MSC 385 Supply Chain Test 4 (Final Exam)
Decks complete; Public version 7 Kartka.ai link: https://app.kartka.ai/shared/decks/iFRKECs7cp4fRydVGXkoF6Ya
-
Lean Systems' Ultimate Goalto achieve a system that matches supply to customer demand
-
Lean Systems' Supporting Goalseliminating disruptions, making the system flexible, and eliminating waste, especially excess inventory
-
Lean Systems' Building Blocksproduct design, process design, personnel/organizational elements, and manufacturing planning and control
-
Warning about Pull SystemsLarge variations in volume, product mix, or product design will undermine the system
-
Requirements for Implementing LeanHigh quality, highly capable production systems, standard parts, a modular design, concurrent engineering, a spirit of cooperation among workers, management, and vendors, and a pull system
-
Differences between project management and general operations managementProject management has a limited timeframe, narrow focus, specific objectives, and it is less bureaucratic
-
Project managers' responsibilitiesEffectively managing the work, human resources, communications, quality, time, and costs
-
Reason why waiting lines can form even when there is enough capacityArrival and service rates are variable
-
Activities that have slack timeActivities that are not on the critical path
-
Fact about the critical pathIt does not have slack time.
-
Reasons to use leanIt reduces waste, continuously improves, minimizes inventory, it has high quality, small lot sizes, quick changeovers, and matches output to demand
-
factor that allows quick changeoversSingle-minute exchange of dies
-
PERTProgram evaluation and review technique
-
PERT chartA sequence of relationships and orders that activities have to be deployed in
-
What to do when deploying activities on a PERT chartNumber the nodes on the chart
-
Number of Individual Steps in the "Mercury Marine Lean" video's process122
-
Number of Production Steps in the "Mercury Marine Lean" video's process27
-
Travel Distance in the "Mercury Marine Lean" video's process20,793'
-
Number of People who touched the unfinished product in the "Mercury Marine Lean" video's process106
-
"HP Stockless Production": Space Used in the Push 6 System2 tables
-
"HP Stockless Production": WIP in the Push 6 System30
-
"HP Stockless Production": Cycle time in the Push 6 System3:17
-
"HP Stockless Production": Rework Quantity in the Push 6 System26
-
"HP Stockless Production": Type of Problems in the Push 6 SystemHidden
-
"HP Stockless Production": Space Used in the Pull 3 System2 tables
-
"HP Stockless Production": WIP in the Pull 3 System12
-
"HP Stockless Production": Cycle Time in the Pull 3 System1:40
-
"HP Stockless Production": Rework Quantity in the Pull 3 System10
-
"HP Stockless Production": Space Used in the Pull 1 System1 table
-
"HP Stockless Production": WIP in the Pull 1 System4
-
"HP Stockless Production": Cycle Time in the Pull 1 System:19
-
"HP Stockless Production": Rework Quantity in the Pull 1 System3
-
"HP Stockless Production": Type of Problems in the Pull 1 SystemVisible
-
Lean systems' ideal lot size1
-
Lean Process Design AspectsSmall lot sizes, setup time reduction, manufacturing cells, quality improvement, production flexibility, a balanced system, little inventory storage, and fail-safe methods
-
Small lot size benefitsSmaller work in progress, lower inspection and rework costs, greater scheduling flexibility, increase production flexibility, and it makes balancing operations easier
-
Lean operating with low inventories basic requirementHave suppliers deliver to the production floor
-
Lean Systems' Vendor Characteristicsthey are a small number of suppliers that are expected to provide frequent, small deliveries of high-quality goods
-
Things that require PERT's useEarly start, early finish, late start, and late finish
-
Work Breakdown StructureA hierarchal listing of what must be done during a project
-
Work breakdown Structure Step 1Identify the project's major elements
-
Work breakdown Structure Step 2Identify each major element's supporting activities
-
Work breakdown Structure Step 3Break down each major supporting activity into a list of activities that will be needed to accomplish it
-
Lean systems' eight wastesExcess inventory, overproduction, waiting time, unnecessary transporting, processing waste, inefficient work methods, product defects, and underused people
-
Excess inventory exampleAnything that is not necessary for the minimum buffers; any inventory above the minimum amount to meet daily demand
-
Overproduction exampleProducing more than is required for the daily demand
-
Waiting time exampleAny time spent waiting for parts; any unproductive time spent waiting
-
Unnecessary transporting exampleMost of the time the unfinished product was moved in the Mercury Marine Lean video
-
Processing waste exampleScraps and reduced yield, such is when a die cut process begins
-
Inefficient work methods exampleWhen people have to move too much or reach too much if moving objects closer together is possible
-
Product defects exampleAny kind of quality problem
-
Underused people exampleFailure to implement line balancing
-
Critical Path DefinitionThe longest sequence of activities from the starting node to the finishing node
-
Reason waiting can occur in infinite source queuing systemsCustomer arrivals are unrestricted
-
Effect when the arrival-rate-to-service-rate increases ;the number of arrivals increases but the service rate stays the sameThe answer's value increases
-
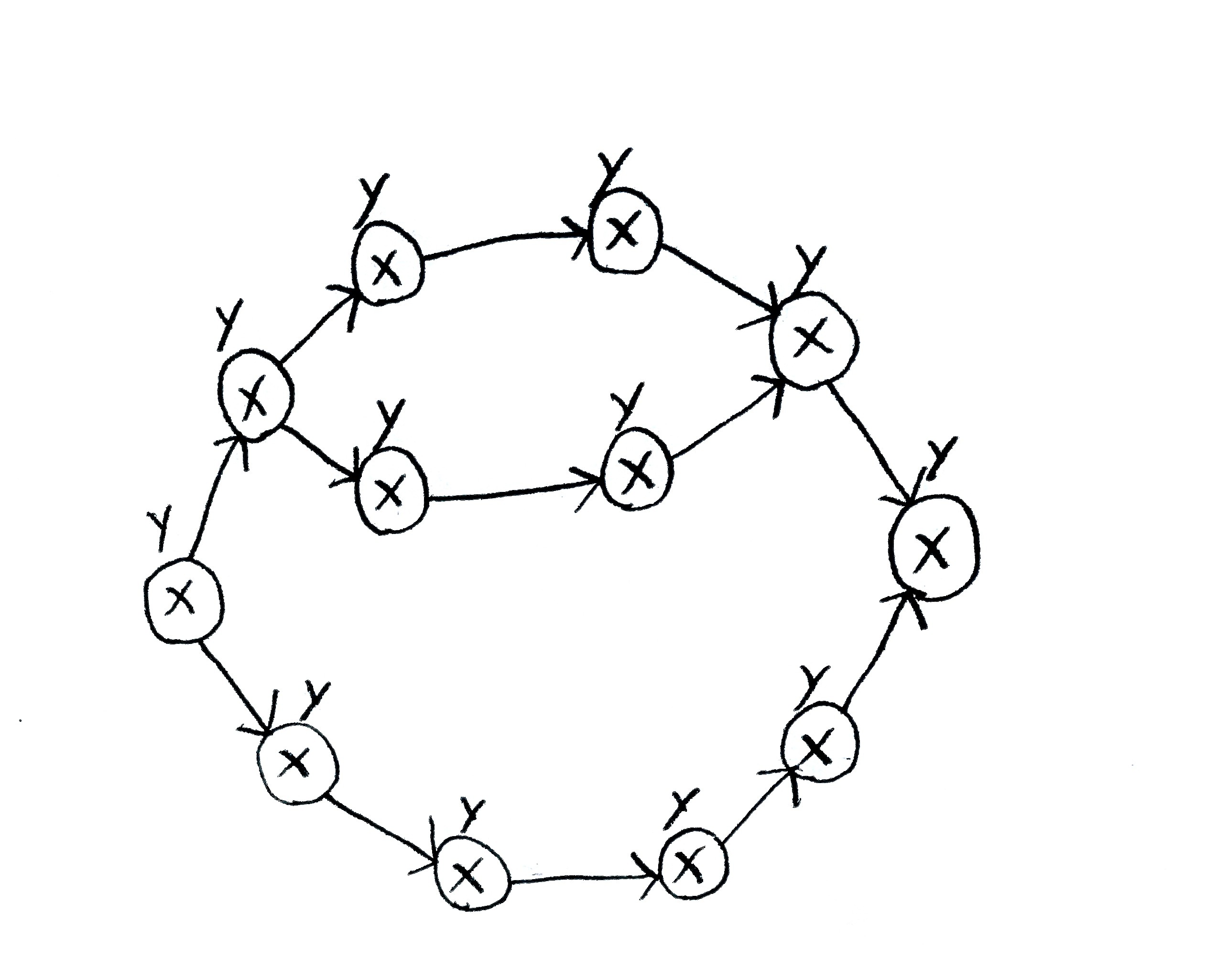 X’s on this PERT chartActivities’ name numbers (i.e., if one is 5, that activity is activity 5)
X’s on this PERT chartActivities’ name numbers (i.e., if one is 5, that activity is activity 5) -
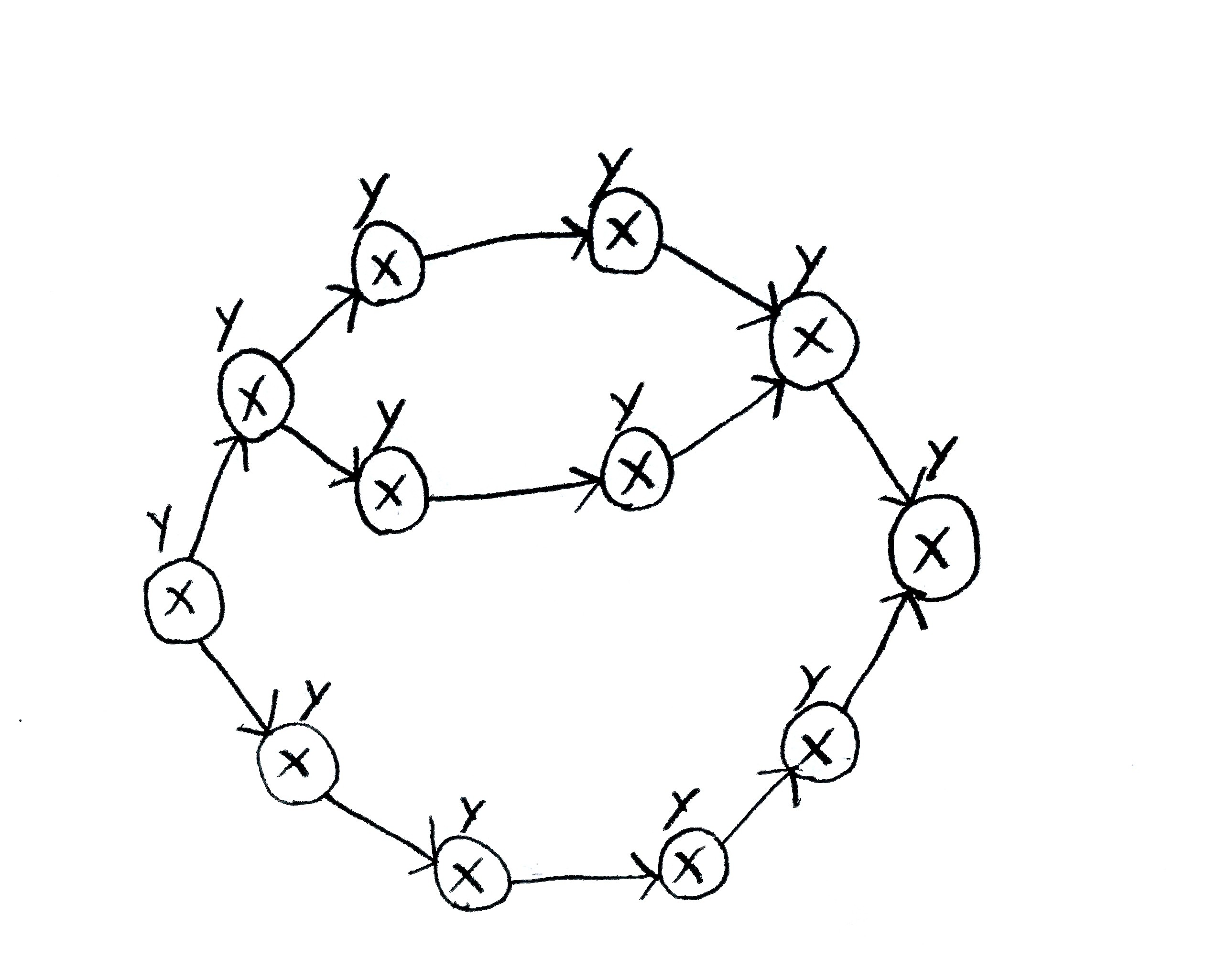 Y’s on this PERT chartActivities’ length numbers (i.e., if one is 5, that activity takes 5 days to complete)
Y’s on this PERT chartActivities’ length numbers (i.e., if one is 5, that activity takes 5 days to complete) -
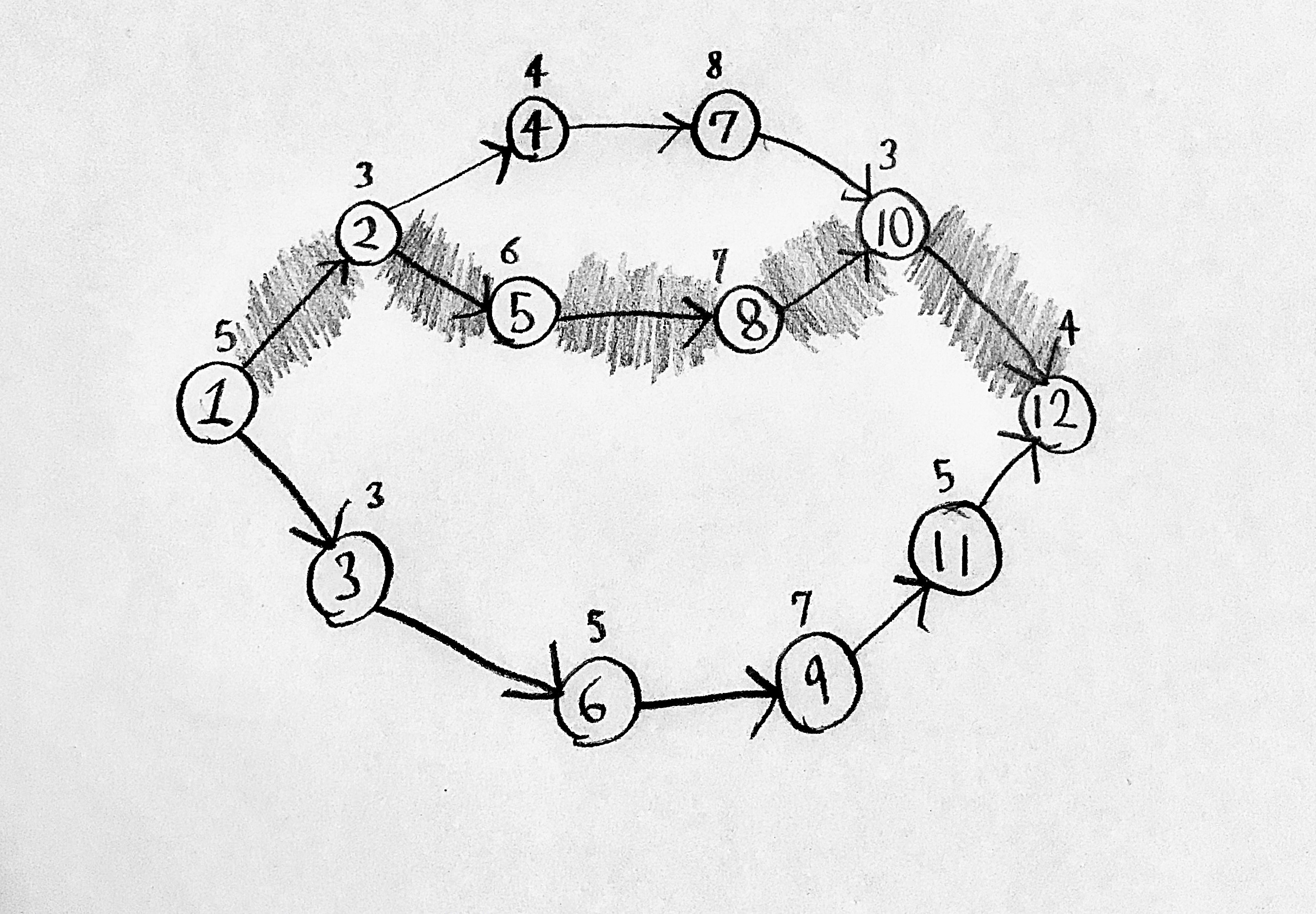 The shaded path’s name on this PERT chart1-2-5-8-10-12
The shaded path’s name on this PERT chart1-2-5-8-10-12 -
How to solve for the critical pathSum each of the paths’ activity numbers separately. The critical path has the highest sum.
-
Crashing a node effectThe node’s length in days is reduced.
-
How to choose which nodes to crashStart on the critical path and crash the cheapest node first.
-
What it means to crash a project for a certain number of daysCrash nodes on the project until all paths are the critical path's length minus the specified number of days or less
-
Effect on a system when its channel utilization is over 100%Its line will keep growing
-
Important step for calculating the number of kanban containersRounding the answer number up; i.e. 1.3 rounds to 2
-
How to tell if you can use fewer containers if the kanban system improvesSet X to zero and re-calculate the number of containers. If the new answer rounds to a smaller whole number than the original, the answer is yes.
-
Project management toolsWork breakdown structure, network diagram, Gantt chart, and risk management
-
Network diagram explanationThis "big picture" visual aid is used to estimate project duration, identify activities critical for timely project completion, identify areas with slack time, and develop activity schedules.
-
Gantt chart explanationThis is a visual aid used to plan and monitor individual activities.
-
Risk Management ExplanationThese are analyses of potential failures or problems, assessment of their likelihood and consequences, and contingency plans.

