-
G6PD (Glucos-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
)
Abnormal amount or function of G6PD, RBCs have inadequate protection from oxidative stress
-
G6PD exacerbators
Foods (like fava beans) or Oxidizing drugs (antimalarial drugs, sulfas and nitrofurantoin)
-
Transferrin
Iron binding protein in the plasma. Transports iron from gut or spleen to bone marrow for use in new RBC synthesis
-
Ferritin
Iron storage protein
-
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Cancer of skeletal muscle
-
Breast Cancer
Genetic Testing- BRCA 1&2, HER and ER
-
Organs relationship w/ blood
Liver-Makes clotting factors and thrombopoietin. Also makes bile salts-important in absorbing vit K and B12)
Kidney- Makes erythropoietin
Bone marrow- creates platelets and RBCs
Spleen- Where old RBCs are recycled. Iron is released by RBCs and carried by transferrin to bone marrow
-
Nutrients needed for RBC synthesis
Iron, Folate and Vitamin B12
-
Types of Anemia
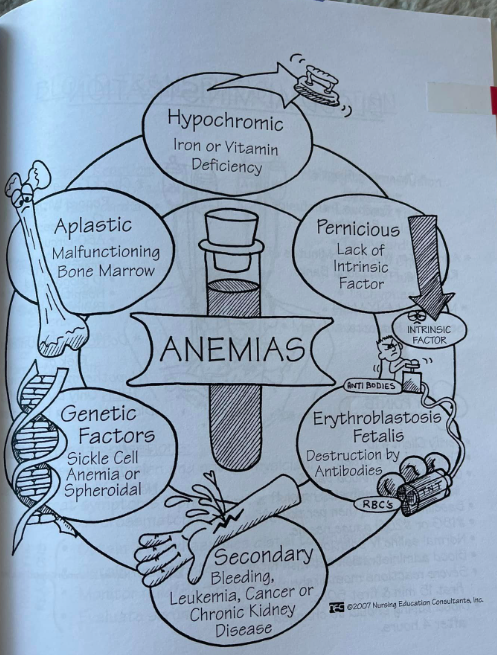
-
Carcinoma
Epithelial origin. Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast
-
Squamous cell tumors
Squamous cell origin
-
Adenocarcinoma
Glandular epithelial cell origin
-
Small Cell Carcinoma
neuroendocrine cell origin
-
Sarcoma
Mesenchymal tissue (cartilage, smooth muscle, skeletal muscles, blood vessels)
-
Lynch Syndrome
Non-polyposis colorectal cancer (can have polyps, but not required)
-
Cancer causing viruses
Epstein bar virus- burtcell lymphoma or burkitt lymphoma
Hep B & C- he;ptocellular carcinoma
HPV- head and neck cancer, anal and genital cancer
-
Hematopoietic cancers (leukemia)
Bone marrow, peripheral blood, lymph node, spleen, or liver origin
-
Melanoma
Originates in the skin
-
proto-onco v oncogenes
Proto-oncogenes- Normal. Active in embryonic and early childhood development.
Oncogenes- mutation in proto-oncogenes. Cancer causing.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease and blood
Reduced erythropoietin synthesis, fluid and electrolyte imbalances can also inhibit erythropoiesis. Iron deficiency is also common. Hemodialysis also reduces RBC lifespan.
-
P53 Tumor Suppressor Gene
Need mutation on both alleles. Inhibits gene expression of p21
-
Neonatal Hemoglobin
Fetal RBCs only live 45 to 70 days (adult RBCs are around 120 days) and are macrocytotic
Hgb drops to its nadir at about 60 DoL, erythropoiesis relatively low until then
Premature infants have a lower nadir
-
Telomerase
An enzyme that maintains chromosome length. Responsible for making cancer cells essentially immortal
-
Hemoglobin S mutation
Replacement of hydrophilic amino acid Valine with hydrophobic amino acid Glutamate, as in sickle cell anemia.
-
Osteosarcoma
Bone
-
Liposarcoma
adipose tissue
-
Chondrosarcoma
cartilage
-
Leiomyosarcoma
Smooth muscle
-
Angiosarcoma
Blood
-
Tertoma
Germ cell
-
Lymphoma
B and T lymphocytes
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
Helps tumors create enough of a blood supply to feed rapid growth in tumors and opens the doorway for cancer cells to metastasis to other parts of the body
-
Example of commonly mutated tumor suppressor gene
P53- the mutation keeps it from "turning on" P21. Without being activated, P21 cannot suppressor tumor growth
-
Von Willebrand Disease
Autosomal dominant, but incomplete penetrance. Reduces platelet adherence to damaged endothelium (longer clotting time). Common presentation mucosal bleeding, nose bleeds (epitaxis), excessive bruising and menorrhagia
-
Virchow's Triad
Endothelial injury (HTN, DM, cancer, other inflammatory diseases), Venous stasis (not moving), Hypercoagulability (cancer, smoke)
-
Role of Endothelium in anticlotting
When intact the endothelium releases platelet aggregation inhibitors i.e. nitric oxide and prostacyclin
-
Prothrombin Time
PT with INR (international normalized ratio). Tissue factor added to anticoagulated blood. Time to clot is measure. Test for for coagulation pathway defects and efficacy of warfarin treatment
-
Partial thromboplastin time
Tests for coagulation pathway defects (including hemophilia A and B) and efficacy of unfractionated heparin treatment
-
Reticulocyte count in anemia
Decreased- Anemia of chronic inflammation
Increased- Hemolytic anemia
-
Schistocytes
RBC fragments

