-
What does the nervous system consist of?
- CNS: brain and spinal cord
- PNS: cranial and spinal nerves, ganglia, sensory neurons
-
What does the brain do?
The brain is the communication and control center of the body. It receives, processes and evaluates many kinds of input and decides on the response/action to be taken and then initiates the response.
-
What structures protect the brain?
- the skull
- meninges
- CSF
-
What does damage to the left hemisphere result in?
Loss of:
- logical thinking
- intellectual abilities
- communication skills
-
What does damage to the right hemisphere result in?
- impairs appreciation of music and art
- behavioural problems
- spatial orientation and relationship recognition
-
What are one of the early changes with acute brain disorders?
Decreased LOC or responsiveness.
-
What are some systemic disorders that may reduce LOC?
- acidosis
- hypoglycemia
-
What is the most serious level of loss of consciousness?
A coma; person doesn't respond to painful/verbal stimuli and body is motionless. Some reflexes may be present.
-
What is a vegetative state?
A loss of awareness and mental capabilities from brain damage. The person is unresponsive to external stimuli, but they still appear to have their sleep-wake cycle.
-
What is locked-in syndrome?
Person has brain damage but is still aware and capable of thinking, they're just paralyzed and unable to communicate.
-
What is the criteria for brain death?
- no brain function
- no brain stem reflexes or responses
- no spontaneous respiration when ventilator is removed (indicates reflex)
- confirming irreversible brain damage
-
Damage to the upper motor neurons results in what type of motor dysfunction?
- interference w/ voluntary movements
- weakness/paralysis on the contralateral (opp. side of the dmg. hemisphere)
-
Damage to the lower motor neurons (spinal cord) results in what type of motor dysfunction?
- weakness/paralysis on the same side at and below the level of damage
- at the area of dmg, muscles are usually flaccid and reflexes are absent
-
What part of the brain is responsible for receiving and localizing basic sensory input?
The somatosensory cortex (homunculus)
-
What is hemianopia?
Loss of vision on one side.
-
What happens to our vision when the optic tract or occipital lobe is damaged?
Visual field is lost on the opposite side of the damaged side. Ex. Optic tract on the left side is dmged and so the visual field on our right eye is damaged.
-
What happens to our vision if the optic chiasm is completely destroyed?
Vision lost on both eyes.
-
Dysarthria is ___.
when muscles used in speech are not working properly (motor dysfunction).
-
What is agraphia?
Impaired writing ability
-
What is alexia?
Impaired reading ability
-
Why does increased intracranial pressure decrease the function of neurons?
Brain tissue becomes compressed and less blood reaches the high-pressure area leading to lowered neural function.
-
What are primary malignant brain tumors also called?
Astrocytomas
-
Describe the two clinical signs of meningitis.
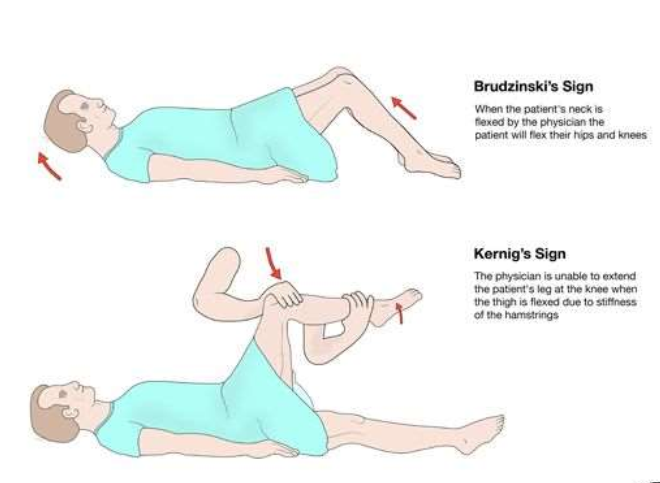
Kernig - resistance to leg extension when lying.
Brudzinski - neck flexion causes flexion of hip and knee.
-
What is the difference between a concussion and a contusion.
Concussion: minimal brain trauma, usually without permanent damage and is caused by a mild blow to the head or whiplash-type injury (rapid movement).
Contusion: bruising of brain tissue --> rupture of bv. Usually from a blunt blow to the head and can lead to possible residual damage.
-
What is spina bifida occulta?
A genetic disorder where the spinous processes don't fuse.
-
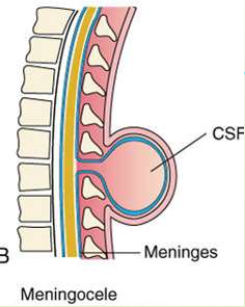
What is meningocele?
Herniation of the meninges due to a sac on the surface (filled with CSF).
-
What is myelomeningocele?
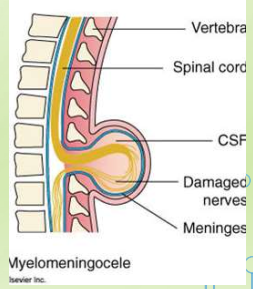
Herniation of spinal cord and nerves along with meninges and CSF.
-
What is status epilepticus?
Continuous seizure without recovery of consciousness.

