-
preemptive, semi-preemptive, reactive
What are the three main PGx approaches that are commonly used?
-
Preemptive
:aims to optimize medication use by have genetic information at the point of prescribing for all patients regardless of demographic or risk parameters.
-
Semi-preemptive
:uses the same principle except for a specifically defined "at-rirsk" population
-
Reactive
: occurs after the patient has already been diagnosed or after a patient is non-responder or toxic responder resulting in a patient needing a treatment that may have a PGx implication
-
Tamoxifen; premenopausal women
______ is not clinically benefit to 50% of _________ and many suffer frequent adverse drug-related events.
-
simvastatin; significant myopathy
The lipid & cholesterol-lowering drug _________ leads to _________ in about 25% of patients.
-
Biomarkers
- objective, quantifiable characteristics of biological processes.
-
pharmacodynamic; efficacy
Interaction of a drug with its biological target is a __________ effect related to ________
-
exposure; AUC
Metabolism affects drug _________ (amount of drug levels in body). This is measured with ________
-
Bioavailability
-the fraction of drug reaching the blood circulation after absorption from GI tract and a first-pass through the liver (portal vein).
-
prodrugs
Are NRTIs active or prodrugs?
-
oxidation, de-alkylation, hydrolysis
What are Phase I (functionalization) reactions?
-
sulfation, glucoronidation
What are Phase II (conjugation) reactions?
-
inactivation
Phase II metabolism typically results in ____________ of the drug.
-
ALDH2*2
-these individuals are deficient in ALDH2 enzyme
-clinical manifestations include: characteristic facial flushing, headaches, nausea, dizziness, and cardiac palpitations
-
missense; glutamate to lysine
What type of mutation is the ALDH2*2 mutation?
-
east asians
Most common ethnic group affected by ALDH2*2 ?
-
ANTABUSE (disulfiram)
-ALDH2 inhibitor
-used to support treatment of alcoholism
-produces acute sensitivity to ethanol by preventing acetaldehyde oxidation to acetate
-
hydroxylation; phase I
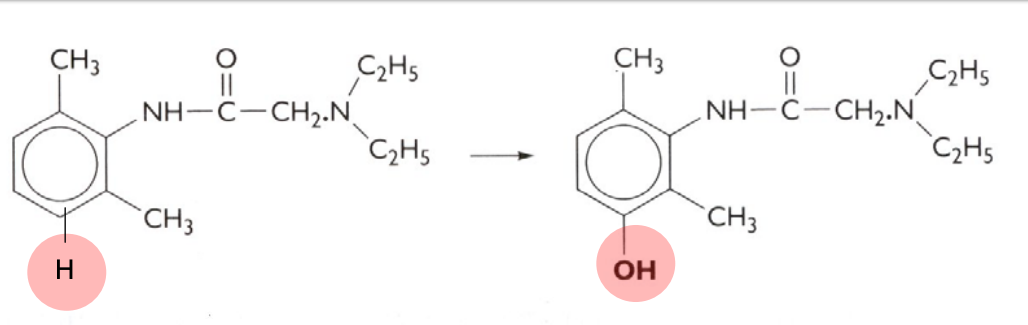
What kind of reaction is this? And what phase does this occur?
-
hydroxylation (aliphatic); phase I
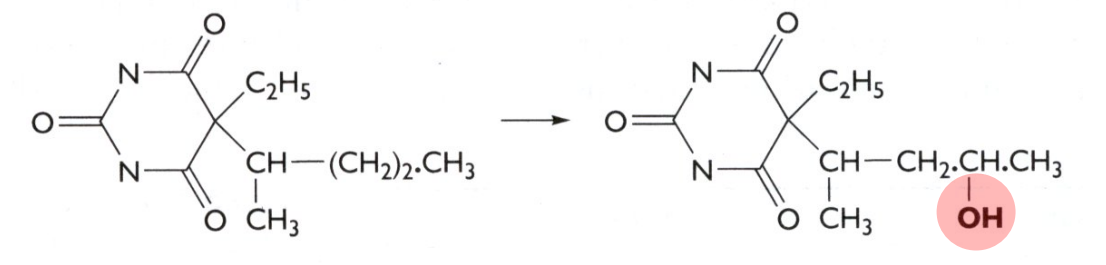
What kind of reaction is this? What phase does this occur?
-
n-dealkylation; phase I
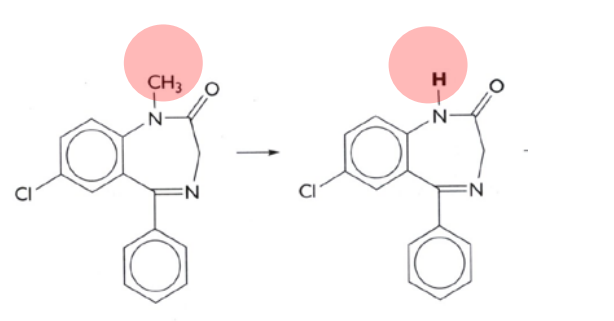
What kind of reaction is this? What phase does this occur?
-
o-dealkylation; phase I
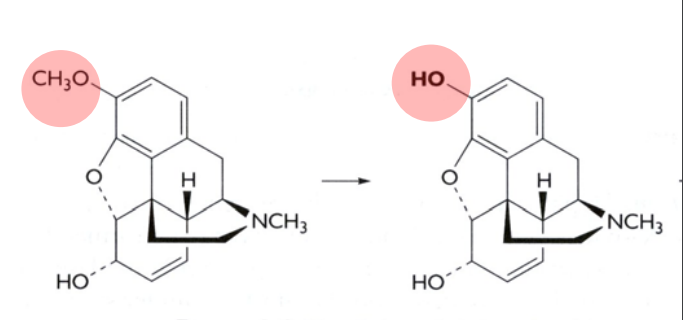
What kind of reaction is this? What phase does this occur?
-
lower logP
Phase I Metabolism generally results in metabolite having _________.
-
ER & mitochondria of hepatocytes
Where are CYP450 enzymes found in humans?
-
family, subfamily, isoform, allele

Blue represents -
Green represents-
Yellow represents-
Number represents
-
CYP2, CYP3
______ and _______ families do most drug metabolisms.
-
phenytoin, CYP2C9
The anticonvulsant drug ________, is first-pass metabolized by _______
-
Efavirenz, active, CYP2B6
_________ non-nucleoside HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). It is a(n) ______ drug. Metabolized by _______
-
codeine, CYP2D6, morphine
__________ is a prodrug metabolized by _______ into the active analgesic ______.
-
grapefruit juice & seville oranges
Which fruit juice inhibits CYP3A4 enzyme, therefore resulting in higher levels of drug concentration?
-
Victims
: substrate drugs directly affected by drug-drug or drug-food interactions
-
Perpetrators
:drugs that interfere with victim drug metabolism
-
Perpetrator inhibitors
- drugs that inhibit enzymes
-results in increased drug concentration
-
Perpetrator inducers
-drugs that increase enzyme function
-results in decrease drug concentration
-
c
LYNPARZA (Olaparib) is a
a. perpetrator inhibitor
b. perpetrator inducer
c. victim drug
-
a
Itraconazole is a
a. perpetrator inhibitor
b. perpetrator inducer
c. victim drug
-
b
Rifampcin is a
a. perpetrator inhibitor
b. perpetrator inducer
c. victim drug
-
Ultrarapid metabolizer
-one functional and more than two copies of functional alleles as a result of gene duplication
-
normal metabolizer
-two functional alleles
or
-one functional and a decreased function allele
-
Intermediate metabolizer
-one LOF allele and a decreased-function alleles
-two decreased function alleles
-
Poor metabolizer
-two LOF alleles
-one LOF and gene deletion

