-
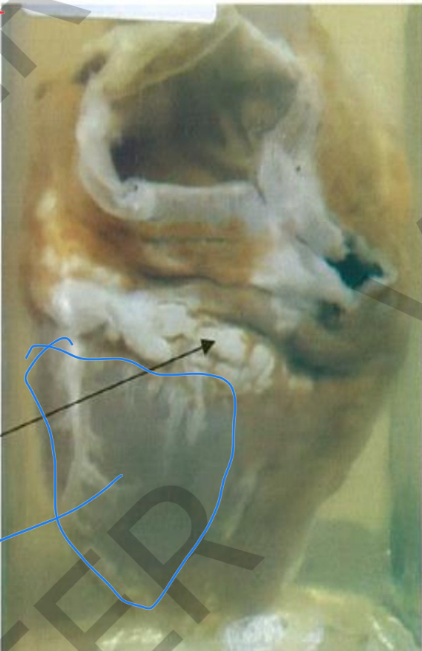
specimen: closed heart gross pathology:
.1 visceral pericardium:
• thickened, rough, reticulated
• Color: opaque yellowish due to fibrin
deposition.
2. Part of fibrin is removed to show the
underlying smooth surface of the heart
Diagnosis: fibrinous pericarditis
-
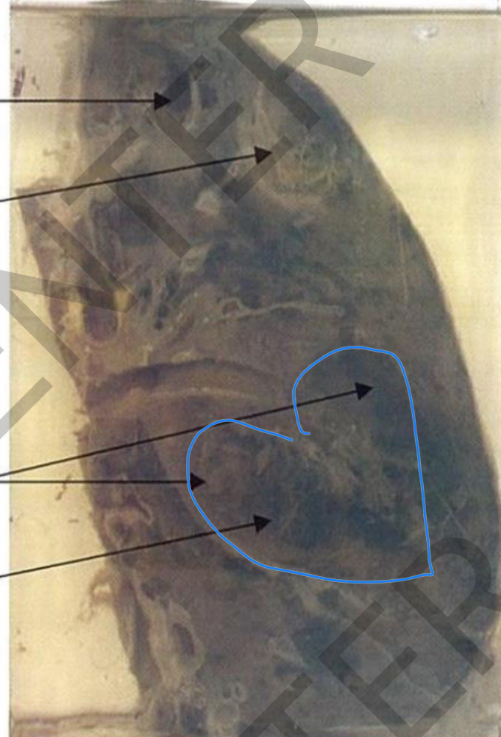
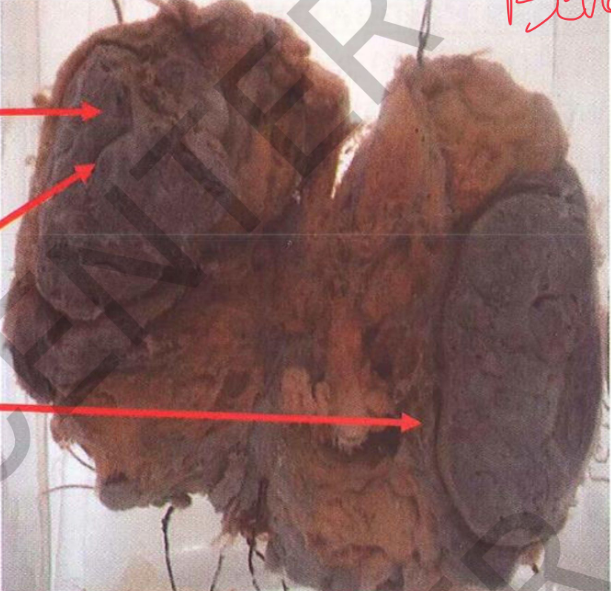
Specimen: Sectioned right lung. Gross Pathology:
Site: upper, middle, lower lung lobes
Size: multiple, variable-sized abcses cavities
Shape: irregularlining.
ecrotic color: yellowishnecrotic
large bilocular cavity (at lower lobe): black shreddy gangrenous lining
covering pleura: greyishwhite fibrous thickening and fibrous adhesions. hilar lymph nodes: enlarged and +
b l a c k anthracosis.
Diagnosis:
1. Multiple lung abscesses with
superimposed gangrene.
2 . P l e u r a l f i b r o s i s a n d a d h e s i o n S D. r T. A R E K
-

Specimen:
Basal part of the lung
Gross Pathology:
Site: Basal part of the right lung
size:largeabscesscavity 10 cm in diameter
Shape: thick fibrous grayish wall
and smooth inner lining. Surrounding lung tissue: collapsed
covering pleura: greywishite fibrous thickening and fibrous
adhesions.
Diagnosis:
Chronic lung abscess.
Pleural fibrosis and adhesions.
-
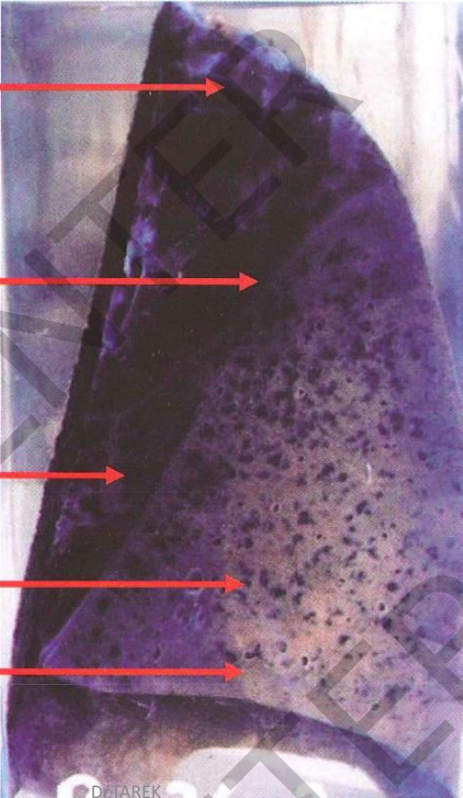
Specimen:
Section in the right lung.
Gross Pathology: Site: lower lobe
Shape: swollen and consolidated color: grayish
cut margins: sharp denoting Consistency: firm
covering pleura: dull, opaque, greyish due to fibrin deposition. ***The upper and middle lobes: collapsed with scattered black
anthracotic spots. Diagnosis
1. Lobar pneumonia, grey
hepatization of the right lower lobe
B-S 2-Fibrinous pleurisy.
3. Anthracosis
-
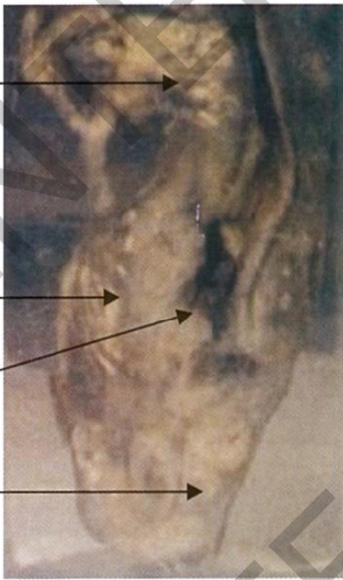
Specimen:
One half of an appendix.
Gross Pathology:
**The appendix: markedly swollen **mucosa lining: necrotic
and dull brown
** wall: perforateidp.
**serosal covering Around the
perforation: dull, opaque and yellowish exudate in the outer
surface.
A piece of omentum is adherent
to the appendix.
Diagnosis:
1. Acute suppurative appendicitis with perforation.
2. Septic peritonitis.
-
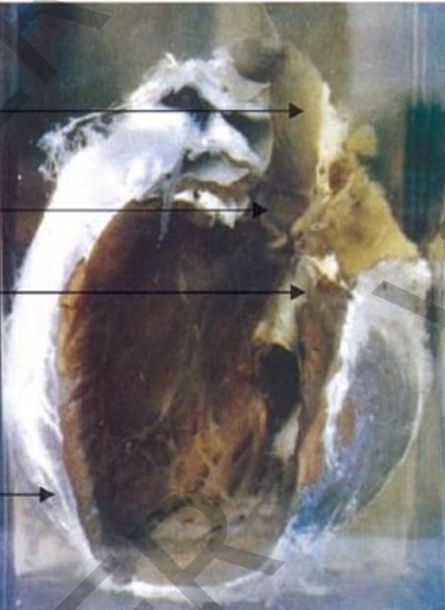
Specimen: heart with open chambers
Gross pathology:
**All cardiac chambers:
hypertrophy and dilatation **Pericardium: wh<ite fibrous adhesions
Diagnosis:
.1 Hypertrophy and dilatation of all cardiac
2. Pericardial fibrosis and adhesions
-

Specimen:
A Slice o f liver
Gross Pathology: Size: reduced surface and the cut
section: nodular. regeneration nodules are
small less than 1 cm, epla yellowish in color
separated by greyish white fibrous strands.
Diagnosis: Liver cirrhosis
-
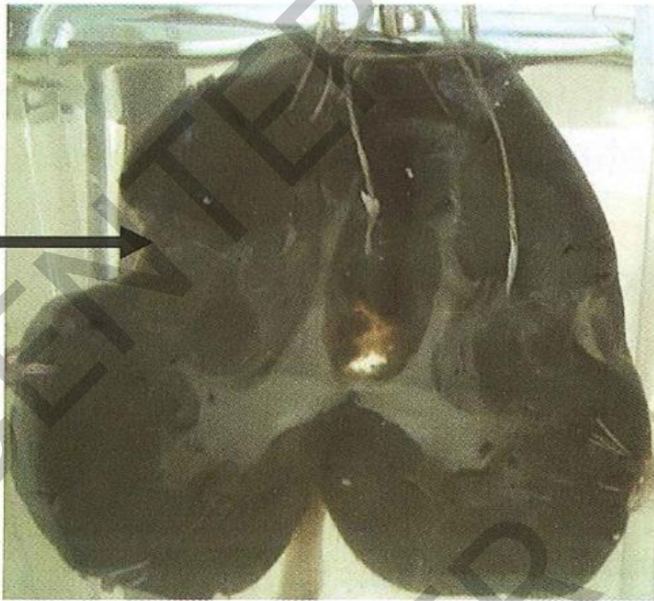
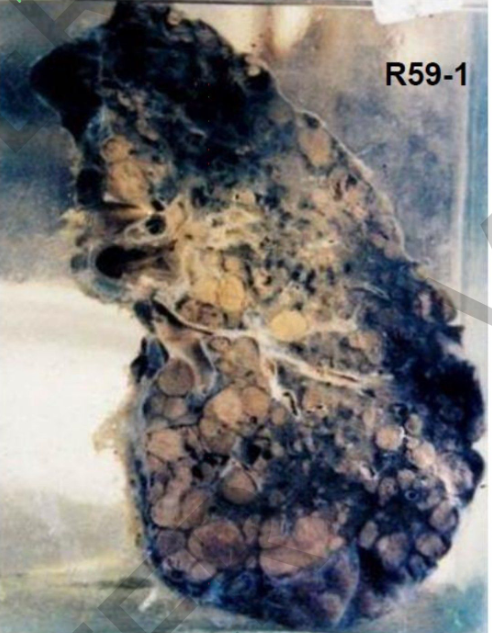
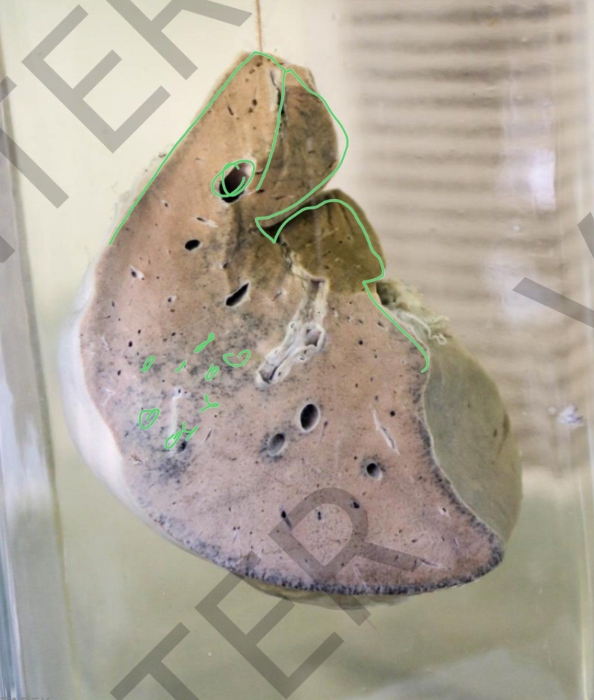
Specimen: bisected kidney Gross pathology:
Outer
surface: multiple depressions (base of
infarctions)
Cut section: Kidney infarcts:
shape: pyramidal
Base: toward the surface.
Color: greyish white with dark margins and
depressed bases (fibrosis.
Diagnosis:
Healed renal infarctions
-
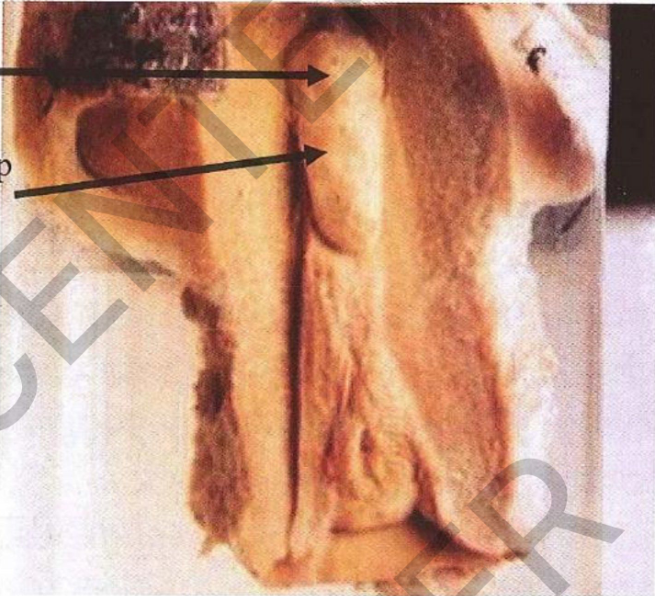
specimen: Open uterus
Gross pathology: oval polyp
Site: posteriorsuperior of the endometrium.
Size: 4 cm in length Surface: smooth
Borders: well defined
Color: greyish white shows tiny cysts
Diagnosis: Endometrial polyp
-
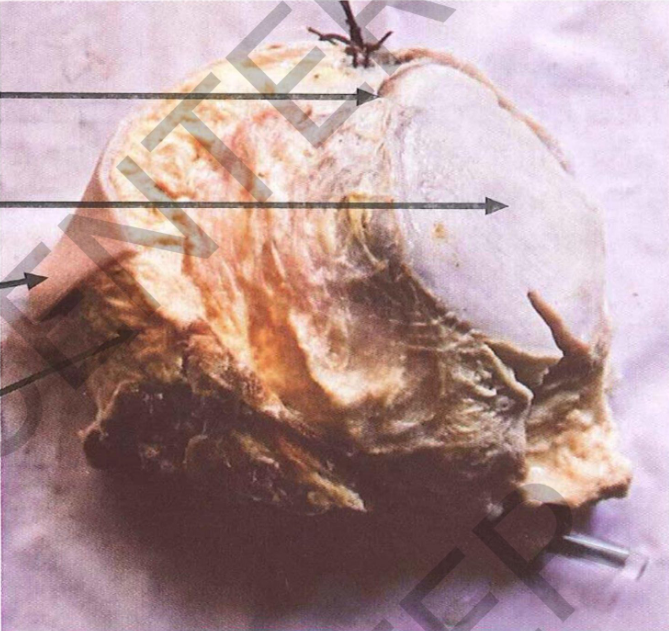
Specimen: Section in breast
Gross pathology: .1 Site: Breast
2. size: 7 cm in diameter 3. color: greyish
4. consistency: Firm
5. Cut section: no slits
6. capsulated mass
Diagnosis: Fibroadenoma
(pericanalicular)
-
Specimen:Section in the breast.
Gross pathology: Site: breast
Size: 6X4 c m
shape: well defined oval Color: greyishwhite
cut section: many slits. Capsule: capsulated
2. The breast fat AROUND THE MASS shows 2 smlal egrauril
greyish white masses(mammary hyperplasia).
Diagnosis
1. Fibroadenoma (intracanaliculartype).
2. Mammary hyperplasia.
-
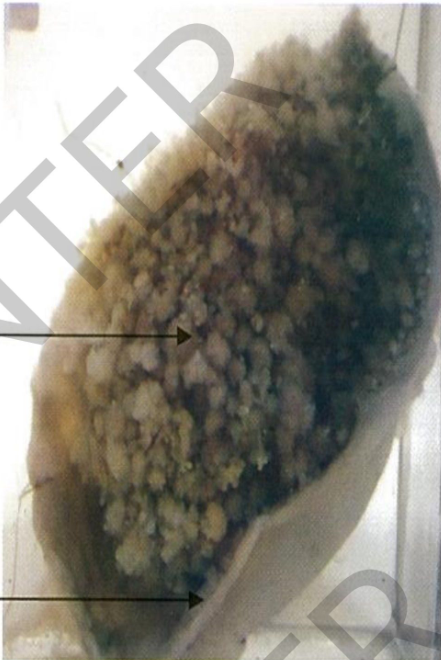
Specimen: Half of ovarian cystic mass
Gross pathology: Site: ovary
Shape: oval unilocular cyst Size: 15X10 cm.
outer surface: smooth
color: greyish
The inner surface: many
small papillae, projecting in the cyst cavity
Diagnosis
Papillary serous cystadenoma of the ovary.
-
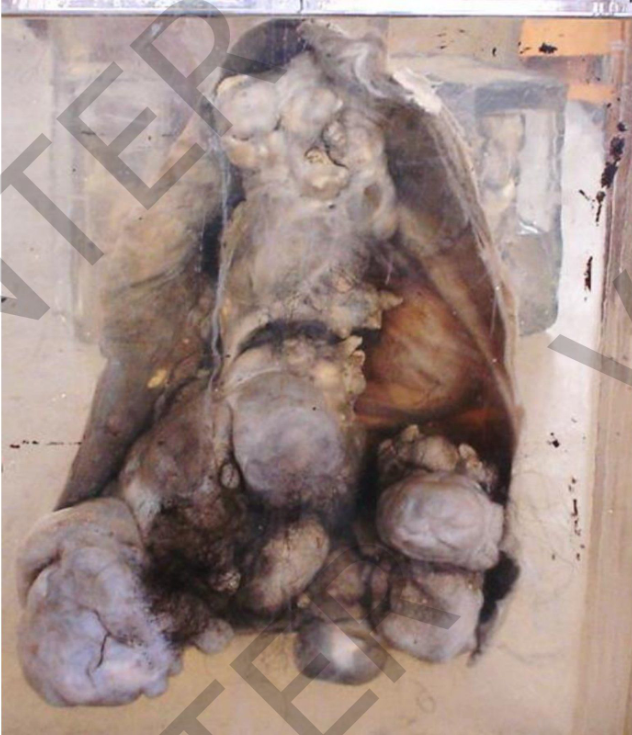
Specimen: Part of a large cystic ovarian mass
Gross pathology:
1. The outersurface is
smooth.
2. Theinner surfaocfethe
cyst shows solid masses
(dermoid ridge). shows different tissue as tufts of
hair, teeth and a tongue like structure.
Diagnosis:
Dermoid cyst (benign cystic
teratoma) of ovary (Ovarian mature teratoma)
-
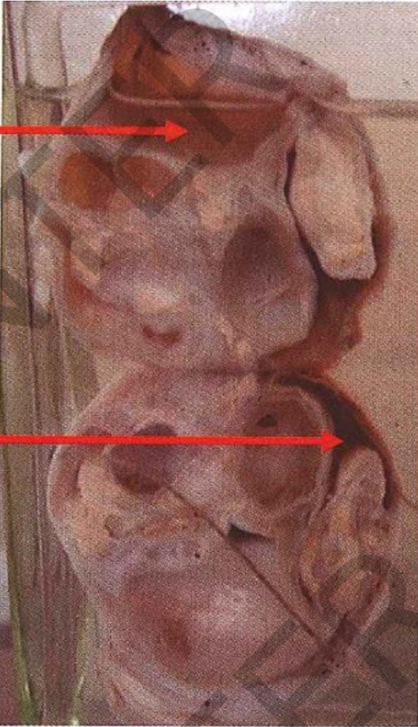
Specimen: bisected testis Gross pathology:
Testis is enlarged
Cut section: replaced
by multi cystic tumor
One of the cysts contains smal tuft fohair
Diagnosis:
Teratoma of the testis
-
specimen:half of a mass
Gross:
Shape: Oval
Size: 20 x 10 cm
Outer surface and cut section: lobulated
Consistency: soft
Color: yellow
Capsule: Fibrous capsule
Diagnosis: lipoma
-

Specimen:
Asegment of small intestine.
Gross Pathology:
bisected intestinal mass
<く covered by intact mucosa.
Shape: globular
capsulated well defined projecting in intestinal lumen
D85-12
color: greyish white in Size: 4 cm in diameter.
proximal part of intestine above the
mass is hypertrophied and dilated (chronic intestinal obstruction).
Diagnosis:
*Fibroma of the small intestine.
Intact mucosa Tumor mass
*Chronic intestinal obstruction
-

Specimen: A part of skull shows:
Site: The outer table of the skull
size: 3 cm in diameter
Shape: projecting globular mass Capsule: non-capsulated
Color: ivory white appearance Consistency: very hard.
The groove seen at its base
represents a failed attempt at manual sawing of the tumor.
Diagnosis:
Compact osteoma (ivory osteoma) of the skull
-
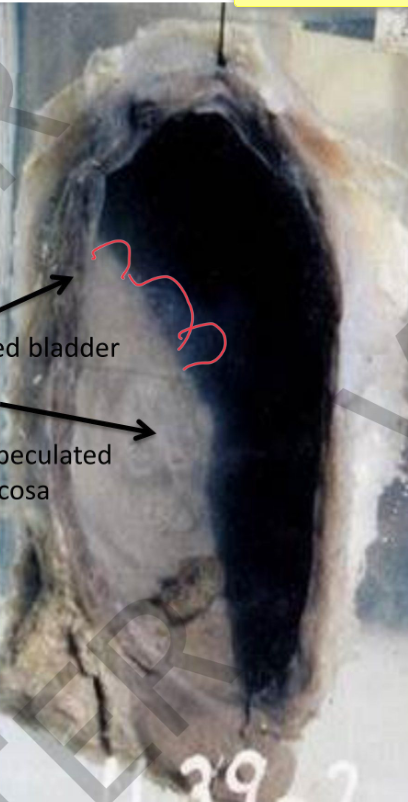
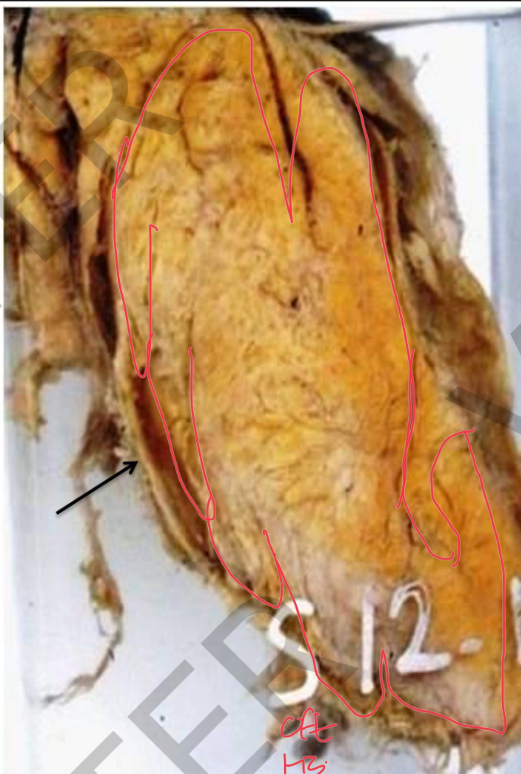
Specimen: Distal part of the ureters, bladder and prostate
Gross Pathology:
1. The BLADDER MUCOSA: at the trigon 3 small polyps projecting in the bladder lumen,
they are greyishwhite with brownish spots of hemorrhage
2. The rest of bladder mucosa shows scattered dirtyyellowishgranularpatches
(sandypatches).
3. The BLADDER WALL
is hypertrophied, dilated and trabeculated.
4. Distal ends of the URETERS are dilated. Diagnosis:
.1 Bilharzialcystitisydnas( patches and polyps).
2. Dilated bladder and bilateral hydroureter.
-
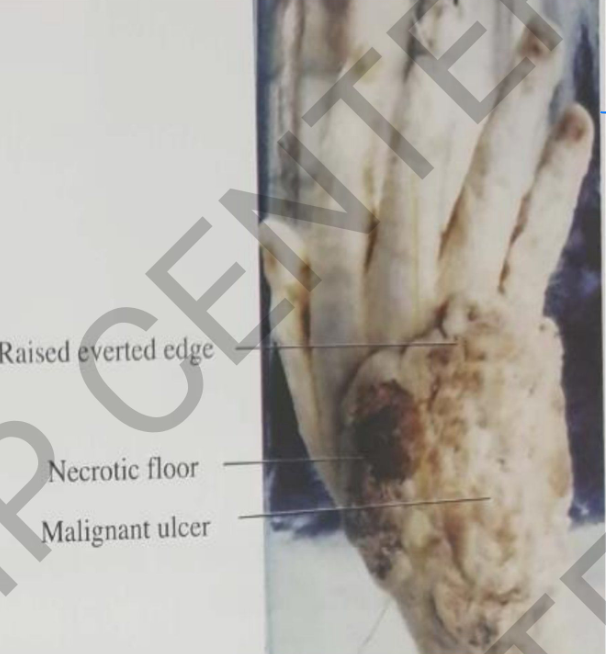
specimen: Right hand
Gross: malignant ulcer
• Site: Dorsum of hand size: (15x12cm)
• shape: irregular
• edges: Raised everted floor: rough necrotic.
Diagnosis:
Ulcerative carcinoma of
hand (squamous cell carcinoma)
-
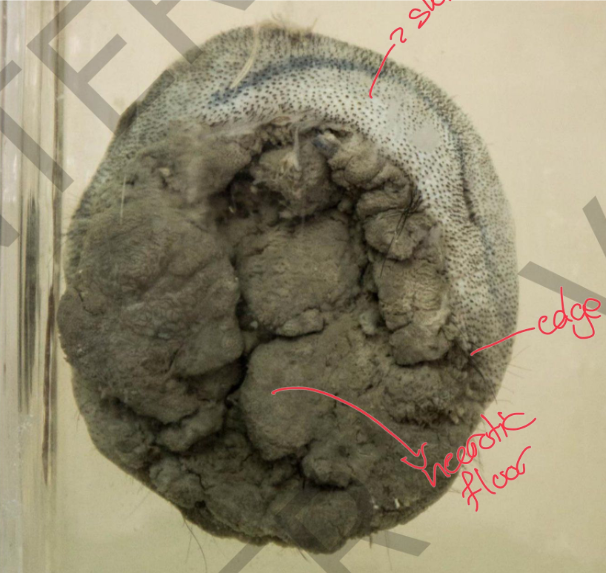
Specimen: part of scalp Gross pathology:
malignant ulcer
• Site: scalp
• size:(8x7cm)
• shape: irregular
• edges: Raised everted
floor: rough necrotic
Diagnosis:
Ulcerative carcinoma of
scalp (squamous cell carcinoma)
-
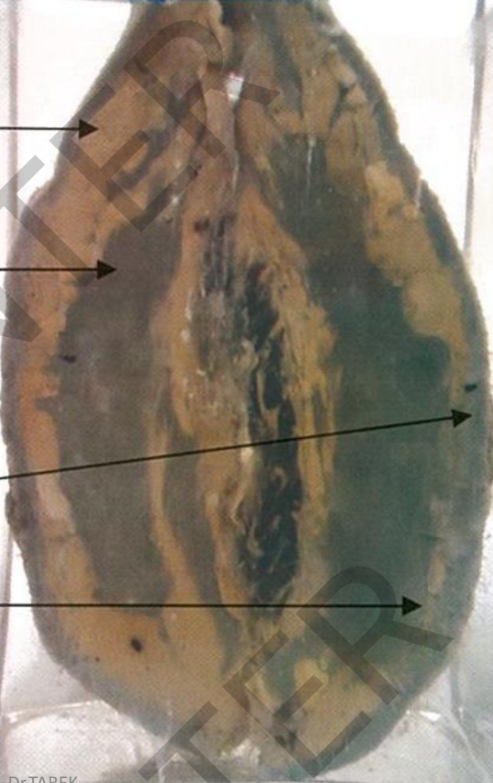
Specimen: A mastectomy
specimen composed of breast,
pectoral fascia and pectoral muscle.
Gross Pathology: Site: breast
size: 6X3 cm.
Shape: irregular
infiltrative non-capsulated color:
greyishwhitem a s s
nipple is infiltrated and retracted.
skin is granular (peaud'orange)
diagnosis:
Infiltrative carcinoma of the
breast
-
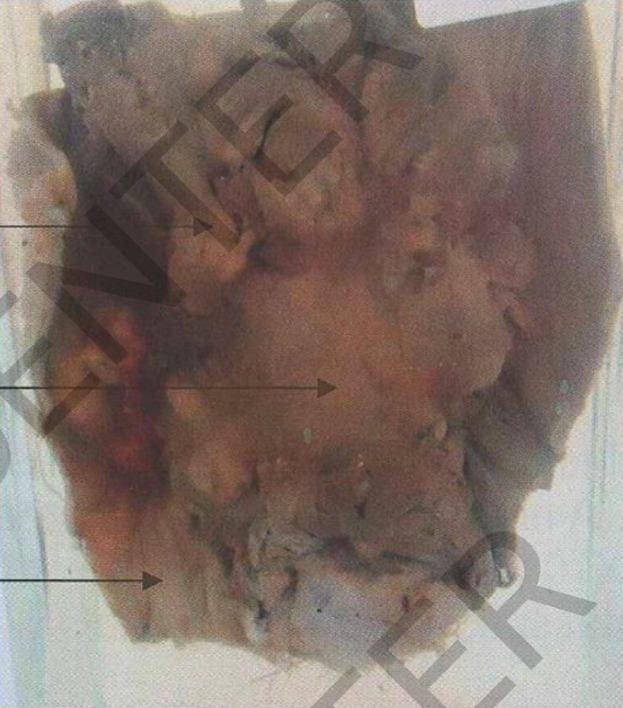
Specimen:
Opened caecum and
appendix
Gross Pathology: Site:mucosaofthe
caecum
Shape: malignant irregular ulcer
Size: 6X5 c m
Edge: raised everted floor: roughnecrotic
Diagnosis:
Ulcerative carcinoma of
the caecum.
-
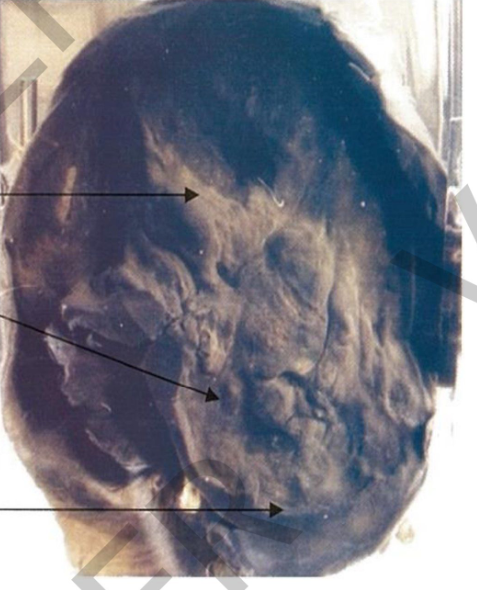
Specimen: opened stomach
Gross:
Stomach:
rigid contracted Gastric wall:
diffusely thickened + infiltrated by grayish tumor
growth
Mucosal folds: obliterated
Diagnosis: Diffuse infiltrative
carcinoma of stomach (linitis plastica).
-
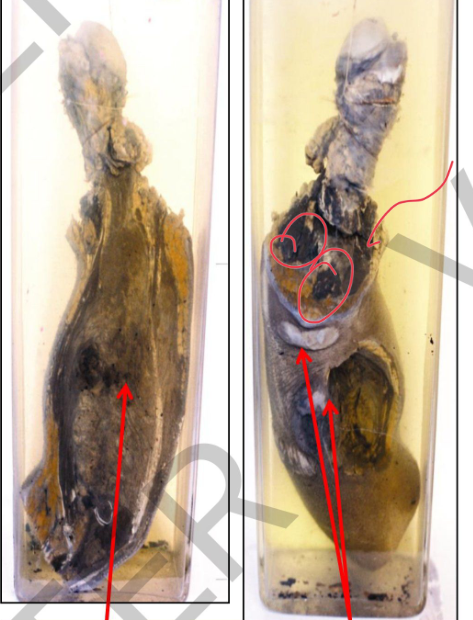
Specimen: Section in the arm
Comment:
Site: lower part of the humerus is destroyed and replaced by a
large infiltratingmass.fleshy
Capsule: noncapsulated
Color: greyish brown.
Cut section: areas of necrosis.
Surrounding muscles and elbow joint are infiltrated
The skin of the arm: multiple projecting scars (keloids) at the sites of cautery
burns.
Diagnosis:
Osteosarcoma of the humerus
Multiple keloids
-

Specimen: shaft of long bone (femur)
Gross pathology: < Site: medullary canal
Capsule: n o n capsulated
Infiltrative mass
Marked destruction and
pathological fracture
Diagnosis: Metastatic tumor of
femur with pathological fracture
-
Specimen:
Sectioned lung.
Gross Pathology:
Site: sub-pleural scattered
non-capsulated
Color: yellownodules Size: Small 2-15 m m
Diagnosis:
Lung metastases
-

Specimen:
Inferior vena cava and
common iliac veins
Gross pathology:
The lumen of the vessel
occluded by dark red thrombi.
Diagnosis:
Thrombosis of the
inferior vena cava and the common
iliac veins.
-
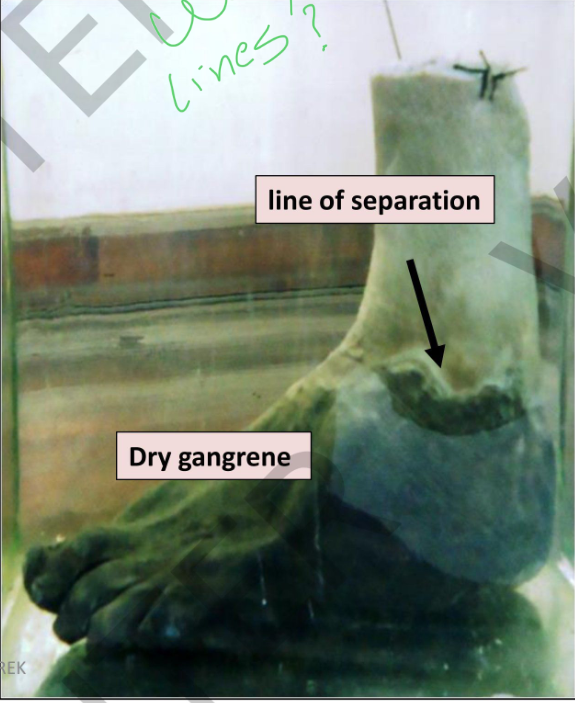
SPECIMEN: Left foot
Gross pathology:
.1 foot is black shrunken and mummified with wrinkled skin ydr(
gangrene).
2. irregular groove (line of separation) at the level of malleoli.
3. cut section: cross section of the
anterior tibial artery in the of the
leg →yellow dnekechit cerscent due to atherosclerosis and an
occluding thrombus.
Diagnosis:
Dry gangrene of left foot (senile
gangrene)
Atheroscelosis and thrombosis of
anterior tibial artery
-
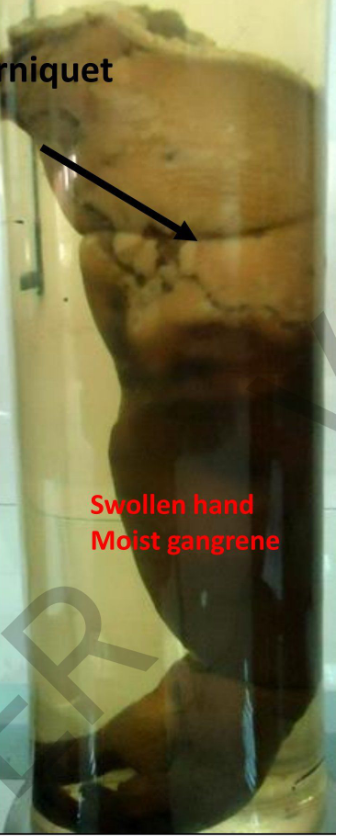
Specimen:
Right Upper limb.
Gross pathology:
1-The distal part of the arm, forearm and hand are gangrenous.
2- The skin is dark brown with maceration.
3- The circular groove, proximal to the gangrenous part is site of a tightly applied tourniquet.
4- N o line of separation
Diagnosis:
Moist gangrene of the upper limb
(due to tightly applied tourniquet)
-
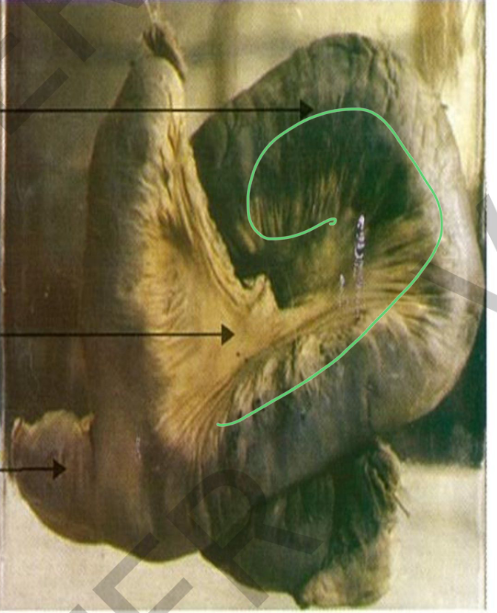
Specimen:
segment of the ileum with its
mesentery.
Gross Pathology: *diverticulum 3 cm in length
arising from the ileum at the anti-mesenteric border.
*The intestine is twisted
(volvulus) →moist gangrene of the wall.
*The mesentery showsdull
h y p e r e m i cp a t c h e s
Diagnosis:
*Meckel's diverticulum. *Intestinal volvulus with
gangrene.
*Acute intestinal obstruction. *Septic peritonitis.
-
Specimen:
A slice of enlarged liver
Gross Pathology:
cut surface: NUTMEG APPEARANCE → alteration of dark red foci of
congestion (central vein and central end of sinusoids) and yellow areas (fatty degeneration in the periphery of the liver lobules).
Diagnosis:
Chronic venous congestion of the liver.
-
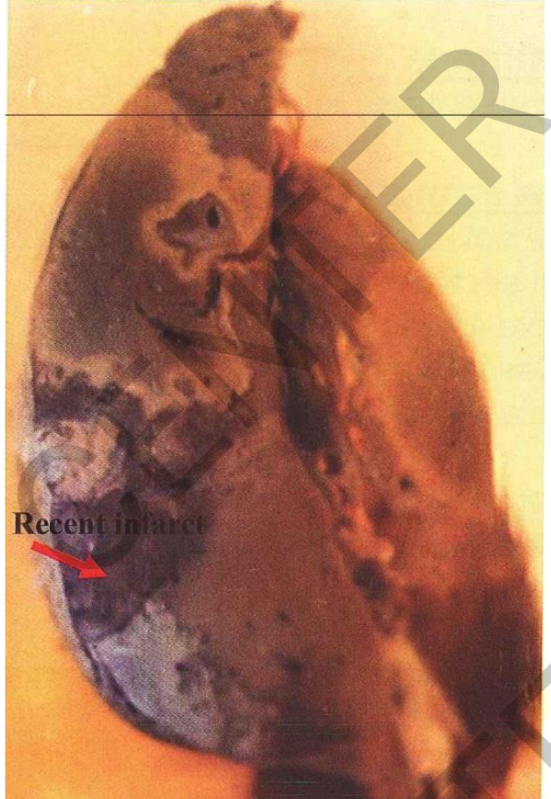
Specimen: Bisected spleen.
Comment:
• Size: enlarged
• Cut section: multiple recent infarctions
• Infarctions are brown with pale periphery
• w e d g e s h a p e d areas o f onictanrfi
• base directed towards the surface
and covered by opaque fibrin deposits (perisplenitis)
• and the apex towards the hilum. Diagnosis:
• Multiple recent splenic infarcts
• Perisplenitis
-

Specimen:
Two slices of the liver.
Gross Pathology:
cut surface: multiple irregular small abscess cavitieswith irregular
D115-5
yellowish necrotic lining. **The very tiny cavities
are due to
post-mortem autolysis
Diagnosis:
Pyaemic abscesses of the liver.
-
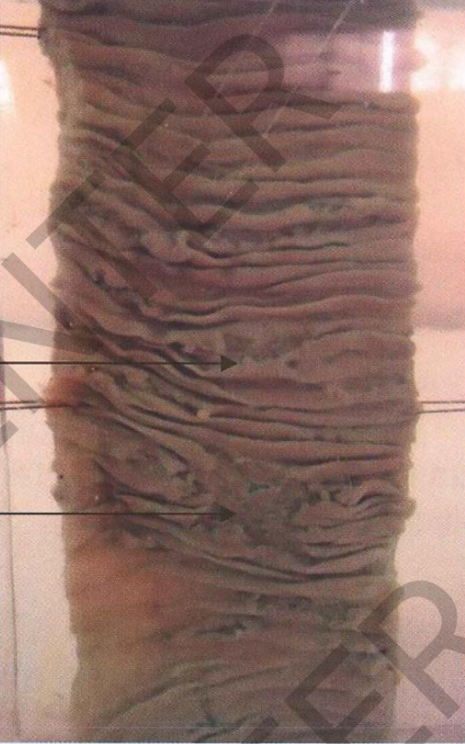
Specimen:
A segment of ileum < Gross Pathology:
Mucosa: multiple
transverse ulcers
Edges: Undermined
floor: yellowishcaseous
Diagnosis:
Secondary intestinal tuberculosis
-
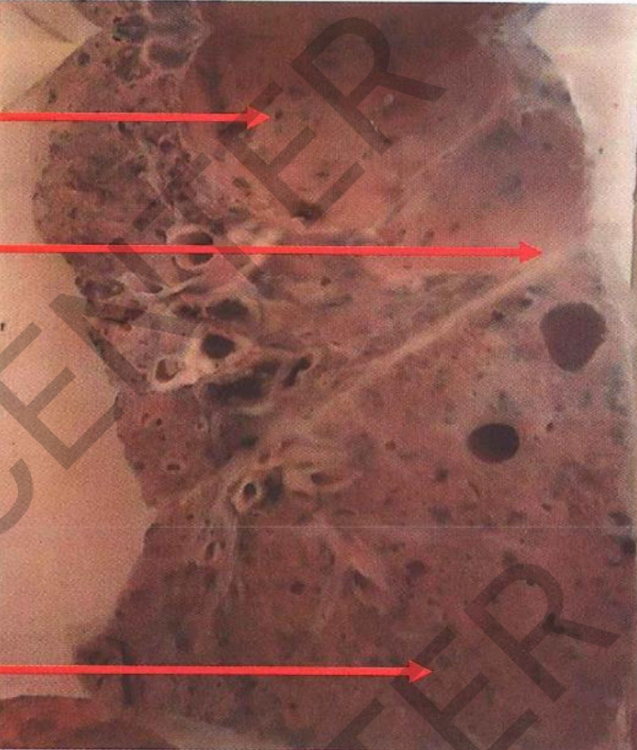
pecimen: Sectioned lung
Gross Pathology: Site: apical cavity
Size: large 9 cm in diameter with a fibrotic wall
Color: yellow caseous lining **traversed by ridges (representing thickened bronchi and blood vessels).
***lower lobe: multiple wolley caseous foc,i (acinar lesions)
The foci at the base get fused (tuberculous
pneumonia).
covering pleura: greyish white fibrous
thickening and fibrous adhesions.
*** tracheobronchial lymph nodes: minimal
tuberculous lesions and anthracosis Diagnosis:
1. Chronic fibrocaseous pulmonary tuberculosis associated with confluent
R45-11
tuberculous pneumonia.
2. Pleural fibrosis and adhesions.
-
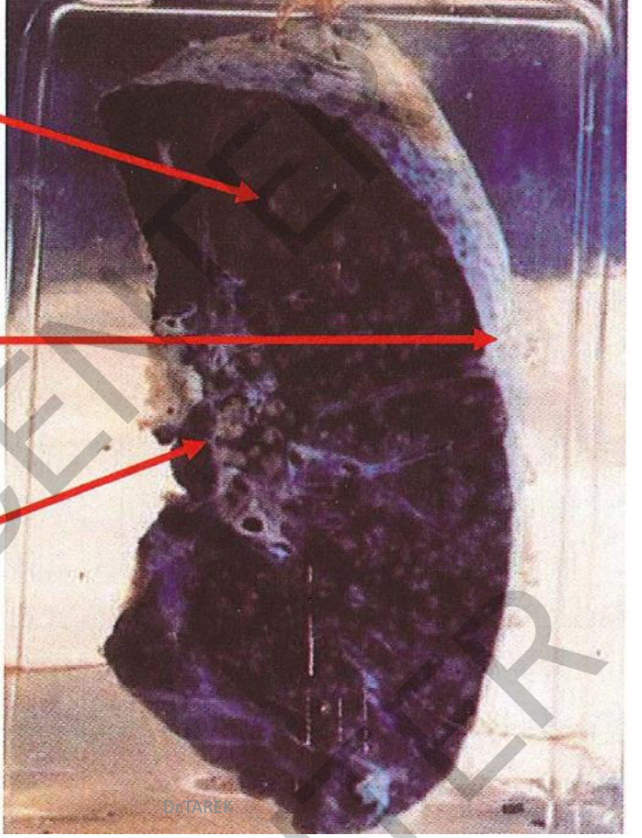
pecimen:
Sectioned lung
Gross Pathology:
cut surface: numerous
scattered small caseous foci (2- 3 mm)
tracheobronchial lymph nodes:
yellowcaseous foci and anthracosis.
a covering pleura: greyishwhite
fibrous thickening and fibrous
adhesions.
Diagnosis:
1. Miliary tuberculosis of the lung.
2. Pleural fibrosis and adhesions.
-
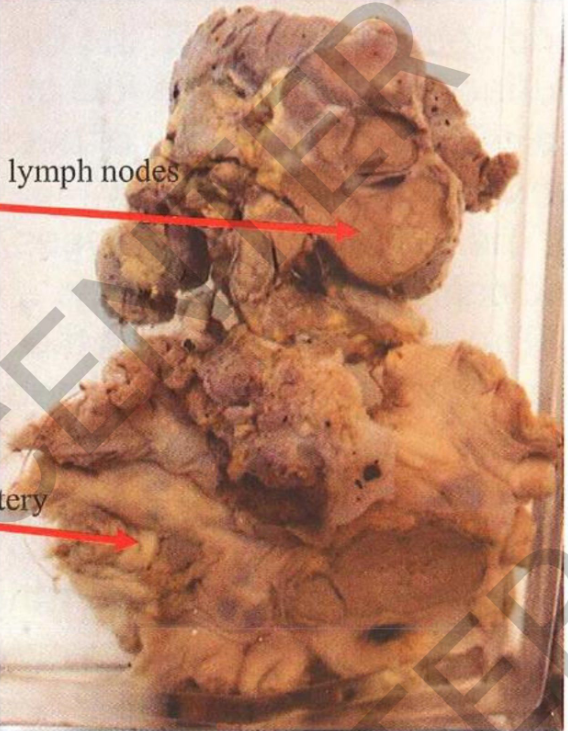
Specimen:
pancreas, mesentery, mesenteric and para aortic lymph nodes
Gross pathology: < Lymph node: enlarged, matted (adherent to each others)
Cut section: yellow a n d caseaous
Nodes are surrounded by greyish fibroustissue
Diagnosis:
- -
Tuberulous lymphadenitis of
mesenteric lymph nodes (tabes mesenterica)
Tuberculosis of para aortic lymph nodes
-

Specimen: Half of foot.
Gross pathology:
1-The cut section:
multiple irregular abscess
cavities showing necrotic contents and black
granular material (fungal colonies of mycetoma)
2- Involves both soft and bony structures of foot
3- open on the skin by nsiuses
Diagnosis: Madura foot
-
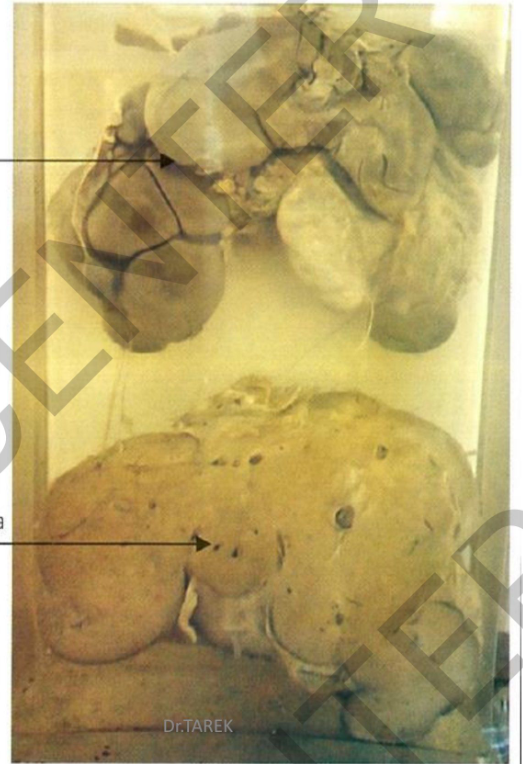
Specimen:
A sectioned liver
Gross Pathology:
The outer surface of the liver
is lobulated, due to fibrous
scarring pulling on the surface. The cut surface of liver shows
multiple healed gummata, greyish white in color.
Diagnosis: Hepar lobatum.
-
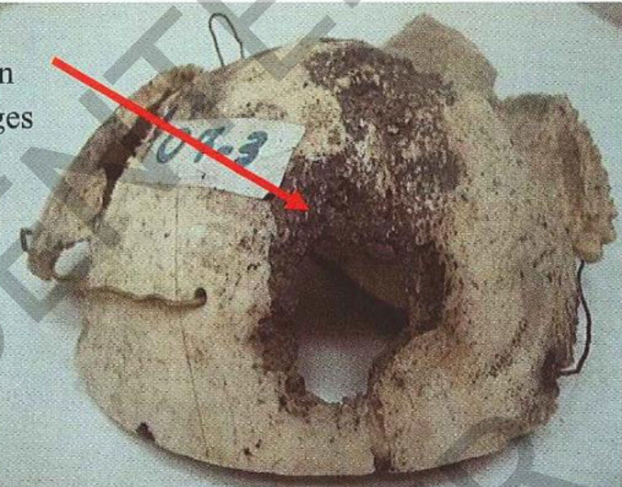
Specimen: part of skull cap
Gross pathology:
Skull shows multiple defectsvariable in size
Shape: irregular
Bone adjacent to these defects shows irregular destruction (worm eaten
appearance)
Diagnosis:
Syphalitic osteitis of skull
-

Specimen:
Foot.
Gross pathology:
1. The skin of the foot is thickened and
nodular.
2. The nodules are
ulcer variable sized and greyish
focal with ulcerations Diagnosis:
Nodular
leprosy
(Lepromatous leprosy)
-
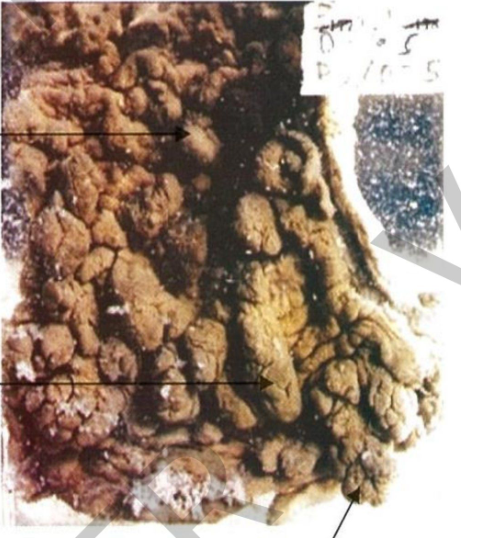
Specimen:
Part of sigmoid colon.
GrossPathology:
Mucosa: Sessile polyps
large number of variable
D70-5
sized grayish sessile, pedunculated or
branching polyps.
Pedunculated polyp
Diagnosis:
Bilharzial polyps of the
colon.
-
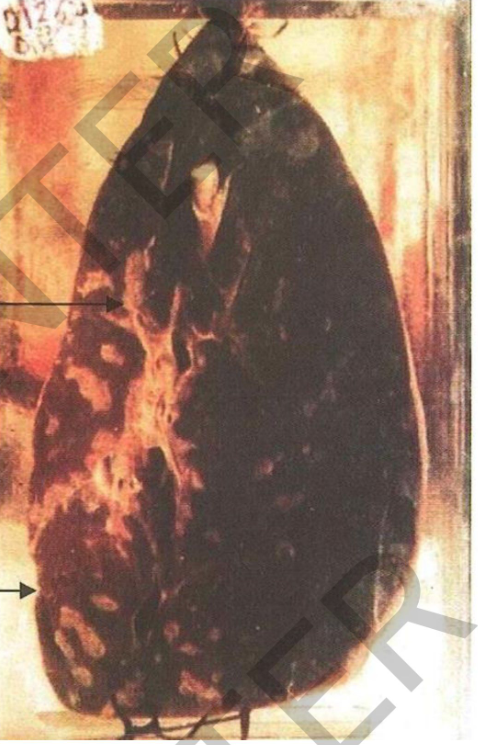
Specimen: Section of the liver
Gross Pathology:
1. The surface of the liver:
irregulardepressions.
2. The cut surface: fibrosed
thickened whitish portal tracts.
3. The tracts cut transversely
appear round, the tracts cut longitudinally appear oval or
elongated.
4. The liver tissue in between
shows no regenerative nodules and is dark brown.
Diagnosis:
Bilharzial peri-portal hepatic fibrosis.
-
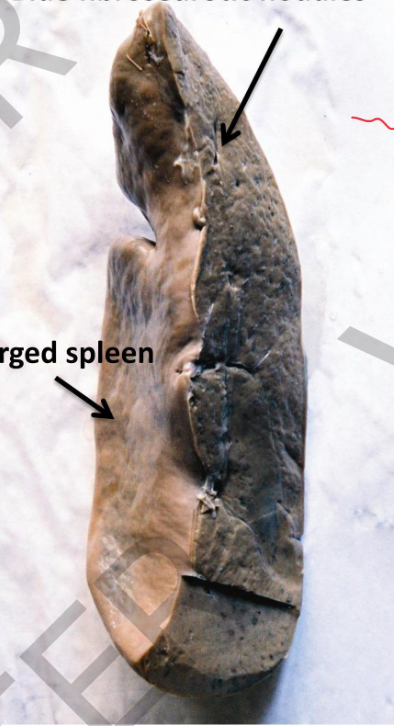
Specimen:section spleen
Gross pathology:
Size: spleen enlarged
Upper part: is treated with potassium
ferrocyanide + hydrochloric acid (prussian blue reaction)
Fibrosedrotic nodules in this part appear pale blue
The lower part: scattered palebrown small foci (unstained fibrosedrotic
nodules)
Diagnosis:
Congestive spleenomegaly with
fibrosedrotic nodules
-
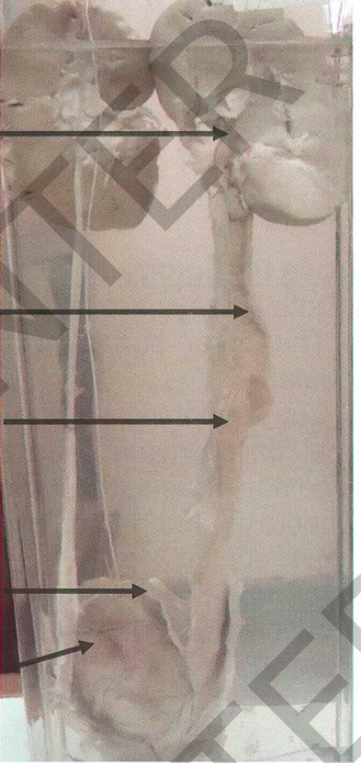
Specimen: Section of both kidneys, both
ureters, bladder and prostate:
Gross pathology:
- The bladder mucosa:scattered ytrdi
owhsliyle granular patches (sandy patches)
and afissured transverse ulcer 2cm
long. - The left ureter: thickened and markedly
dilated, its mucosa shows dirty yellowish
granular patches (sandy patches).
- The left pelvis and calyces: dilated and
their with scattered dirty yellowish granular patches. (sandy patches)
Diagnosis:
Hydronephrosis Hydroureter
1. Bilharzial cystitis with sandy patches and fissured ulcer.
2. Bilharzial ureteritis with sandy patches.
3. Left hydroureter and hydronephrosis.

