-
6 phases of the waterfall model
Requirements, Design, Implementation, Verification, Deployment, Maintenance
-
Waterfall model: steps of the requirements phase
Identify Stakeholders-> Gather requirements-> Analyze requirements-> Requirements specification-> Validate requirements.
-
Three types of requirements in software design
Functional, non-functional, domain (complying with standards)
-
Waterfall model: steps of the design phase
Requirements specification-> Design -> UI/UX design-> System architecture-> Design document
-
Waterfall model: steps of the implementation phase
Design Document->Code development -> Compile and build
-
Waterfall model: steps of the verification phase
Built product -> Verification -> Validation -> Testing
-
Waterfall model verification phase: difference between verification and validation
Verification: are we building the product right? // Validation: are we building the right product?
-
Waterfall model: steps of the deployment phase
Verification -> Prepare release -> Launch on platforms -> Monitor performance
-
Waterfall model: steps of the maintenance phase
Deployment -> Provide support -> Implement updates -> Fix bugs
-
Object oriented design and analysis aims to make software that is _________, __________ and ___________
Modular, reusable and flexible
-
Modularity definition
The degree to which a system is built of discrete components such that a change to one of them has minimal impact on the others
-
Reusability definition
The degree to which an asset can be used in other systems or when building other assets
-
Flexibility definition
The degree to which code can be adapted to changing requirements
-
Quality attribute: Functionality - 3 components
Completeness, correctness, appropriateness
-
Quality attribute: Reliability - 3 components
Maturity, fault tolerance, recoverability
-
Quality attribute: Usability - 3 components
Understandability, learnability, operability
-
Quality attribute: Efficiency - 3 components
Time behavior, resource utilization, capacity
-
Quality attribute: Maintainability - 3 components
Modularity, reusability, analyzability
-
6 elements of a use case + 1 optional
Actors, preconditions, trigger, postconditions, basic flow, alternative flow(s) (edge cases), supplemental requirements (optional)
-
Requirement priorisation mnemonic
MoSCoW (Must have, should have, could have, won't have this time)
-
Relationships and interactions between objects - define association
A simple connection between objects
-
Relationships and interactions between objects - define aggregation
A 'uses a' or 'has a' relationship, can be one-to-one, one-to-many or many-to-many. The part can exist without the whole.
-
Relationships and interactions between objects - define composition
A strong form of aggregation. The parts cannot exist without the whole. Strong 'contains a' relationship. Example a Car class has an Engine class
-
Components of a CRC card
Class Name, responsibility, collaborators
-
Define robustness
A system's ability to handle errors and unexpected situations gracefully
-
3 fundamental design principles
DRY (Don't repeat yourself), KISS (Keep it simple, stupid) and YAGNI (You aren't going to need it)
-
3 more design principles
Separation of concerns, Principle of least astonishment, law of Demeter
-
7 GRASP principles
Information expert (responsibilities go to the class with the most related information), Creator, Controller, High Cohesion, Low coupling, Polymorphism, Pure fabrication
-
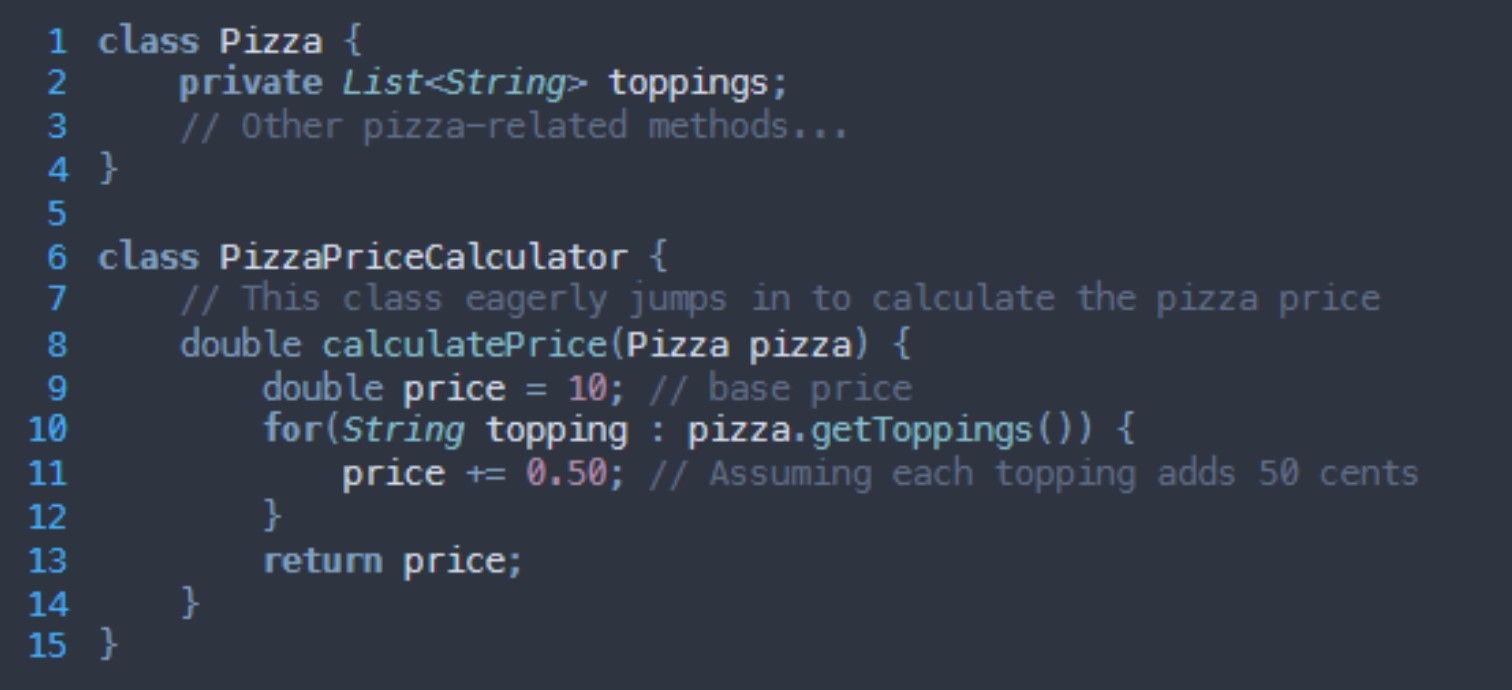
What grasp principle is being broken here?
Information expert
-
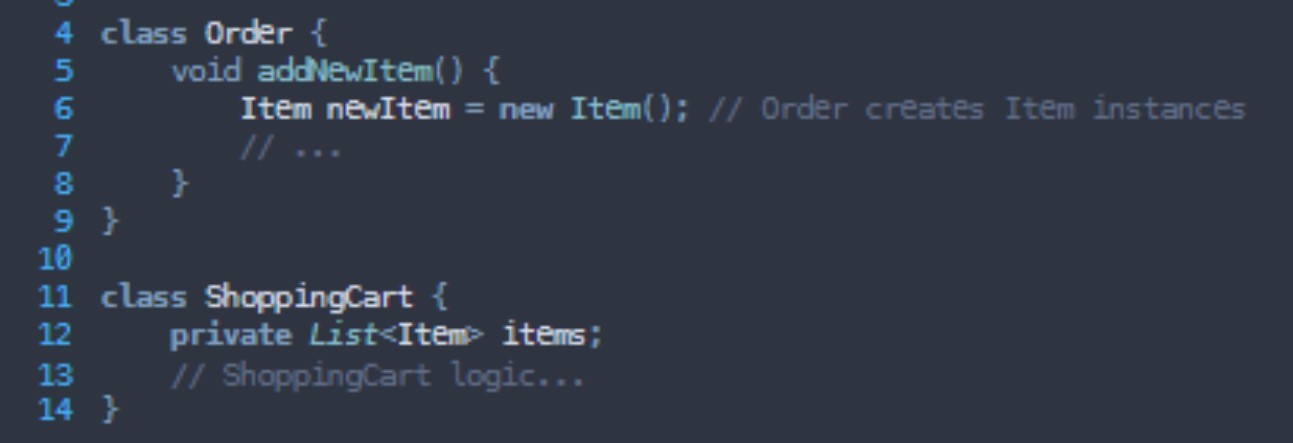
What grasp principle is being broken here?
Creator
-
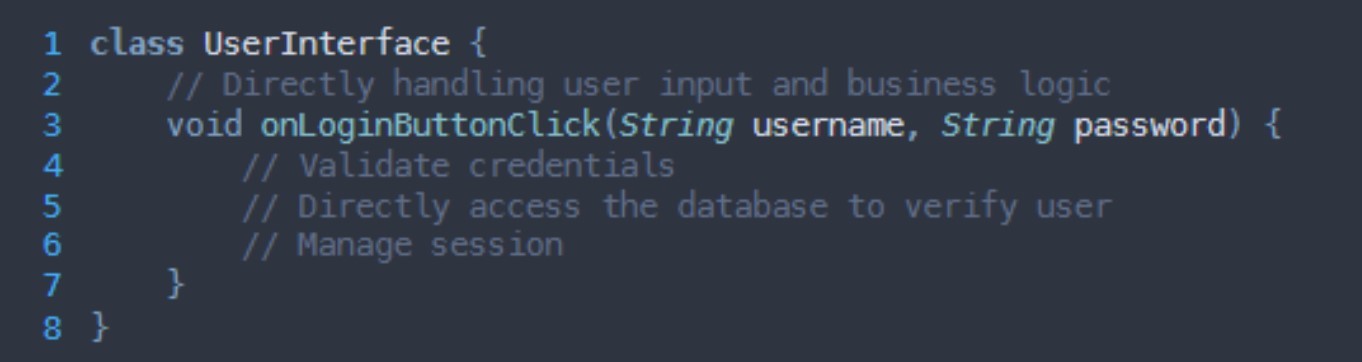
What grasp principle is being broken here?
Controller
-
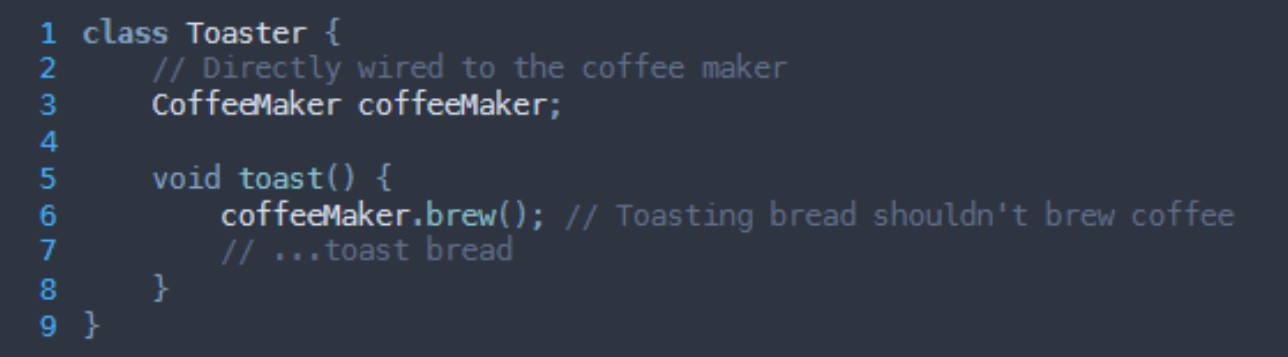
What grasp principle is being broken here?
Low coupling
-
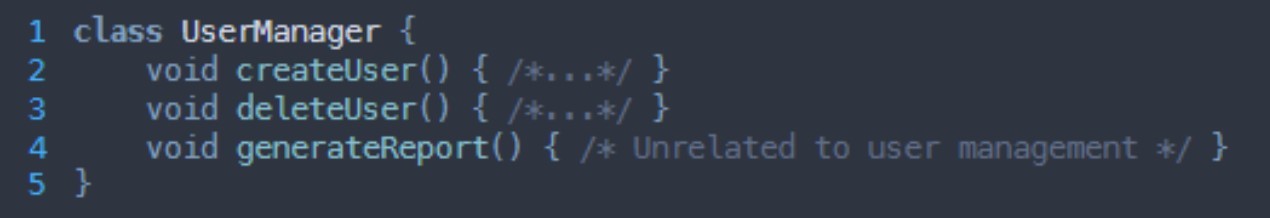
What grasp principle is being broken here?
High cohesion
-
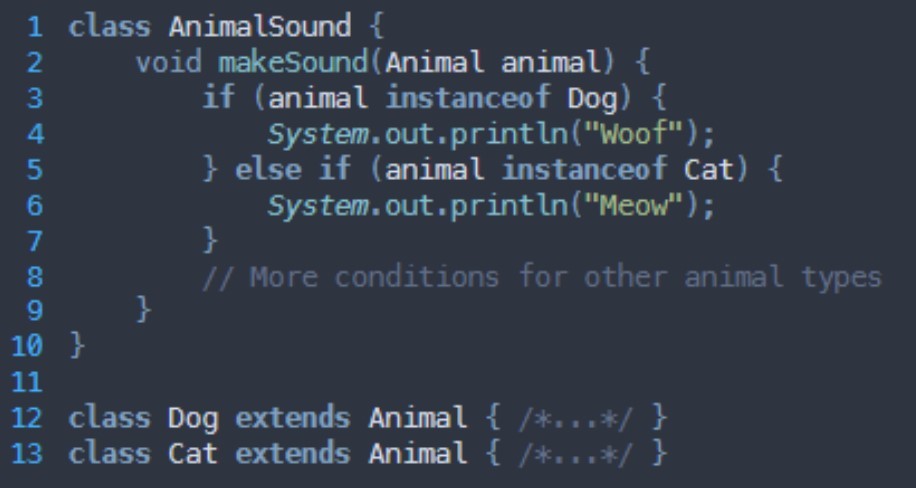
What grasp principle is being broken here?
Polymorphism
-
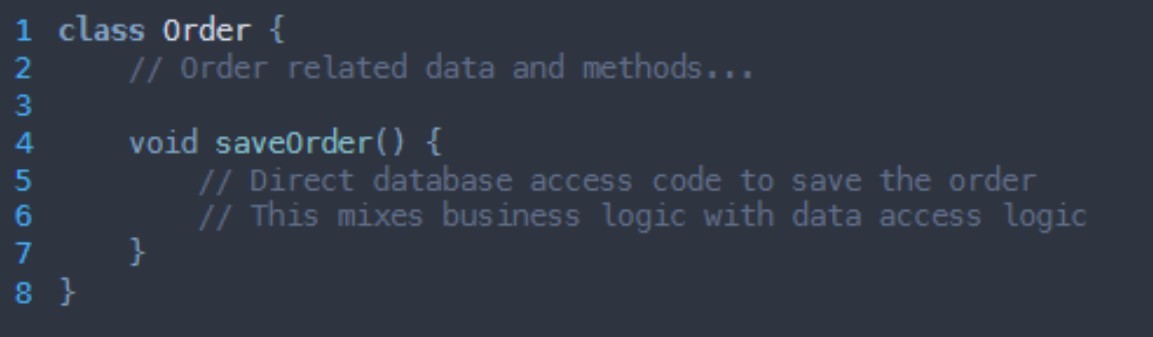
What grasp principle is being broken here?
Pure fabrication
-
What does GRASP stand for?
General responsibility assignment software patterns
-
5 SOLID principles
Single responsibility, Open/closed, Liskov Substitution, Interface segregation, dependency inversion.
-
What is the Liskov substitution principle?
Ensuring that subclasses can replace their superclasses without altering the program's correctness
-
What is the dependency inversion principle?
Depending on abstractions rather than concrete implementations. Abstractions should not depend on details, details should depend on abstractions
-
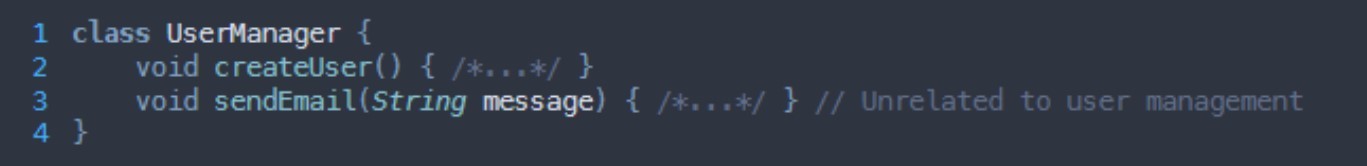
What SOLID principle is being broken here?
Single responsibility
-
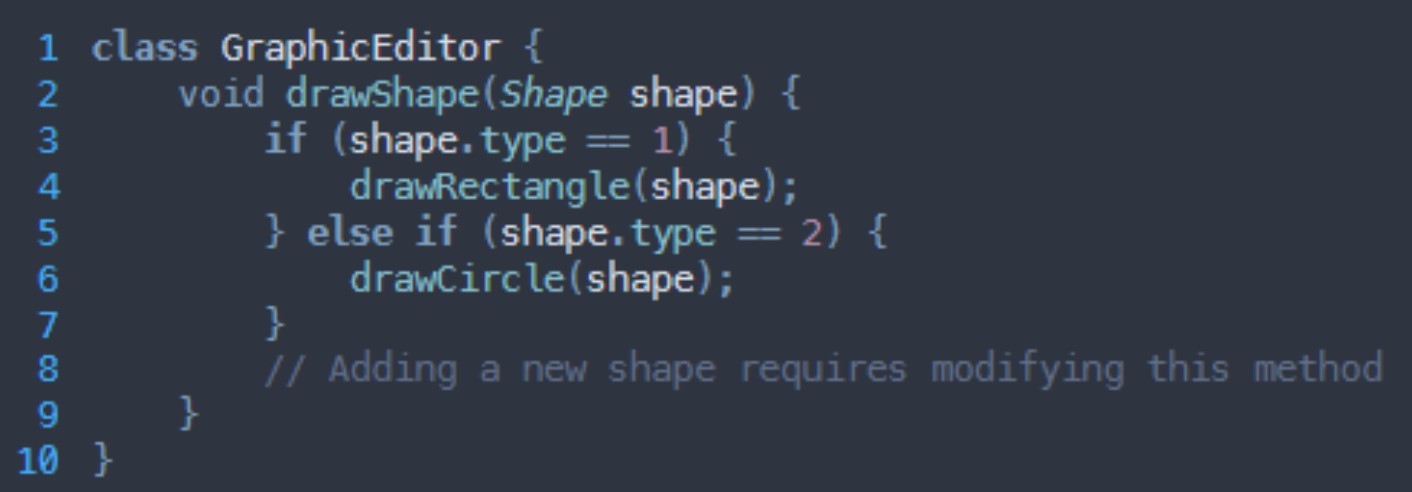
What SOLID principle is being broken here?
Open/closed
-
Open for ________, closed for __________
extension, modification
-
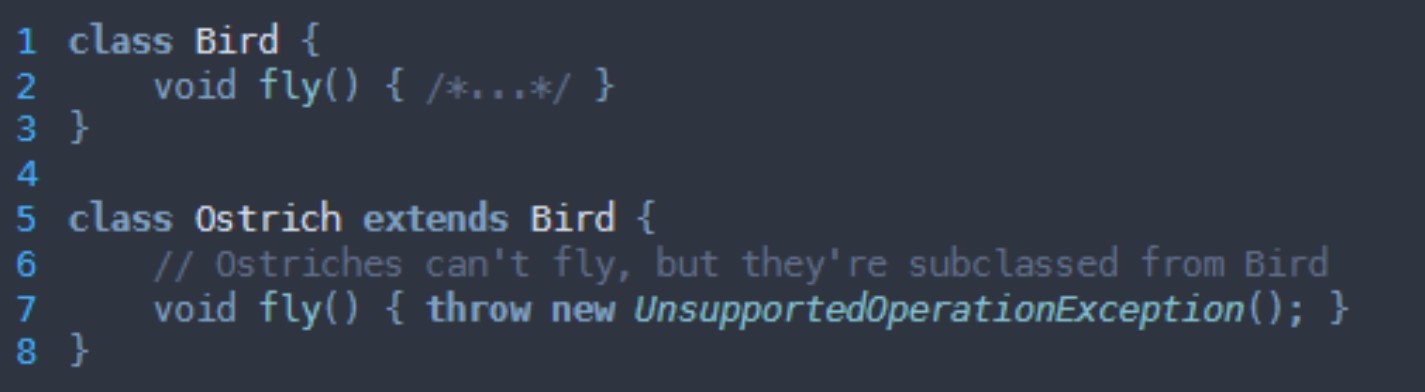
What SOLID principle is being broken here?
Liskov substitution
-
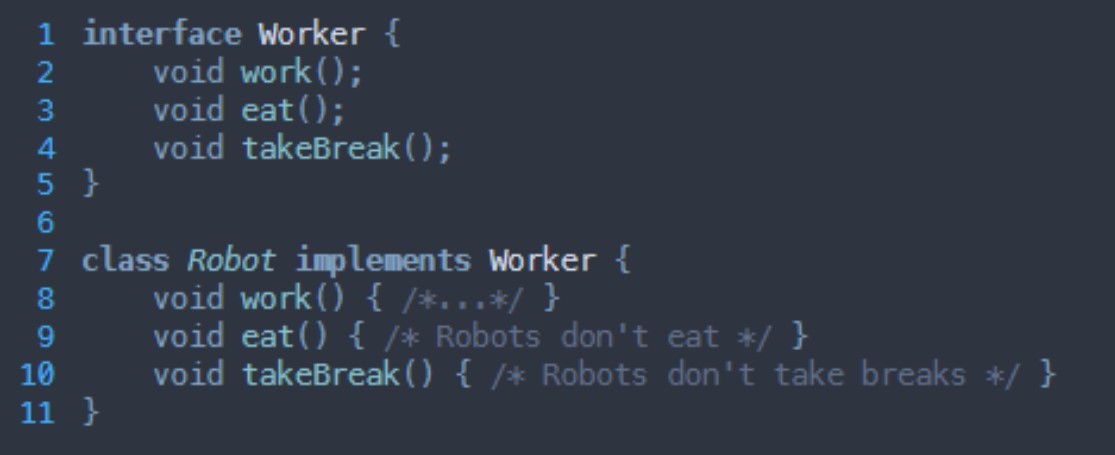
What SOLID principle is being broken here?
Interface segregation
-
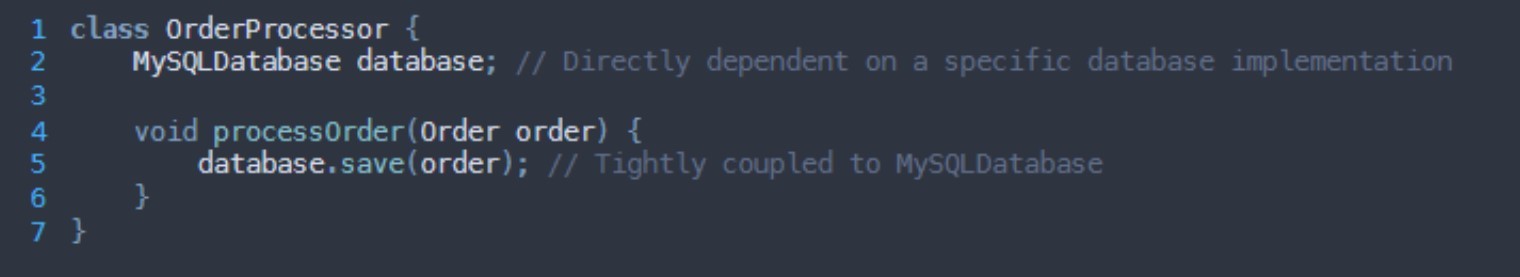
What SOLID principle is being broken here?
Dependency inversion
-
Mnemonic for grasp principles
Clip chp
-
5 types of code smells mnemonic and what it stands for
CD COB - Change preventers, Dispensables, Couplers, Object-Orientation Abusers, Bloaters
-
Define the bloater code smell and give examples.
Oversized code (classes, methods, etc). Eg: Long method, Large Class, Long Parameter List, Primitive Obsession, Data Clumps
-
Long method solutions
Extract method, replace temp with query, group parameters into objects
-
Large class (a class with too many responsibilities) solutions
Extract class, extract subclass/extract interface
-
Long parameter list solution
Use objects to group parameters or replace parameters with method calls.
-
Define primitive obsession
Overuse of primitive types instead of small objects for simple tasks.
-
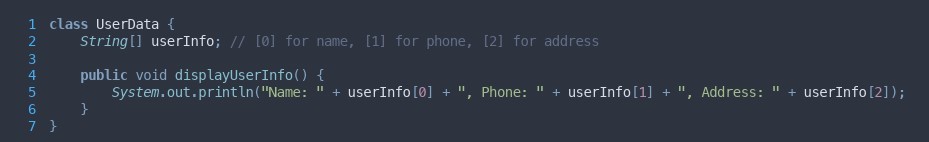
What code smell is present here? How do you fix it?
Bloater - Oversized code - primitive obsession. Create objects that store these three values instead of having them all grouped in a single array.
-

What kind of bloater code smell is displayed here?
Data clump. Related data appears together but is not grouped into a data structure.
-
What principle does the Object-Oriented Abuser code smell - switch statements violate?
Open/closed principle
-
Change preventer code smell definition
Code that necessitates widespread changes for a single adjustment.
-
What category of code smell does duplicated code fall under?
Dispensables
-
What category of code smell does feature envy fall under? What is feature envy?
Couplers. A method that seems more interested in a class other than the one it actually is in.
-
What principle do message chains violate?
Law of demeter
-
Object diagram definition
Class instances at a specific time
-
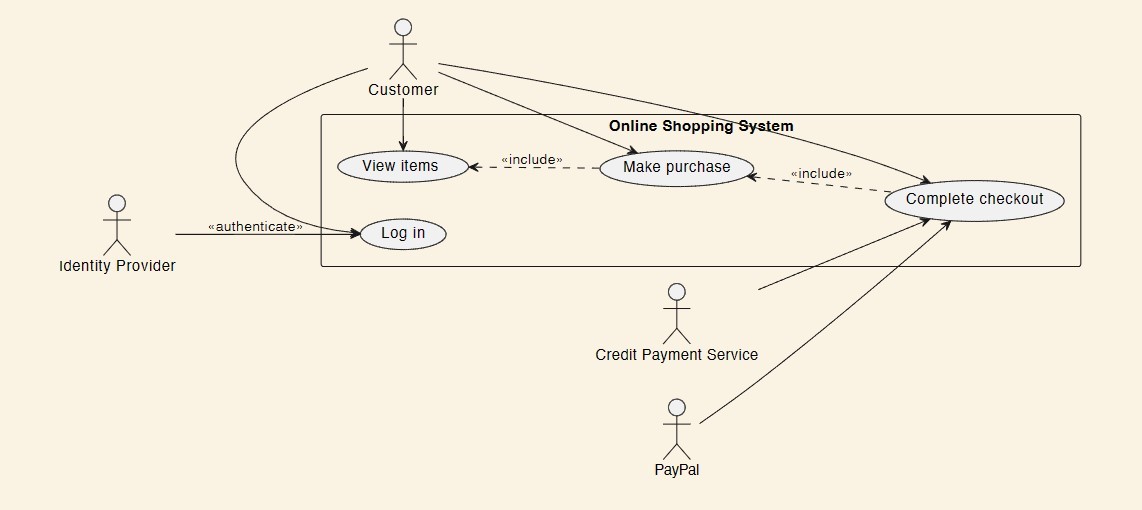
What diagram is this?
Use case diagram
-
What does <<include>> mean in a use case diagram?
A use case (action) that is always executed in another use case
-
What does <<extend>> mean in a use case diagram?
Optional or conditional behavior between two use cases (actions)
-
No answer required: example of a class diagram with associations
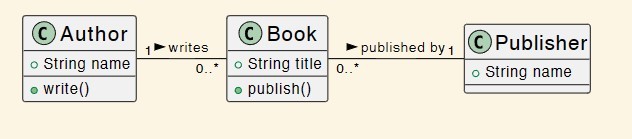
-
Class associations: define multiplicity
How many instances of one class can be associated with an instance of another class.
-
Symbols for public, private and protected in class diagrams
+, - and #
-
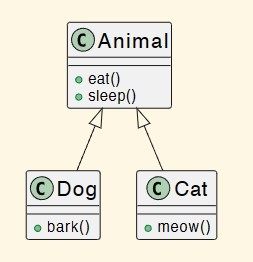
What does the white arrow represent?
Inheritance
-
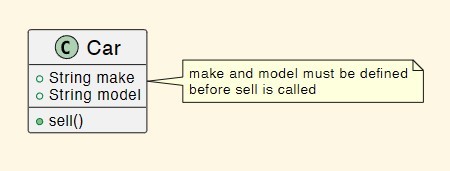
What does the yellow textbox represent?
A constraint
-
What category of diagrams do use case and class/object diagrams belong to?
Behavioral
-
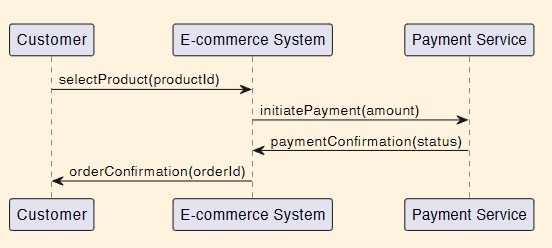
What type of diagram is this?
Sequence diagram
-
What do the narrow white rectangles represent in sequence diagrams?
The active period of an object
-
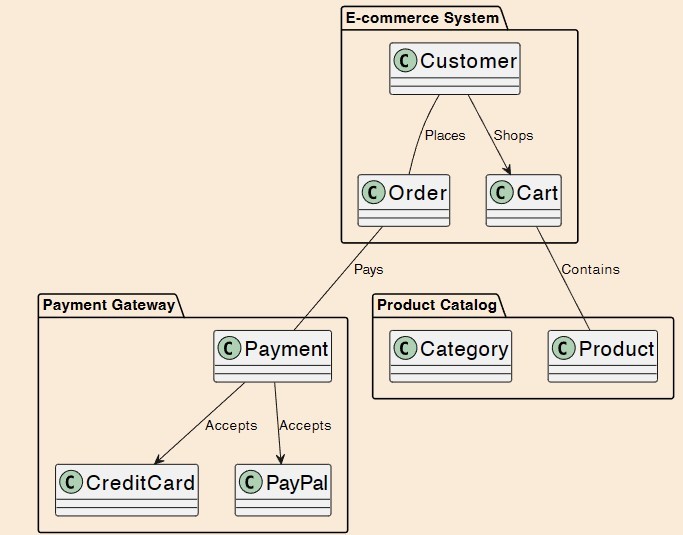
What type of diagram is this?
Package diagram
-
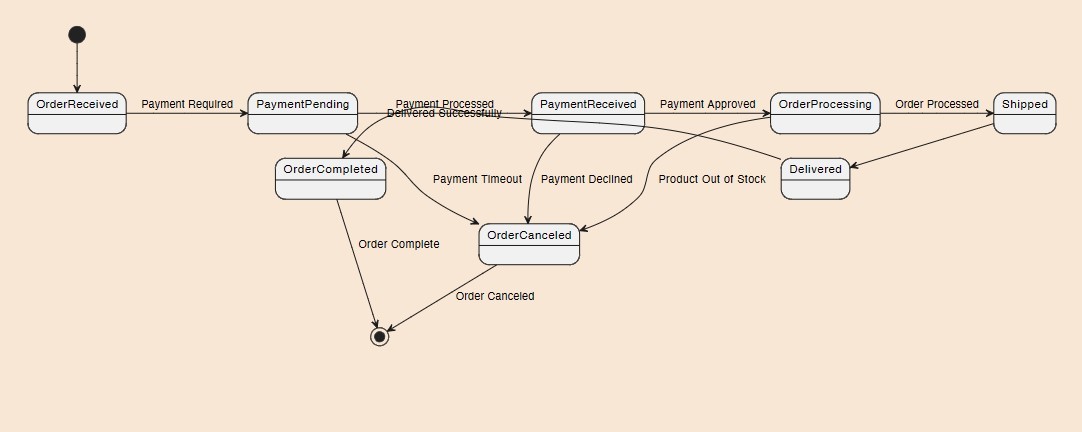
What type of diagram is this?
State diagram
-
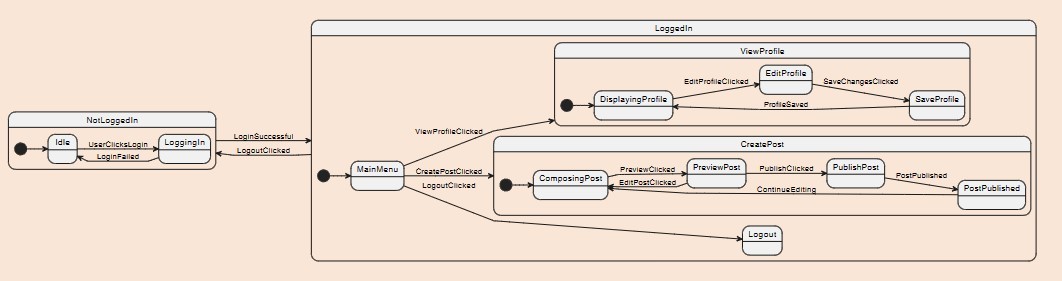
What type of diagram is this?
Composite state diagram
-
What category of diagrams do sequence, package and state diagrams belong to?
Interaction
-
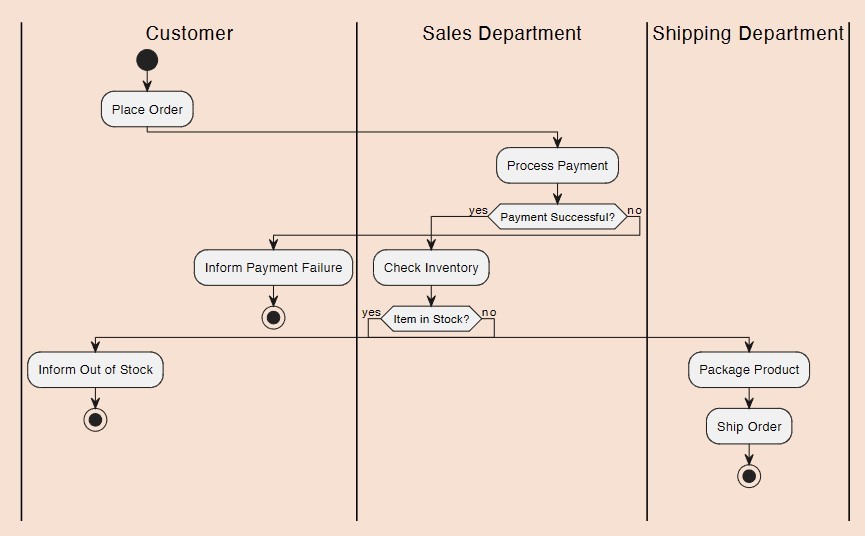
What type of diagram is this?
Activity diagram
-
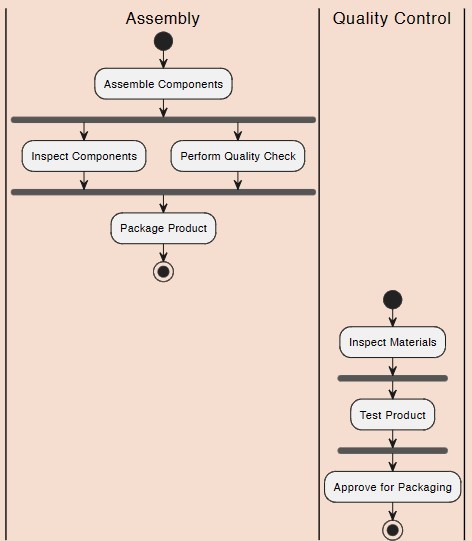
What type of activity diagram is this?
Parallel processes
-
Notes multiplicity UML class diagram

-
3 types of design patterns
Creational, Structural, Behavioral
-
3 creational design patterns we learned
Factory, abstract factory, singleton
-
4 components (types of classes) of the factory design pattern
Factory, concrete factory, product, concrete product
-
Factory design pattern - basic UML class diagram
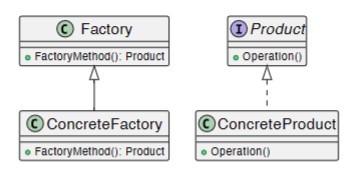
-
Notes abstract factory UML
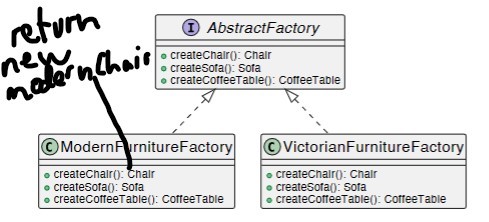
-
Notes simple factory
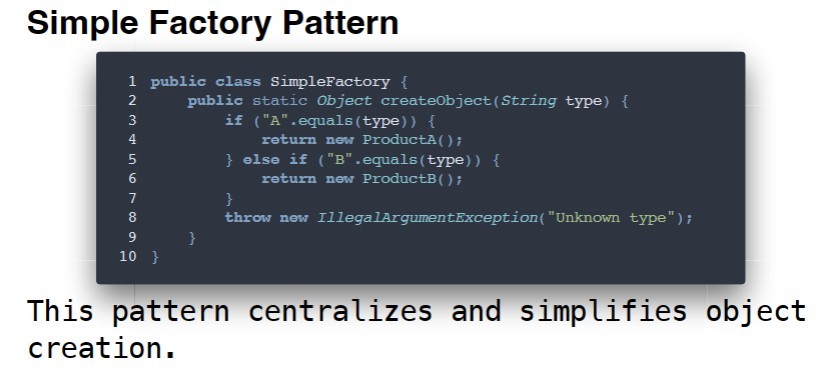
-
Singleton pattern basic java code
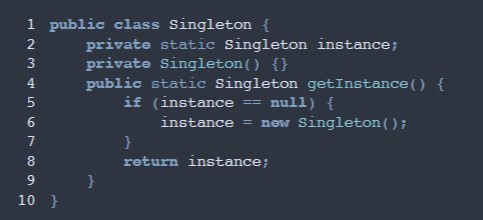
-
Factory method pattern definition/function
A creational design pattern that provides aninterface for creating objects in a superclass, but allows subclasses toalter the type of objects that will be created
-
What principle does Singleton violate?
single responsibility
-
Decorator design pattern UML diagram
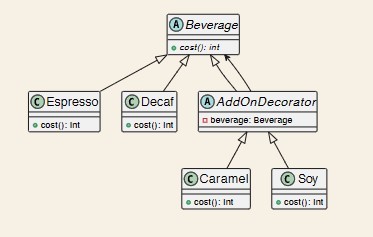
-
Adapter design pattern UML diagram
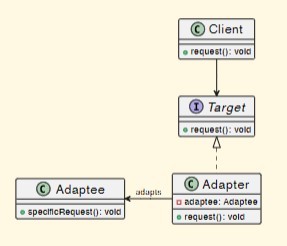
-
Difference between adapter and facade design patterns
Adapter wraps one object,while Facade works with an entire subsystemof objects.
-
Which design pattern is best suited to allow clients to interact with sensitive objects such as a bank account?
Proxy (specifically a protection proxy)
-
3 types of proxy patterns
Remote, virtual, protection
-
Proxy design pattern - define remote proxy
Facilitates access to objects located in different address spaces.
-
Proxy design pattern - define virtual proxy
Delays the creation and initialization of expensive objects until needed.
-
Proxy design pattern - define protection proxy
Controls access to an object based on access rights.
-
Proxy design pattern UML diagram
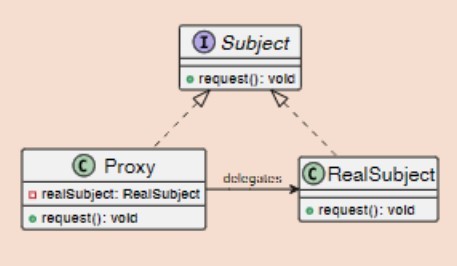
-
The strategy design pattern focuses on using ________ over __________
composition, inheritance
-
Strategy design pattern UML

-
Observer UML
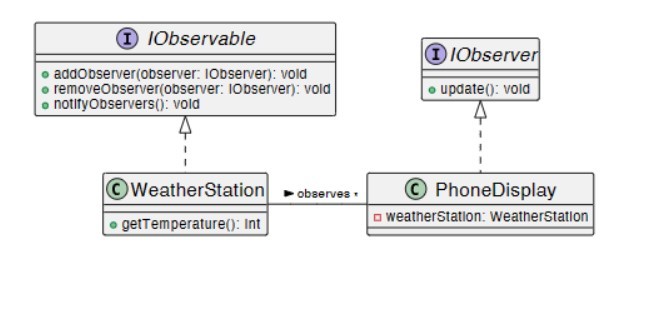
-
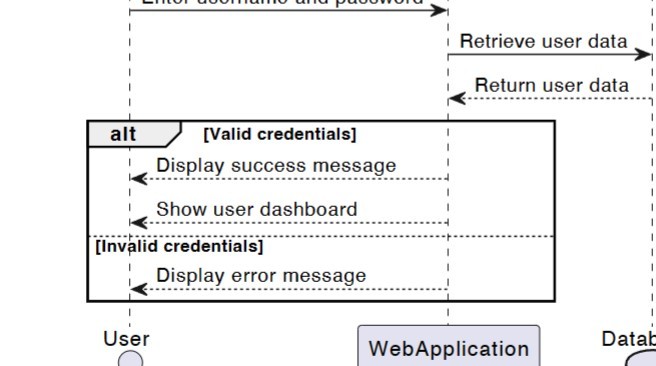
Alt boxes in a use case diagram