-
Huntington Disease (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Dominant
-
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Dominant
-
Marfan Syndrome (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Dominant
-
Neurofibromatosis (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Dominant
-
PKU (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Recessive
-
Cystic Fibrosis (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Recessive
-
Sickle Cell Anemia (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Recessive
-
Tay-Sachs Disease (Inheritance Pattern)
Autosomal Recessive
-
Rett Syndrome (Inheritance Pattern)
X-Linked Dominant
-
Fragile X (Inheritance Pattern)
X-Linked Dominant
-
VitD Deficient Ricketts (Inheritance Pattern)
X-Linked Dominant
-
Hemophilia A
X-Linked Recessive
-
G6PD (Inheritance Pattern)
X-Linked Recessive
-
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (Inheritance Pattern)
X-Linked Recessive
-
Penetrance of CF
100%
-
Penetrance of PKU
100%
-
Expressivity of CF
Very variable. Even within the same family
-
Karyotype
the number and visual appearance of the chromosomes in the cell nuclei of an organism or species.
-
Karyotype of Turner Syndrome
Single X chromosome
-
Karyotype of Down Syndrome
Trisomy of chromosome 21
-
Common complications of Trisomy 21
1.Decreased intellect
2.Physical deformities (large tongue, wide set eyes)
3. Life limitting
-
Common Complications of Turner's Syndrome
1. Short Stature
2. Congenital heart disease
3. Ovarian Dysfunction
4. Life expectancy around 50 years
5. Higher incidence of learning disabilities but usually normal intellect
-
Penetrance of Huntington Disease
100%
-
Common complications of Huntington Disease
As abnormal protein accumulates in neurons, it causes neurodegenerations. Result is progressive motor dysfunction and death. Usually in a schizophrenic state.
-
Characteristic of Trinucleotide Repeat disorders
1. CAG and CGG common repeats
2. Number of repeats goes up with each generations
3 Higher number of repeats= earlier onset of diseases and increased severity of disease
4. Counseling often includes warnings against reproduction
-
TNR disorders
1. Huntington Disease
2. Fragile X
-
Mitochondrial DNA Disorders
Passed almost exclusively through maternal lines (eggs contain high number of mitochondria. Sperm contain almost none)
-
Most common Mitochondrial DNA disorder
Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)- results in vision loss at an early age
-
Karyotype of Klinefelter Syndrome
XXY
-
Common Complications of Klinefelter Syndrome
1. Tall stature
2. Long Arms
3. Sparce body hair
4. High voice
5. Normal life expectancy
-
Allele
one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome. One allele is inherited from each parent
-
Homo and Heterozygous
Having the same version of an allele, and having two different versions of the allele
-
Red flags for genetic anomalies
GENES:
G-Groups of Anomalies are present. (things you don’t often see and multiple present)
E-Early or extreme presentation
N- Neurodevelopmental delay or neurogenerative diseases
E-Exceptional Pathology (finding several different cancers simultaneously or finding in organs or structures of bilateral organs)
S- Surprising Lab values (repeat to ensure)
-
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Treatment
1. low protein and low phenylamine diet
2. otherwise or without detection, will lead to cognitive delays
3. Early intervention improves outcomes, including in the Newborn Screening
-
Mono genetic disorder
Only one gene is affected
Examples: Marfan syndrome and hereditary breast cancer
-
Marfan Syndrome
monogenetic disorder. single gene mutation of FBN1, is autosomal dominant but about 25% of cases are random mutation
-
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer
Need a mutation of both BRCA1 and BRCA 2 (tumor suppressor genes)
-
Multifactorial genetic disorder
results from combination of genetic, environmental and lifestyle. Often more than one gene contributes to genetic component. Examples: CAD and Major Depressive Disorder
-
Difference between genetic alterations and epigenetic alterations
Genetic alterations- alterations at the gene level
Epigenetic alterations- alterations in the expression of genes. Influenced by lifestyle and environmental factors (chemical exposure, drugs, aging, and diet)
-
Mechanisms of epigenetic modification
1. Histone modification
2. DNA methylation
3. Non-coding DNA expression
-
Histone Modification
1. Histone is responsible for how tight the DNA is wound. By altering the winding of the DNA, it can become more accessible to target OR if tighter, decrease the likelihood of it replicating through transcription.
2. Acetylation: makes gene more accessible vs deacetylation: decreases the likelihood of transcription.
-
DNA Methylation
The addition of a Methyl group to the DNA sequence, stabilizes the DNA and reduces transcription rates. *like a sleeve. Slides over the genome and tells it to be quite.
-
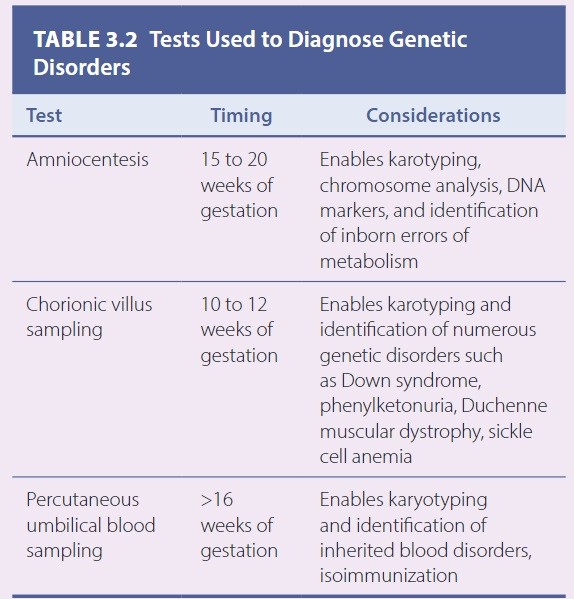
Common Prenatal Screening Tests
-
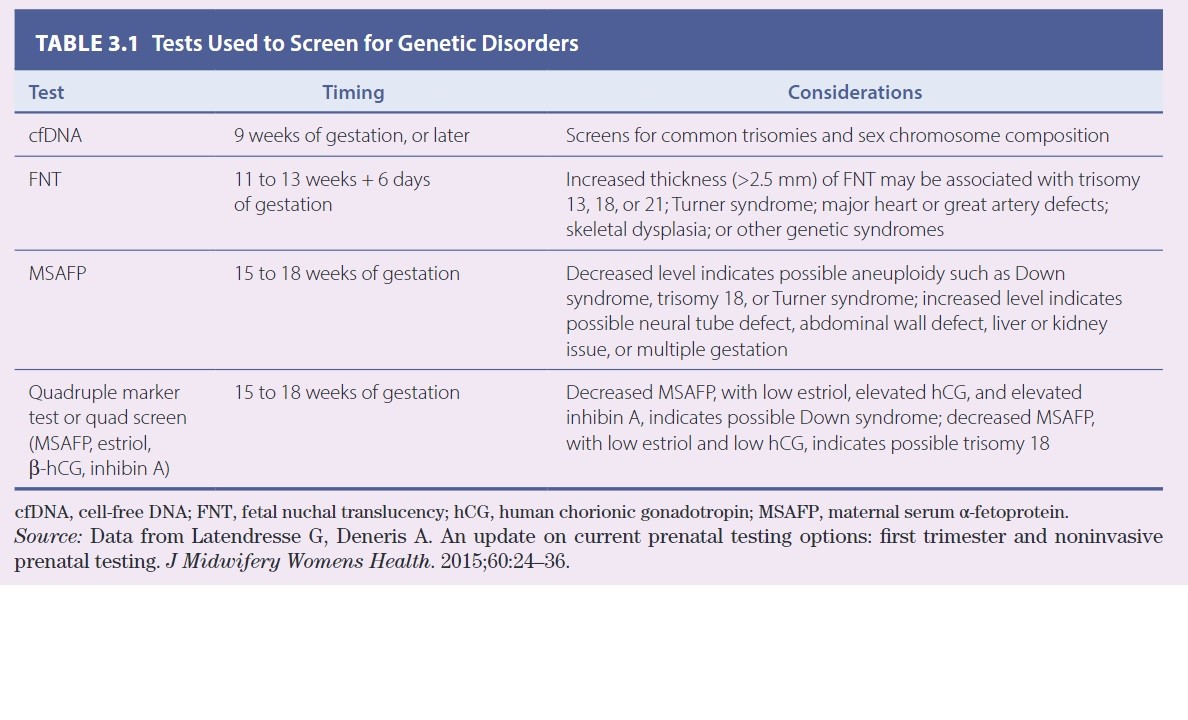
Prenatal Diagnostic Test