-
Bacteria are ___ organisms. Meaning they have no nuclear membrane.
prokaryotic
-
Compared to viruses, bacteria require living tissue to survive. True or false?
False; they don't need tissue.
-
Bacilli are ___-shaped organisms.
rod
-
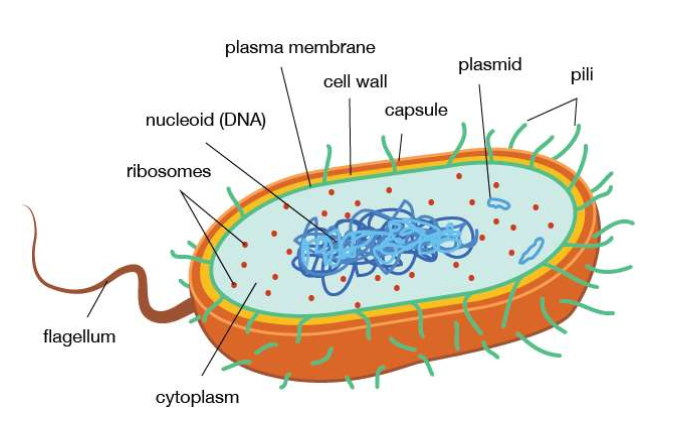
What kind of cell is this?
A bacteria
-
How does a virus infect a human?
Attaches to a host, and enters its genetic material inside the cell.
-
Where is the cell membrane in gram positive bacteria?
Inside the cell wall.
-
Where is the cell membrane in gram negative bacteria?
Between both sides of the cell wall (peptidoglycan).
-
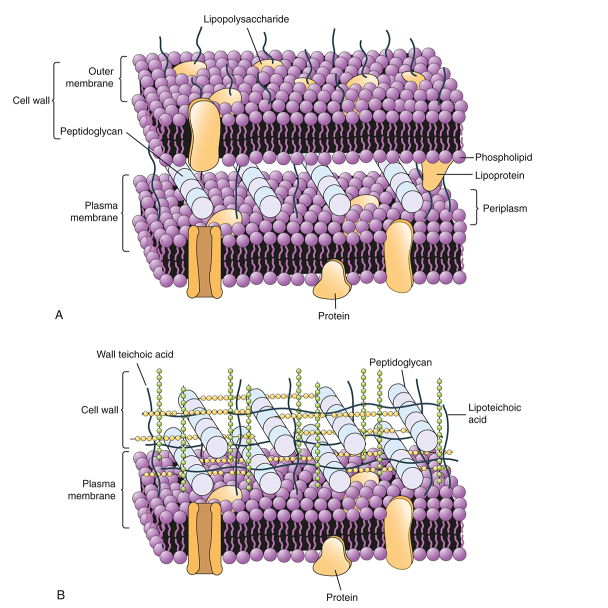
Which one is gram positive, and gram negative bacteria?
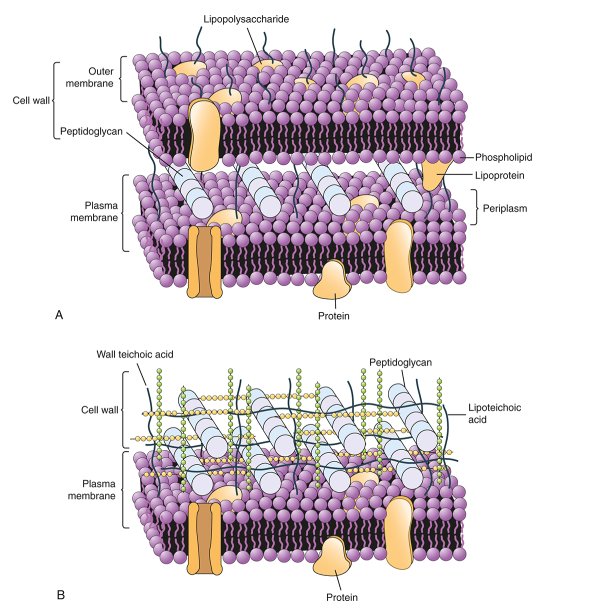
A is gram negative, B gram positive.
-
In some bacteria they have a capsule, or "slime layer". What does this layer provide?
Offers extra protection and adhesion to surfaces.
-
Where are endotoxins found, how are they released, and what do they do?
- Found in the cell wall of gram negative bacteria.
- Released after the bacterium dies.
- May cause fever, general weakness or serious effects to the circulatory system (endotoxic shock).
-
What is the process in which bacteria reproduce by?
Binary fission: division of the cell that produces two identical daughter cells.
-
Describe the process of how viruses duplicate.
1. Virus attaches itself to host cell
2. Penetrates the cell
3. Releases its DNA and RNA, which takeover the host cell.
4. The host cell begins to synthesize more of the virus.
5. The new viruses are released from the host cell by lysis (breakdown) and go on to infect more cells.
-
What is a retrovirus?
A virus containing only RNA. Once it infects the host cell, it inserts its RNA so that the cell can convert the virus's RNA into DNA.
-
Why are viruses so hard to control?
Because they hide inside the host's cells, have various mixtures from other strains which can easily lead to new combinations.
-
Fungi are ___. Meaning their nucleus is encased in a cell membrane.
Fungi are eukaryotic.
-
What are some characteristics of protozoa?
- unicellular
- no cell walls
- motile
- many shapes
-
What is a sexually transmitted protozoa?
Trichomoniasis - has a flagella, found in reproductive systems of both sexes and attaches to the mucous membranes causing inflammation.
-
What are prions?
Agents that change the shape of proteins in a the host's brain cells.
-
What is something that prions do NOT have, but bacteria and viruses do?
They don't have genetic material.
-
What are some factors that might reduce host resistance to an infection?
- age
- genes
- stress
- chronic disease
- immunodeficiency
-
What is virulence?
The degree of pathogenity (capacity to cause disease) of a specific microbe.
-
Microbes may be classified as nonpathogenic. What does that mean?
That they don't cause disease, are part of normal body flora and/or often beneficial.
-
What are endospores?
A latent form of bacterium which may be produced. They have a coating which is highly resistant to heat, but they can't reproduce in this form.
-
Viruses are mainly intracellular parasites, however some are extracellular. What are extracellular viruses called?
Virion
-
Viruses contain a protein coat called a capsid. True or false?
True; it can even change and mutate very quickly.
-
Candida is the causative agent for ___.
thrush and vaginitis
-
What is histoplasmosis?
A fungus causing lung infection, can become serious for the immunocompromised. It's transmitted by inhaling animal droppings.
-
What is pneumocytis carinii?
An opportunistic organism causing pneumonia. Common in HIV patients and is almost a positive sign that someone has HIV.
-
What is malaria?
A non-motile protozoa, transmitted by mosquitos and found in warm climates. They eventually cause the RBCs to rupture which releases new microbes in the blood.
-
Name some examples of protozoa.

-
What are helminths and how do they enter the body?
They are flat or roundworms. They enter the body through breaking the skin or through the digestive system.
-
Name some examples of helminths.

-
What parts of the body are considered sterile (ie lacking resident flora)?
- lungs
- brain
- blood
- bladder
- kidneys
-
What is a reservoir?
The source of the infection (can be a person showing obvious signs or a person showing none).
-
Name some modes of transmissions of infections.
- direct contact (no intermediary, direct touch)
- indirect contact (contact involving contaminated objects)
- droplet (transmission from respiratory or salivary secretions)
- aerosol (sneezing, coughing, infecting the new host when they inhale the particles)
- vector-borne (insect or animal being the host, malaria)
-
What does breaking the cycle of infection look like?
1. Reservoir is located and removed
2. Portal of exit blocked
3. Adequate sanitization
3. Sterilization of area
-
What is pathogenicity?
The capacity of microbes to cause disease.
-
What are the local and systemic signs and symptoms of infection?
Local:
- inflammation
- purulent exudate (bacteria)
- serous exudate (virus)
- lymphadenopathy
Systemic:
- fever/chills
- fatigue and weakness
- headache
- nausea
-
What is the difference between bactericidal and bacteriostatic?
Bactericidal - kills microorganisms
Bacteriostatic - inhibits reproduction
-
What is the difference between broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum?
Broad-spectrum - kills both gram positive and negative bacteria
Narrow-spectrum - kills either gram positive or gram negative bacteria but never both

