-
Generic vs. Trade/Brand Names
1. They have same chemical composition
2. They have the same therapeutic effect.
3. Generic names are always lowercased. Brand names are capitalized.
-
Prescription vs. OTC Drugs
1. Prescription requires physician. Prescription typically stronger than OTC.
2. OTC can be bought any store
-
Pharmacodynamics
1. The effects of drugs on the body.
-
Pharmacokinetics
1. The process of a drug movement throughout the body. (ADME)
a.) Absorption
b.) Distribution
c.) Metabolism
d.) Elimination
-
Pharmaceutics
1. How do different drugs forms affect absorption and onset? (liquid vs pill)
-
Absorption (Pharmacokinetics)
1. Route of administration.
2. Food
3. Drug form (enteric coating)
4. Bioavailability
5. Acidic Environment
-
Absorption Routes
1. Enteral (via GI tract)
a.) Oral (PO)
b.) Rectal
c.) Sublingual and Buccal
2. Parenteral (Injection)
a.) Intramuscular (IM)
b.) Intravenous (IV)
c.) Subcutaneous (SC or SQ)
3. Topical / transdermal
4. Inhaled
5. Vaginal
6. Nasal, Otic, Optic
-
Oral Medications
ex: tablet, capsules, powder, liquid
1. Saliva in the mouth causes the disintegration agent to swell, creating channels for the saliva. Fast-dissolving granules dissolve and the tablet disintegrates.
-
Rate of Absorption by type of medication
1. Liquid
2. Suspension
3. Powder
4. Capsule
5. Tablet
6. Coated Tablet
7. Enteric-coated tablet
-
Distribution (Pharmacokinetics)
1. Movement of drug from circulation to body tissues. Influenced by blood flow. Blood brain barrier, protein binding.
-
Distribution - Protein binding
1. Highly protein-bound drugs can't activate receptors unless they are free.
2. Won't free drugs unless receptors are saturated.
3. Can enhance or detract from drugs performance.
4. Multiple highly protein bound drugs
5. Stopping or starting a drug that binds to a plasma protein changes the free drug levels of other protein-bound drugs.
-
Metabolism (Pharmacokinetics)
1. Occurs mostly in liver
2. First pass effect, gets absorbed by gi tract and metabolized by liver, by time it is in systemic circulation 0-45% availability.
-
Excretion (Pharmacokinetics)
1. Elimination of the drug or its metabolites
2. Renal disease can impair excrement of drugs.
3. Renal function includes: creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (bun), glomerular filtration rate (gfr)
-
Serum drug levels
1. Half life == time to decrease to 50 percent
2. Highly protein-bound drugs have a longer half-life
1. Onset
2. Peak
3. Duration
1. We check serum drug level s to monitor doses that are close to toxic doses, monitor unexpected responses, suspected drug overdose.
-
Pharmacodynamics
1. Drug actions on target cells
2. What the drug does to the body
3. Changes that occur in the body.
-
Agonist (causes action)
1. Binds to a receptor
2. Activates a receptor
3. Acts similar
4. Produces response, or responses a greater than normal responses
-
Antagonist (prevents action)
1. Binds and prevents activation of receptor
2. Blocks a receptor (produces block response, less than normal response)
3. Reverses a response
4. Competitive / non-competitive inhibition
-
Black-box warning
1. FDA warning
2. Notes serious safety risks and important instructions
3. Patient education.
-
Special Populations for Pharmacology
1. Obstetrics / Pregnancy / Breasting feeding women
2. Pediatrics
3. Geriatrics
-
Pregnant / Lactating women
1. Risk/benefit assessment
2. choice of drug depends on stage of pregnancy.
3. Lowest effective dose for the shortest amount of time is optimal
4. Inclusion of patient and family in teaching.
5. Most systemic drugs taken by mouth reach the infant in breast milk
6. Discuss all medications and supplements with a provider.
-
Pregnancy Risk Categories
Cat A - no risk in human studies
Cat B - no risk in animal studies
Cat C - risk cannot be ruled out
Cat D - evidence of risk
Cat X - contraindicated
-
Pediatrics
1. dosages are calc based on weight
2. family/caregiver teaching
-
Geriatrics
1. decreased organ function
2. polypharmacy
3. medication adherence
1. Absorption - Gi changes (increase in pH) decreased peristalsis, nutrition, swallowing.
2. Excretion - Kidney function - GFR / creatinine
3. Distribution - decreased cardiac output, decreased muscle mass, increased fat, decreased albumin.
4. Metabolism - liver function decreases (AST, ALT)
-
Drug Interactions
1.Additive = drugs do same thing
2. Synergistic = effects of drug are greater
3. Antagonistic = effects of drug is blocked or decreased
Drug-food - can increase or decrease blood levels
-
Patient teaching
Responsible for instructing pts on meds
1. purpose
2. generic vs trade name
3. route
4. schedule
5. side-effects
6. precautions, contraindications,
7. Cognition (developmental level, language, readiness to learn)
8. evaluate knowledge of what they just learned.
-
Nursing process (ADPIE)
ADPIE
1. assessment
2. diagnosis
3. plan
4. interventions
5. evaluate
-
Adrenergic
1. bind to adrenergic receptors throughout the body. a1 a2, b1, b2. stimulates fight or flight system in PNS, autonomic nervous system.
-
Adrenergic agonists
1. Pupils dilate
2. saliva inhibited
3. airway dilate
4. HR increases
5. stomach inhibits digestion
6. Liver releases glucose
7. Kidneys release adrenaline
8. Bladder relaxes
9. Reproductive system decreases bloodflow.
-
Adrenergic receptors
1. two types: alpha and beta
2. adrenergic drugs bind directly to one or more of these receptors to induce various physiological effects.
-
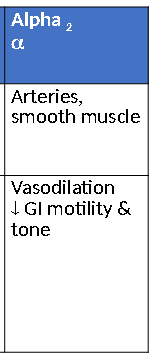
Alpha1 receptor

-
Alpha2 Receptor
-
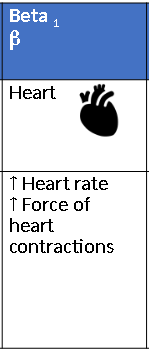
Beta1 Receptor
-
Beta2 Receptor

-
Epinephrine
1. Adrenergic agonist
2. acts on both alpha/beta receptors
3. Indications - cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis, hypotension due to septic shock, asthma and mydriasis during intraocular surgery.
4. Routes - IV, IM, SC
5. Side effects - restlessness, angina, anxiety, restlessness, tachycardia, dizziness, shakiness, tingling/numbness to hands and feet, arrhythmias.
-
doxazosin (Carduara)
1. a1 blocker
2. Indications - HTN and BPH benign prostate hypertrophy
3. side effects - orthostatic hypotension (first dose phenomenon), tachycardia, headaches, dizziness.
4. Contraindications - children, history of hypotension or syncope
-
doxazosin (cardura) nursing intervetions
1. first dose phenomena and dose increases - monitor orthostatic bp and pulse
2. Do not administer at bed time
3. Instruct to rise slowly
4. precautions 12 hrs after 1st dose and dose increases
5. instruct to report in increase in headaches and dizziness
-
Beta Blockers
1. Selective block b1
2. Non-selective block b1 and b2
3. TE - decrease HR, decrease BP, decrease heart contraction, slow conduction
4. Names end in -olol, -ilol, -alol
5. Selective - Atenolol, Metoprolol
6. Non-selective - Propranolol
7. Indications - HTN, angina, MI, HF
8. Never stop taking abrupbtly (black box warning)
-
Selective Beta Blcokers
1. Atenolol and Metoprolol
2. SE - Bradycardia, hf, fatigue, weakness, orthostatic hypotension, sudden withdrawal = mi or angina.
3. Contraindications - bradycardia, mod-serve hf, children
-
Selective beta blockers nursing considerations
1. don't stop suddenly. tapper off 1-2 weeks
2. change positions slowly
3. avoid hazardous activities until stable
4. check pulse prior to each dose report if less than 60bpm
5. teach pts how to monitor bp and hr at home
6. absorption of metoprolol enhanced with food.
7. take at same time each day.
-
propranolol (Inderal)
1. non-selective beta blocker
2. side effect - bronchoconstriction, hypotension, bradycardia
3. contraindications: pre-existing respiratory conditions (asthma), bradycardia)
4. NC - taper off med, monitor hr and bp
-
tamsulosin (Flomax)
1. a1 antagonist
2. indications - BPH (benign prostate hypertrophy)
3. TE - increase urine flow, decrease urgency, frequency, nocturia
4. SE - bradycardia, dizziness, headaches, hypotension, altered ejaculations', retrograde ejaculation.
5. Contraindications - women, children, concurrent with viagra.
6. Interaction - concurrent use of antihypertensive meds
-
alpha antagoinst nursing interventions
1. monitor bp/hr signs of hypotension
2. no hazards activity until effects are known
3. change positions slowly
4. take 30 minutes after same meal every day
5. monitor for headaches and use mild analgesic for headaches
6. teach altered ejaculation
-
albuterol (Proventil, Ventolin)
1. beta2 agonist
2. indication - treats bronchospasms, acute asthma attacks
3. short acting use only as needed
4. Side effects: tachycardia, palpations, tremors, chest pain, insomnia
5. Antidiabetic drugs may require increased dosing
-
beta2 agonist nursing interventions
1. take at or near bed time
2. use before glucocorticoid inhaler
3. avoid caffeine
4. short acting vs long acting
5. monitor for tachycardia
-
Alpha/Beta blockers
1. TE - decrease HR, decrease heart contractility, decrease resistance in blood vessels, decrease cardiac output, increase excretion of water and sodium
-
carvedilol (Coreg)
1. alpha/beta blocker
2. se - hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, bradycardia, asthma exacerbation
3. contraindications: bronchial asthma ,lactation/pregnancy, bradycardia
4. Nursing interventions - do not stop abruptly, no hazards activities until effects are known, monitor for signs of worsening hf, monitor and teach how to manage orthostatic hypotension, monitor hr report > 60 bpm, take with food.

