-
___________ ___________
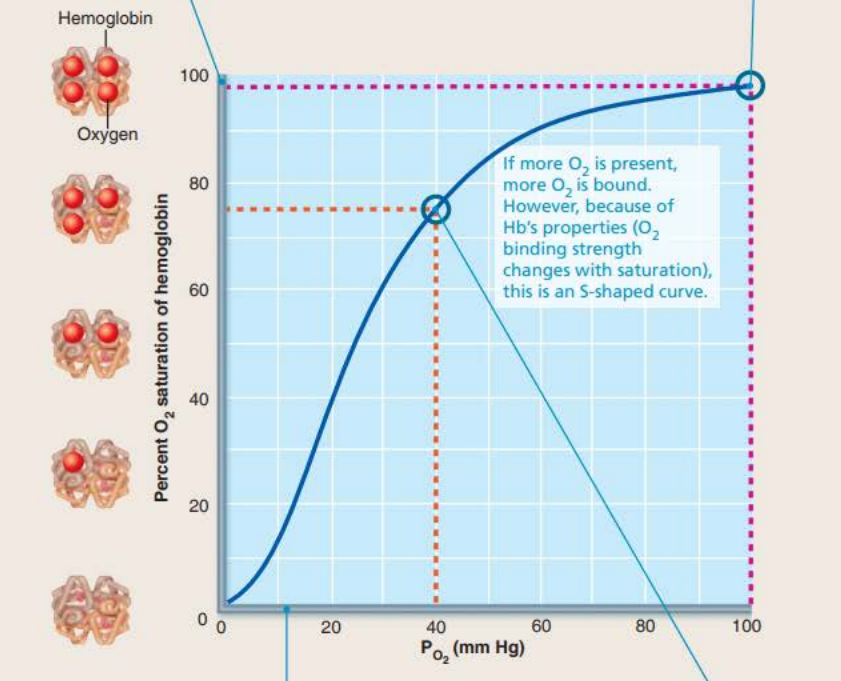
98% hemoglobin saturation
20 vol %
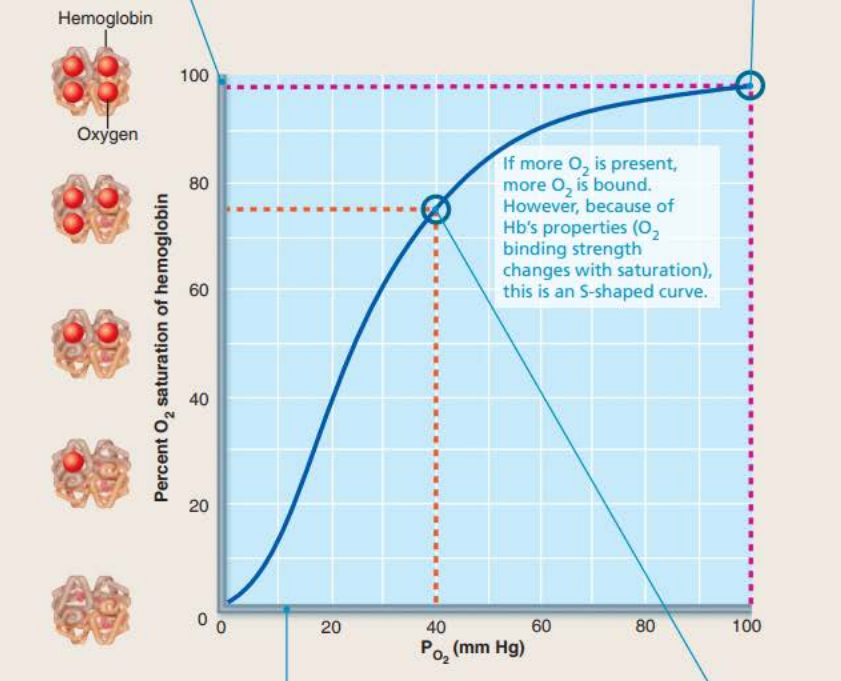
arterial blood
-
_________ __________
75% hemoglobin saturation
15 vol %
venous blood
-
what percentage of oxygen is dissolved in blood?
1.5%
-
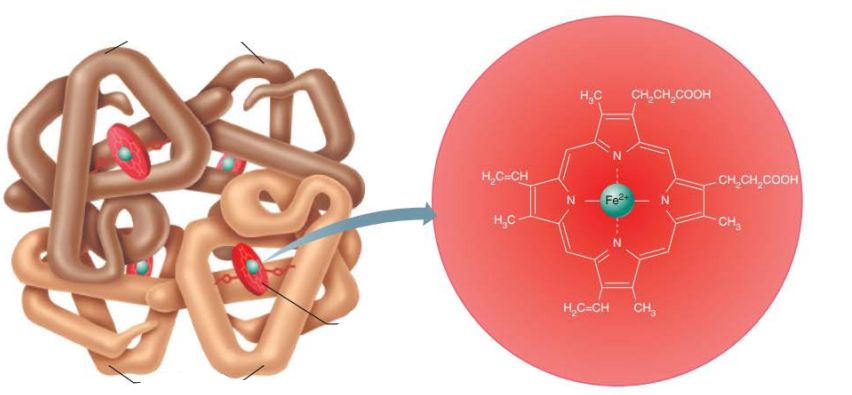
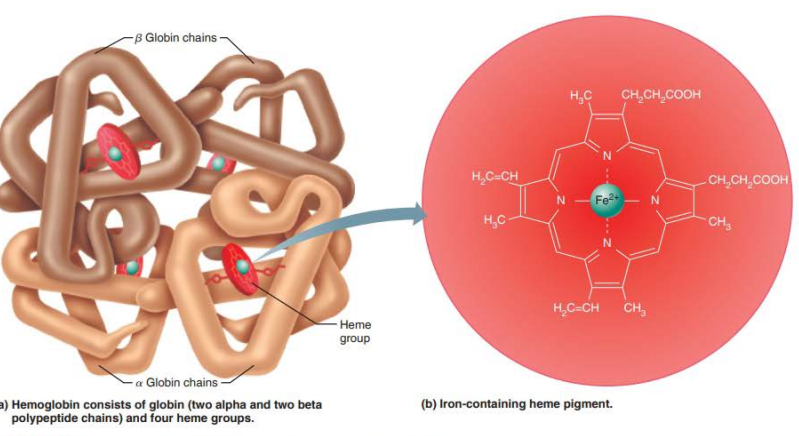
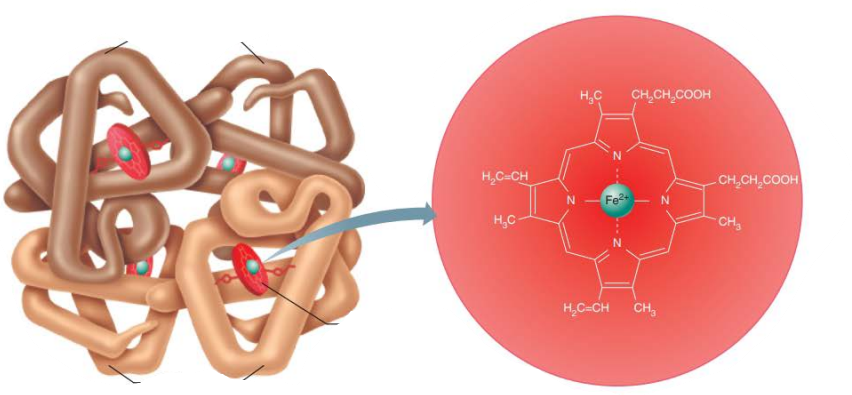
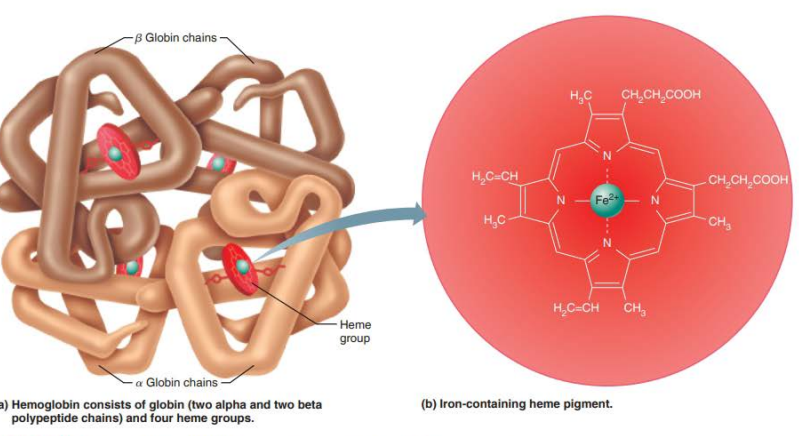
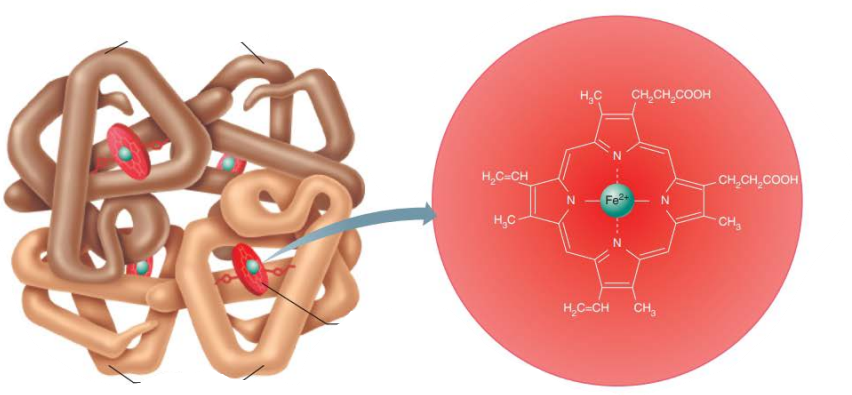
____________________
Oxygen bound to hemoglobin
3d shape
Ruby red color
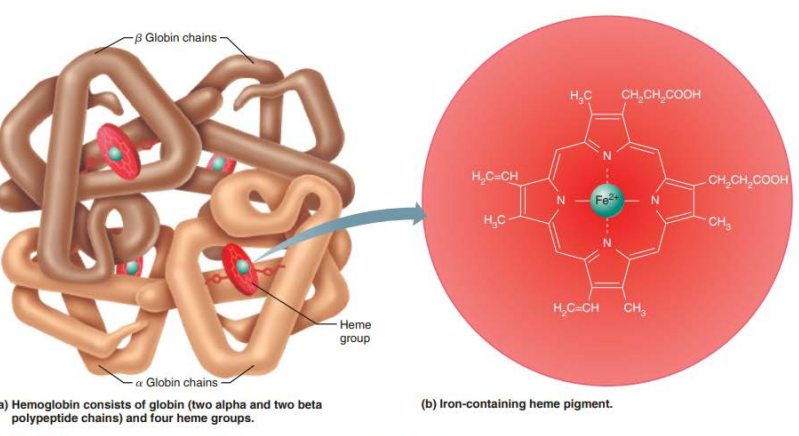
Oxyhemoglobin
-
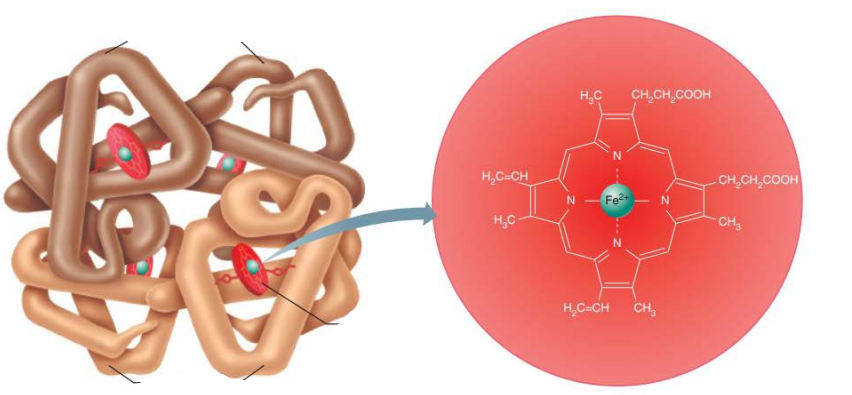
_____________________
Hemoglobin that has released oxygen
Dark red color
Deoxyhemoglobin
-
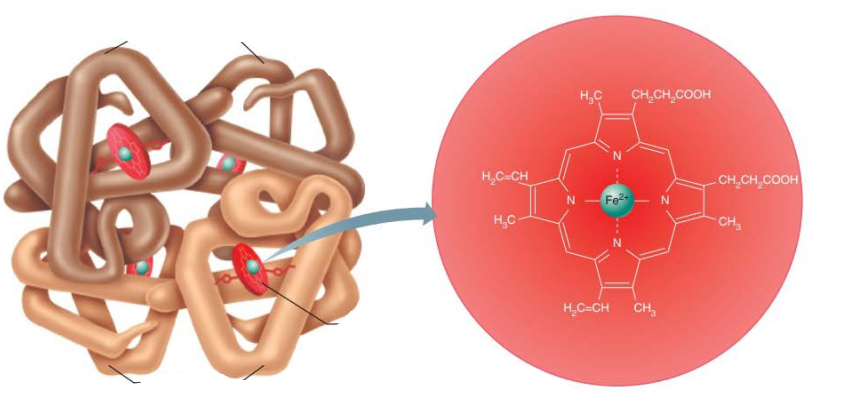
what is the difference between fully saturated and partially saturated hemoglobin?
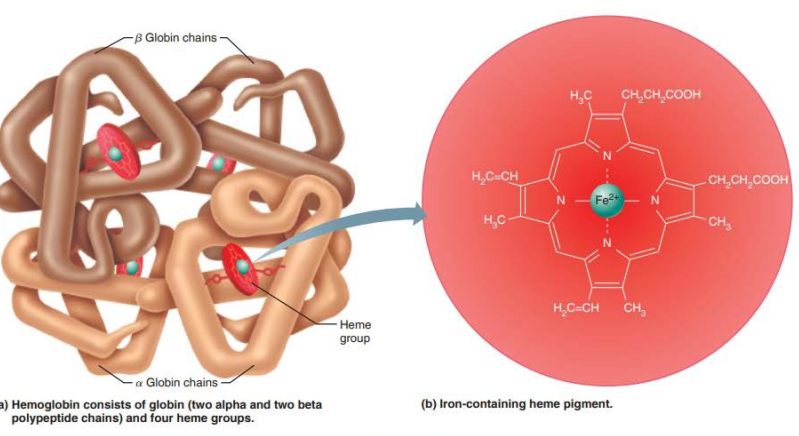
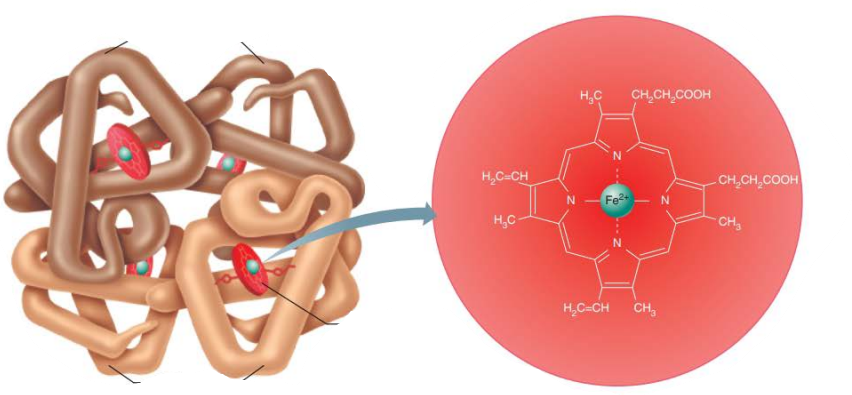
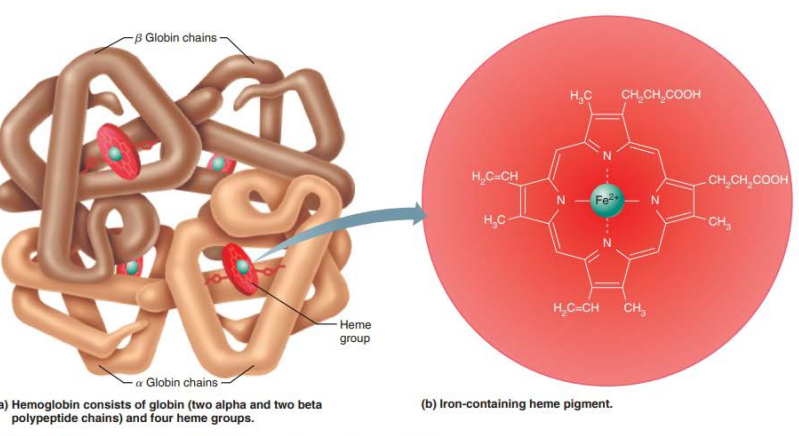
fully saturated hemoglobin has all 4 oxygen molecules bound to all 4 heme groups
-
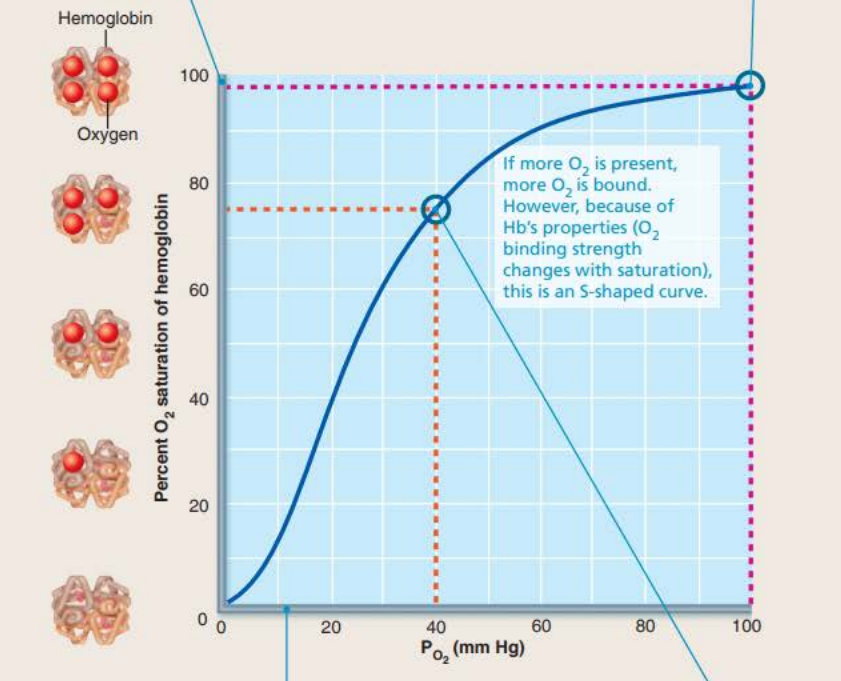
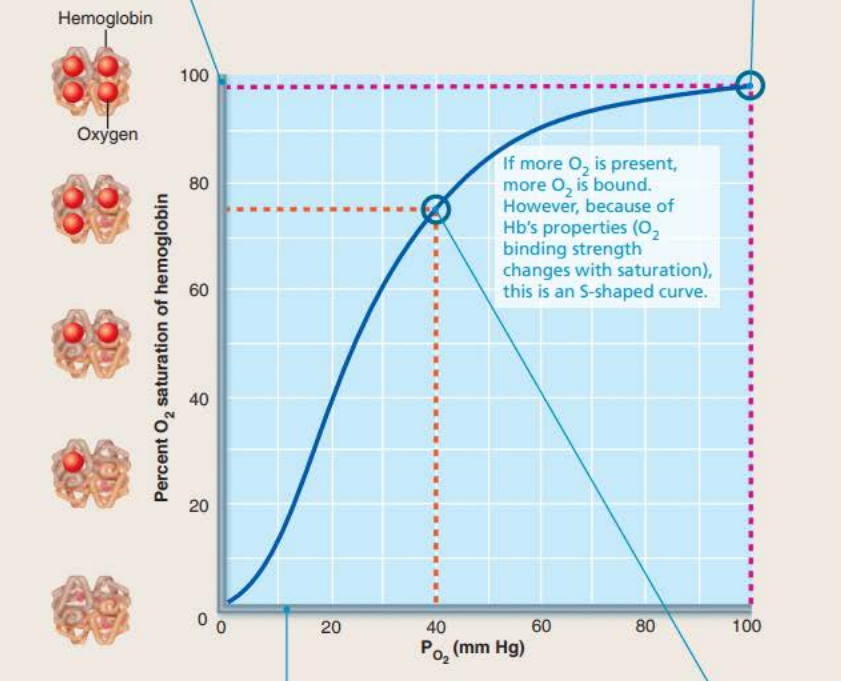
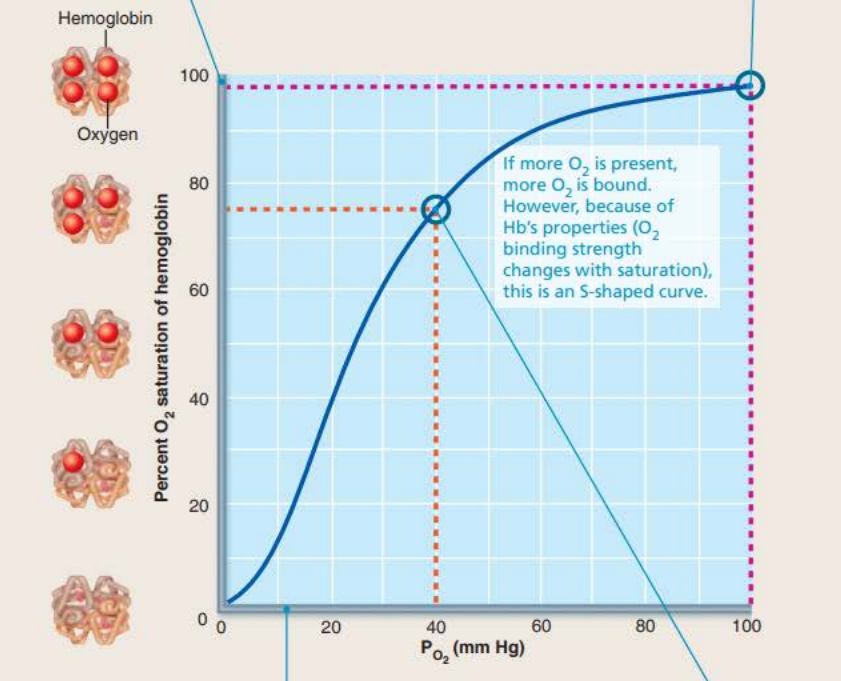
Affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen changes with the extent of oxygen saturation
The ________ of each consecutive _______ molecule to a _____ ______ changes the shape and increases the ______ for the next binding
The unloading of each consecutive oxygen molecule to a heme group changes the _______ and increases the affinity for the __________ of the next
binding
oxygen
heme group
affinity
unloading
-
Partial pressure of oxygen in tissues during exercise
__ __ __
Tissues are ____________ _______ and require ______ dropping the _________ ________
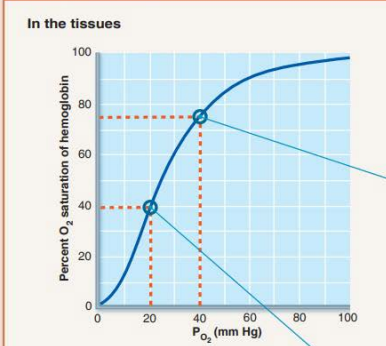
20 mm Hg
metabolically active
oxygen
partial pressure
-
Percent Saturation of hemoglobin during exercise
____ __________ ________
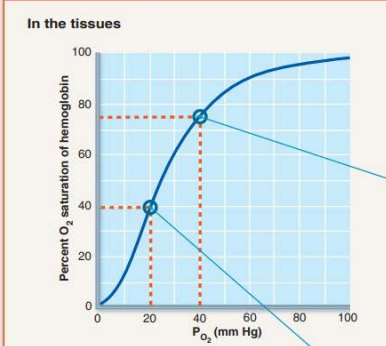
40% hemoglobin saturation
-
name 3 factors that cause the oxygen-dissociation curve to shift to the right
1.
2.
3.
increase in temperature
increasing H+
increase in BPG
-
an increase in temperature ________ __________ ________ ___ __ and __________ ________ _________ from the blood causing the curve to shift to the _____
the release of oxygen becomes _______
lowers hemoglobin's affinity for O2
enhances oxygen loading
right
easier
-
an increase in H+ ________ __________ ________ ___ __ and __________ ________ _________ from the blood causing the curve to shift to the _____
the release of oxygen becomes _______
lowers hemoglobin's affinity for O2
enhances oxygen loading
right
easier
-
an increase in BPG ________ __________ ________ ___ __ and __________ ________ _________ from the blood causing the curve to shift to the _____
the release of oxygen becomes _______
lowers hemoglobin's affinity for O2
enhances oxygen loading
right
easier
-
what is BPG?
when is it produced?
2,3-biphosphoglycerate
when RBC metabolize glucose
-
True or False
BPG, a increase in H+, and temperature all change the 3D shape of hemoglobin
true
-
Decrease in ____________ , Pco2, ___, or __
Changes 3d shape of hemoglobin
_________ HB’s affinity for oxygen
___________ oxygen loading from the blood
causes the curve to shift to the ____
the release of oxygen becomes _______
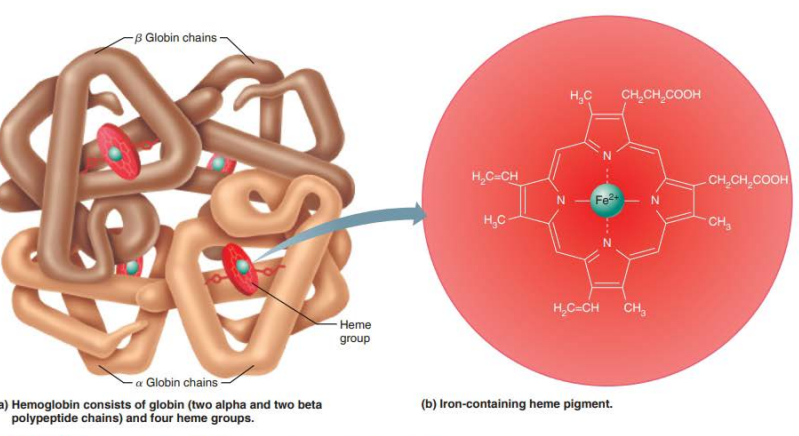
temperature, BPG, H+
increases
decreases
left
harder
-
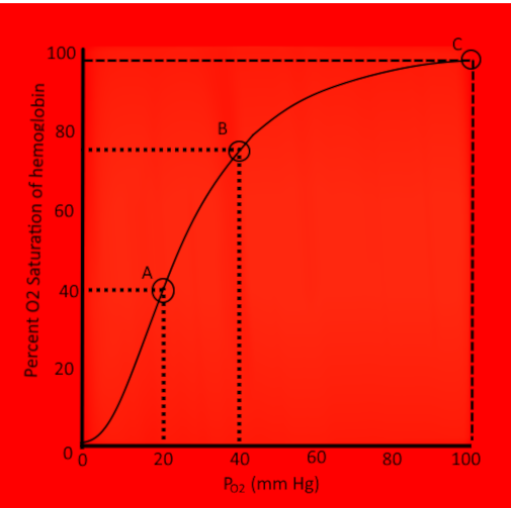
A:
B:
C:
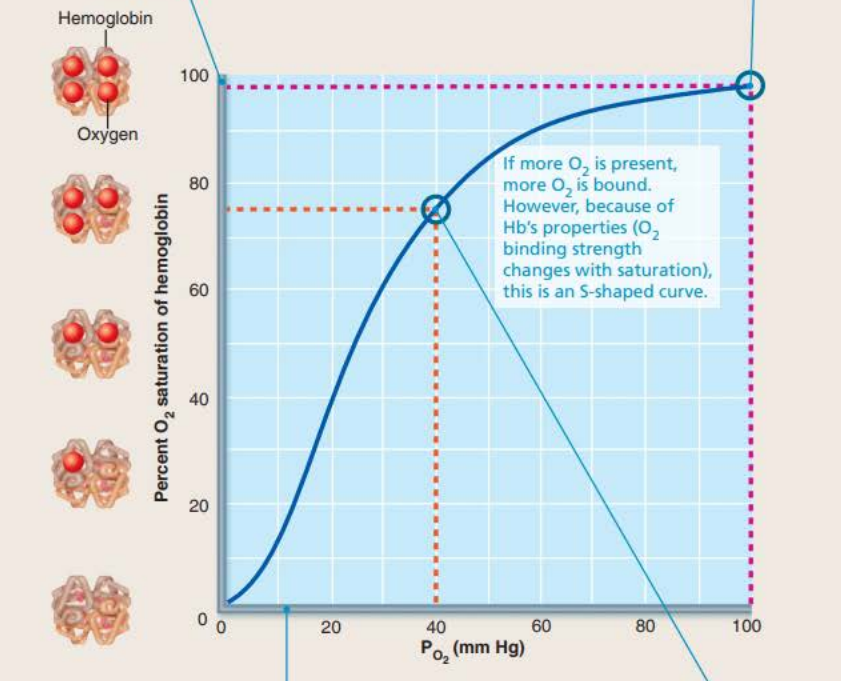
40% HB saturation in tissues during exercise
75% HB saturation in tissues during rest
98% HB saturation in lungs

