-
Standard Chemotherapy
-acts on all rapidly dividing normal and cancerous cells
-cytotoxic
-
Targeted therapeutics
-act on specific molecular targets that are associated with cancer
-designed to interact with a defined molecular target
-cytostatic
-represented by small molecules or biologics
-
cytostatic
-block tumor cell growth or proliferation
-
D
What cancer affects men the most?
a) lung & bronchus
b) colon & rectum
c) breast
d) prostate
-
C
Which cancer affects women the most?
a) lung & bronchus
b) colon & rectum
c) breast
d) thyroid
-
A
Which cancer has the highest mortality rate?
a) lung & bronchus
b) colon & rectum
c) breast
d) thyroid
-
pancreatic, liver, lung, esophagus
What are the most lethal cancers? Order from most lethal to least.
-
In situ
-early cancer that is present only in the layer of cells in which it began
-
Localized
-cancer that is limited to the organ in which it began, without evidence of spread
-
Regional
-cancer that spread beyond the original (primary) site to nearby lymph nodes or organs and tissues.
-
Distant
-cancer that has spread from the primary site to distant organs or distant lymph nodes
-
Cell competition
a term used to describe when cancer cells proliferate and kill surrounding wild-type cells via apoptosis so that the total cell number does not change.
-
capecitabine (xeldoa) ; Carboxlesterase; 5-fu
__________ is the prodrug or inactive form. It is metabolized by _______ into it's active form ______________.
-
1-5%; DPD; FUH2
What percentage of 5-FU is converted in the body? What enzyme converts in into its inactive metabolite? What is the inactive metabolite?
-
DPYD; rate-limiting
_________ gene encodes dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), an enzyme that catalyzes the ______________ step in fluoropyrimidine metabolism.
-
True
The FDA-approved drug label for 5-fluorouracil states that no dose has been proven safe in individuals with absent DPD activity. T/F?
-
1 normal function + 1 no function allele or 1 decreased function; 2 decreased function alleles
DPYD intermediate metabolizer
-
2 no function alleles; 1 no function + 1 decreased function
DPYD poor metabolizer
-
SERMs, growth inhibitor, prodrug,
Tamoxifen
- drug class
-active or prodrug
-
HR+; pre & post menopausal women
Tamoxifen is used for the treatment of both early and advanced ______ and _____________.
-
ER+ & HER2-
What groups do we have targeted therapeutics for in breast cancer patients?
-
prevents ER signaling in cancer cells by binding to ER- resulting in receptor dimerization and causing an inactive complex; results in decreased ER signaling
Explain tamoxifen moa.
-
CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP3A4/5, CYP2D6
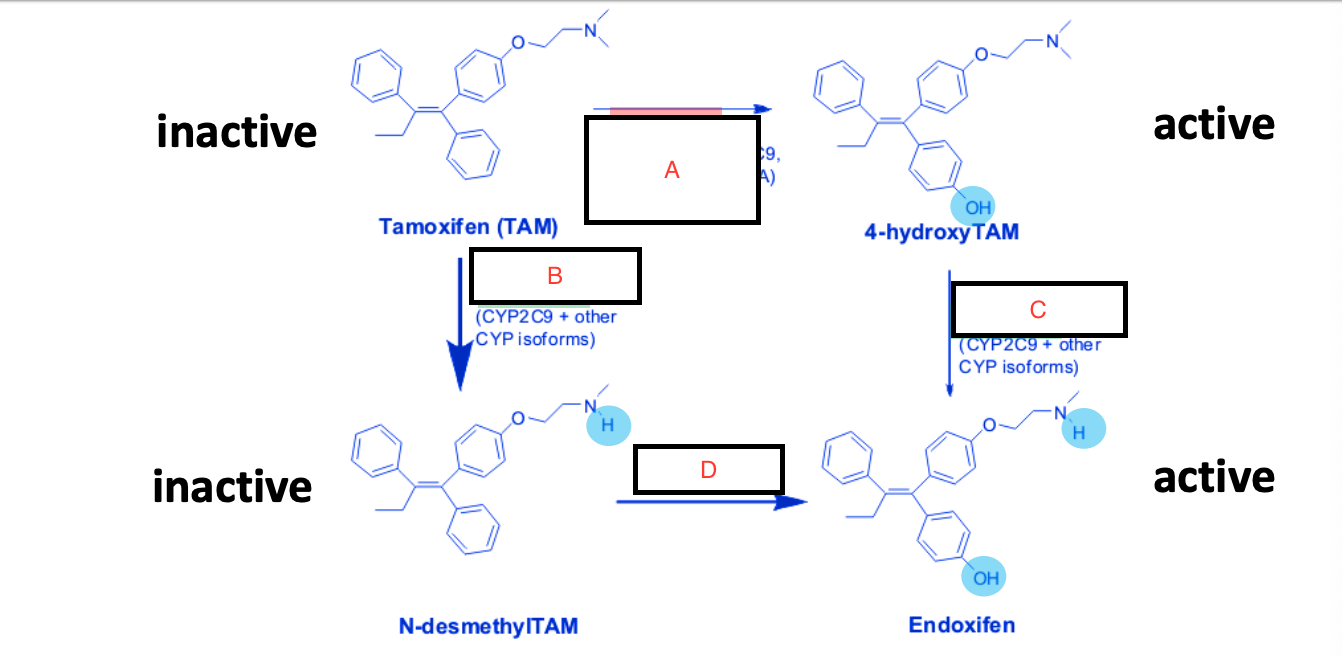
A-
B-
C-
D-
-
d,e
Which drug(s) is a strong inhibitor of CYP2D6; thus interfering with Tamoxifen metabolism?
a) Venlaflaxine
b) Setraline
c) sitalopram
d) fluoxetine
e) paroxetine
-
b, c
Which drug(s) is a weak inhibitor of CYP2D6; thus interfering with Tamoxifen metabolism?
a) Venlaflaxine
b) Setraline
c) citalopram
d) fluoxetine
e) paroxetine

