-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a ___.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a group of chronic respiratory disorders.
-
Why is COPD so dangerous?
Because it can cause irreversible and progressive dmg to the lungs. It may even lead to cor pulmonale (RCHF).
-
What significant change occurs when a pt. has emphysema?
The destruction of the alveolar walls and septae --> permanently inflated alveolar air spaces.
-
What does the breakdown of the alveolar walls result in?
1. a) loss of SA for gas exchange
b) loss of pulmonary capillaries
c) loss of elastic fibers --> affects lungs ability to recoil on expiration
d) decreased support for other structures --> collapse of walls and additional obstruction.
2. Fibrosis and thickening of walls (chronic irritation and frequent infections)
a) narrowed airways
b) weakened walls
3. Progressive difficulty with expiratory airflow
a) air trapped
b) overinflation of lungs
c) flattened diaphragm
-
What occurs during advanced emphysema (and significant loss of tissue)?
1. Damaged alveoli cling together, forming large air spaces --> makes the lungs look like they have large holes (blebs).
2. Large blebs may rupture --> pneumothorax (collapsed lung; air leaking into the space between lung and chest wall).
3. Hypoxia increases respiration (compensation) from the increased CO2.
4. More frequent infections from difficult to remove secretions and airway defenses are impaired.
5. Pulmonary HTN and RCHF may develop.
-
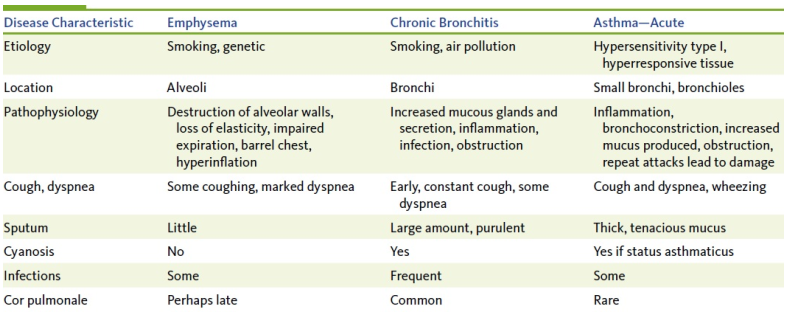
Differentiate between emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
-
Describe chronic bronchitis and its basic pathophysiology.
There's significant changes in the bronchi (from constant irritation).
-
The repeat inflammation, obstruction, and repeated infection from chronic bronchitis can all lead to what?
- inflamed and swollen mucosa
- hypertrophy and hyperplasia of mucous glands
- fibrosis and thickening of bronchial walls
- low O2 lvls
- severe dyspnea --> fatigue
- pulmonary HTN and cor pulmonale (RCHF)
-
What are some signs and symptoms of chronic bronchitis?
-tachypnea and shortness of breath
- frequent thick and purulent secretions
- hypoxia
- cyanosis
- hypercapnia
- polycythemia
-
What is pulmonary edema?
The collection of fluid in the alveoli and insterstitial area. It reduces O2 diffusing into blood and interferes with lung expansion.
-
Pulmonary edema may develop when:
- inflammation in lungs --> ^ permeability of capillaries allowing more fluid to come in
- plasma protein lvls are low --> decreases osmotic pressure (pull) therefore; hydrostatic (push) > osmotic
- pulmonary HTN
-
What is a pulmonary embolus?
- blood clot/mass that obstructs a pulmonary artery
-
Where do most pulmonary emboli originate from?
DVT in legs
-
What is atelectasis?
The collapse of a lung or part of a lung (lobe) --> decreased gas exchange and therefore hypoxia.
-
Name some mechanisms that can result in atelectasis?


