, n/v, euphoria, and weakness
-
Other opioid analgesics
1. hydrocodone/acetaminophen (vicodin)
2. fentanyl
3. hydromorphone (dilaudid)
4. meperidine (Demerol)
-
Contraindications for Opioids
1. head injuries
2. cns or respiratory depression
3. hypovolemia/hypotension
4. asthma
5. concurrent alcohol use
6. suspected or known ileus or gi obstruction
-
Opioid overdose
1. unconsciousness
2. very small pupils
3. slow or shallow breathing
4. vomiting's
5. inability to speak
6. limp arms and legs
7. pale skin
8. pale / blue lips and fingernails
-
Patient education opioid analgesics
1. prevent constipation
2. safety driving..
3. refills, know what you have
4. store securely
5. never share
6. take only what you need
-
naloxone (narcan)
1. opioid antagonist
2. emergency use: iv, nasal spray, auto-injector
3. reverse respiratory and/or CNS depression
4. SE: nasal dryness, edema, congestion and inflammation, headache, HTN and musculoskeletal pain.
-
Pathology of Osteoporosis
1. brittle fragile bones, impaired skeletal strength, porous bones, decreased bone mass
2. result of hormonal changes or deficiency of calcium or vitamin D
3. Risk: women over 50, natural/surgical menopause
4. Prevention: calcium + vit. D; weight bearing exercises; limit alcohol, no smoking.
-
DEXA scan / bone density
1. Test done on bones that are most likely to fracture
2. t-score: bone density compared with what is normally expected in a healthy young adult of the same sex
3. Z-score: number of standard deviations above or below what's normally expected for someone your age, sex, weight, ethnicity.
-
Drug categories to treat osteoporosis
1. selective estrogen receptor modulators
2. bisphosphonates
3. calcitonin
4. calcium supplements
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulator (raloxifene)
1. raloxifene (evista)
2. TE: prevent/treat osteoporosis postmenopausal women
3. PO daily
4. SE: increased risk of stroke, PE, DVT, and hot flashes
5. Contraindications: pregnant or breast feeding, history of DVT
6. NI: education on clot prevention, use contraception's, no estrogen replacement therapy concurrently, continue DEXA scans and routine lab work (cholesterol)
-
Bisphosphonates
1. Used to treat and prevent osteoporosis: postemenopausal osteporosis; gluccocorticoid related osteoporosis; age related osteoporosis in men
2. Prevent fractures, future pain and halt bone loss
3. PO, IV, and SQ
4. Take calcium and vitamin D supplements one hour after oral bisphosphonates.
-
Bisphosphonates side effects
1. renal impairment (gfr and creatinine)
2. Temporary hypocalcemia
3. Muscle and joint pain
4. Esophagitis
5. Osteonecrosis of the jaw (rare)
6. Return to baseline bone density after stopping medication
-
Bisphosphonate nursing interventions
1. renal function
2. dental issues
3. serum calcium
4. continue routine dexa scans
5. muscle and joint pain
6. esophagitis
-
Alndronate (Fosamax)
1. TE: prevention or treatment of osteoporosis
2. PO daily or once week
3. SE: irritation of the upper gi mucosa/esophagitis, musculoskeletal pain, ONJ (rare), vision changes
4. Contra: Barret's esophagus, dysphagia or other esophageal diseases, hypocalcemia, renal insufficiency, invasive dental procedures and can't sit or stand for 30 minutes.
-
Gout pathololgy
1. uric acid crystals
2. hyperuricemia
3. severe joint pain, redness, stiffness, and swelling
-
Colchicine
1. acute gout attack
2. action: inhibits leukocytes to the inflamed site
3. SE: abdominal pain, diarrhea, n/v
4. take with food
5. contraindications: renal or gi problems.
-
Allopurinol (zyloprim)
1. not an anti-inflammatory
2. lowers serum uric acid levels
3. prophylactically prevents gout
4. SE: rash, diarrhea, nausea, elevated liver enzymes, visual changes.
5. Contraindications: previous skin reactions to allopurinol, elevated liver enzymes
6. Increase fluid intake and take with food
7. Annual eye exam for prolonged use.
8. NC: increase fluids. monitor urine output; take with food; lab monitor; avoid alcohol; foods high in purines

