-
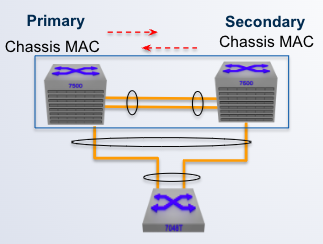
MLAG Primary/Secondary roles
- MLAG peers ___ a primary and secondary status within an MLAG domain
- Initially, switch with the lowest system MAC is elected MLAG primary
- Primary and Secondary status determine Layer 2 protocol operation
- Also generate a Mlag System ID to be used for L2 operation
negotiate
-
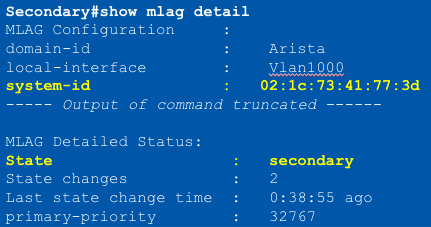
MLAG Primary/Secondary roles
- MLAG peers negotiate a primary and secondary status within an MLAG domain
- Initially, switch with the ____ system MAC is elected MLAG primary
- Primary and Secondary status determine Layer 2 protocol operation
- Also generate a Mlag System ID to be used for L2 operation
lowest
-
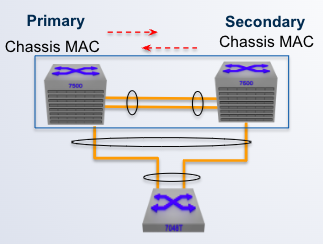
MLAG Primary/Secondary roles
- MLAG peers negotiate a primary and secondary status within an MLAG domain
- Initially, switch with the lowest system MAC is elected MLAG primary
- Primary and Secondary status determine ___ protocol operation
- Also generate a Mlag System ID to be used for L2 operation
layer 2
-
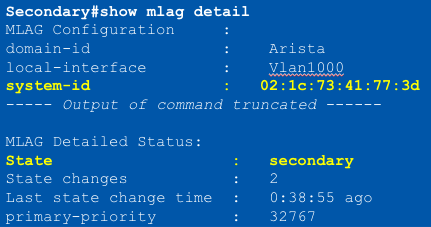
MLAG Primary/Secondary roles
- MLAG peers negotiate a primary and secondary status within an MLAG domain
- Initially, switch with the lowest system MAC is elected MLAG primary
- Primary and Secondary status determine Layer 2 protocol operation
- Also generates an Mlag ____ to be used for L2 operation
System ID
-
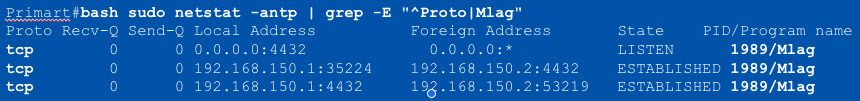
MLAG Peer Link
Peer-link control traffic uses both UDP and TCP with port number ___
4432
-
MLAG Peer Link
Used to transport ___ and primary/secondary election (___)
keepalive messages, TCP
-
MLAG Peer Link
There is no ___ of MAC addresses from packets received on the peer link. MLAG peers rely on the MAC address sync for the same.
data plane learning
-
MLAG Peer Link
Used to tunnel ___ and to sync learned MAC addresses between MLAG peers
control traffic
-
MLAG Peer Link
There is no data plane learning of MAC addresses from packets received on the peer link. MLAG peers rely on the ___ for the same.
MAC address sync
-
MLAG Peer Link
Used to transport keepalive messages and ____
primary/secondary election
-
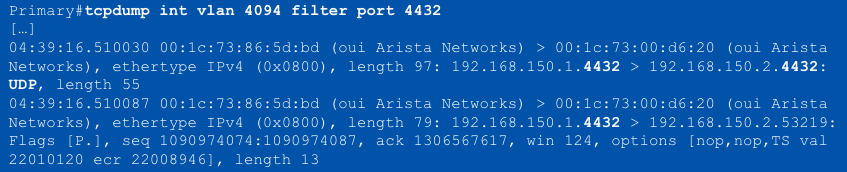
tcpdump filter for capturing MLAG peer-link control traffic:
'tcpdump int vlan 4094 filter port 4432' or the BASH equivalent, ____
bash tcpdump -nevi vlan4094 port 4432
-

Peer SVI MAC addresses are installed as ____ MAC addresses over peer-link when MLAG is active.
statically learned
-

Peer SVI MAC addresses are installed as statically learned MAC addresses over ___ when MLAG is active.
peer-link
-
MAC Address Synchronization
- For any new MAC address learned on an L2 port, the local switch will ___ the MAC address and ___ the peer through the MLAG control plane.
install, notify
-
MAC Address Synchronization
- When notified of a new MAC, the peer will install the MAC address in its address table.
- If the MAC was learned over an active-active MLAG ____, the peer will record the MAC as learned over the ____.
port-channel
-
MAC Address Synchronization
- When notified of a new MAC, the peer will install the MAC address in its address table.
- If the MAC was learned over an ____ MLAG port-channel, the peer will record the MAC as learned over the port-channel.
active-active
-
MAC Address Synchronization
- When notified of a new MAC, the peer will install the MAC address in its address table.
- For active-partial/orphan links, the peer will learn the MAC over the ____.
peer link
-
MAC Address Synchronization
- When notified of a new MAC, the peer will install the MAC address in its address table.
- For ____, the peer will learn the MAC over the peer link.
active-partial/orphan links
-
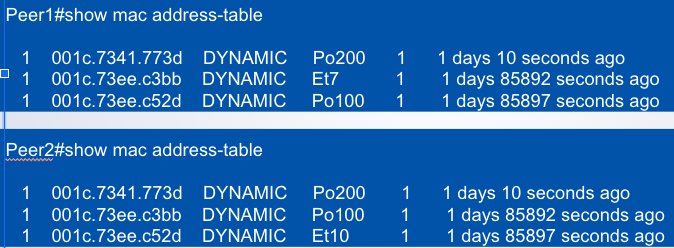
MAC Address Synchronization
Po100 is the peer link
Host 001c.7341.773d is attached to an ___
MLAG port-channel
-
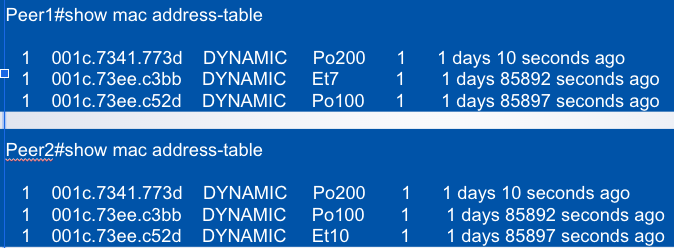
MAC Address Synchronization
Po100 is the peer link
Host 001c.73ee.c3bb and host 001c.73ee.c52d are each attached to an ___
orphan link
-
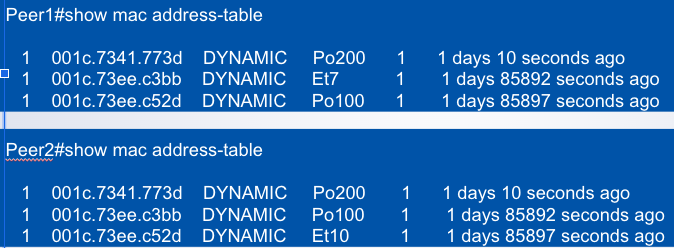
MAC Address Synchronization
Po100 is the peer link
Host 001c.73ee.c52d is attached to Switch ___
Peer2
-
To see which mac was learned by a peer as opposed to by dataplane learning use command: ____
show mac address-table mlag-peer
-
The MLAG primary controls all ___ operations
STP
-
Only the global STP configurations on the MLAG current primary will be in effect for selecting STP type, ____ etc.
bridge priority
-
STP configuration should be ___ on the MLAG primary and secondary for seamless failover.
the same
-
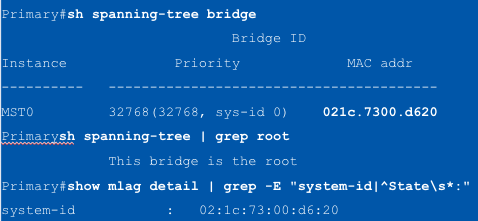
Switches in MLAG use the MLAG System ID (MSI) as a common logical ___
bridge ID
-
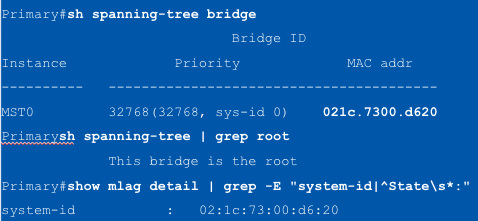
All ___ will utilize the MLAG System ID (MSI) as the bridge ID
BPDUs
-
While the STP agent runs on the secondary, it ___ manage the protocol state machines and is often listed in documentation as ‘not running on the secondary’.
does not
-
STP control traffic is advertised from secondary to primary for processing via the peer-link on the ____
MLAG VLAN
-
BPDUs are transmitted ___ the primary and ____ by the secondary
from, forwarded
-
BPDUs are encapsulated in the ___ traffic
UDP peer link
-
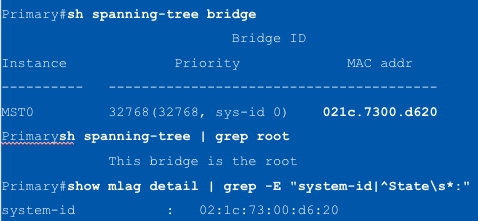
If the logical bridge is the root then both peers will show ___
"This bridge is the root"
-
STP control traffic is advertised from ___ to primary for processing via the peer-link on the MLAG VLAN
secondary
-
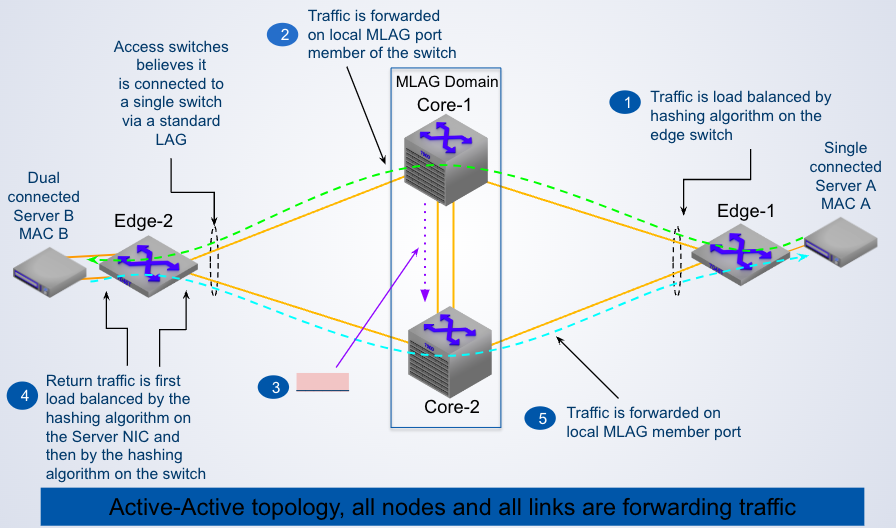
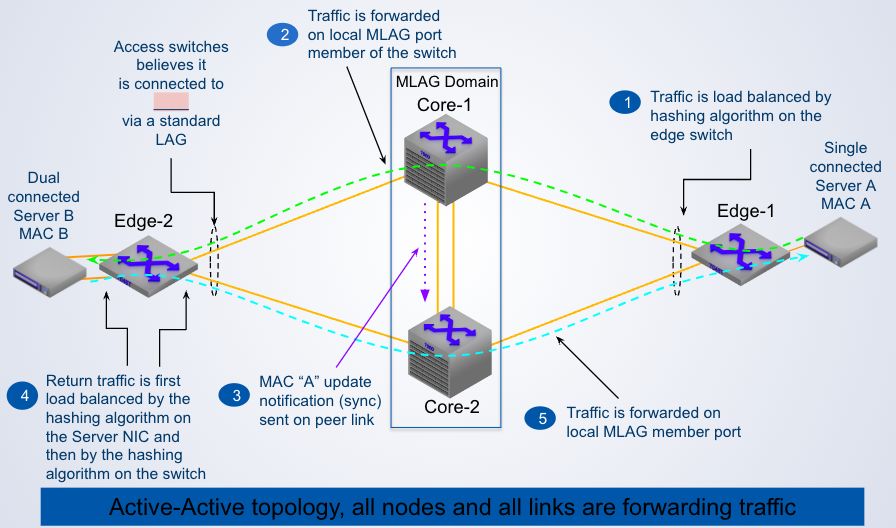
Step 3 shows Core-1 performing _____ over the peer link to notify Core-2 with information about ____
MAC Address Synchronization, MAC "A"
-
Switch Edge-2 believes it is connected to a __ via a standard LAG
single switch
-
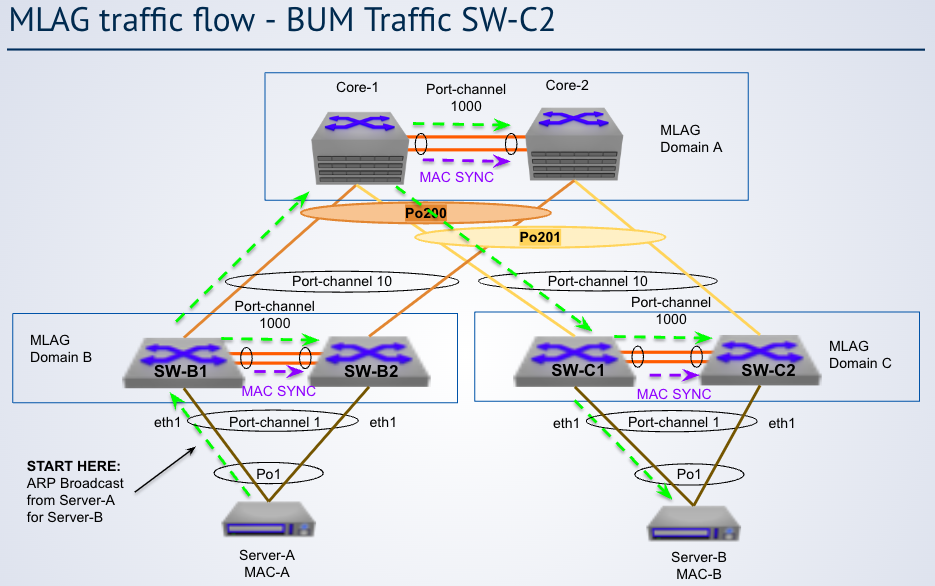
BUM traffic
In the diagram, MAC Syncs are sent from receiving switches to their peers because ___
There is no data plane learning of MAC addresses from packets received on the peer link.
-
BUM traffic
In the diagram, peer switches do not forward broadcasts on their port channel links because ___
the receiving switch's MLAG port is active
-
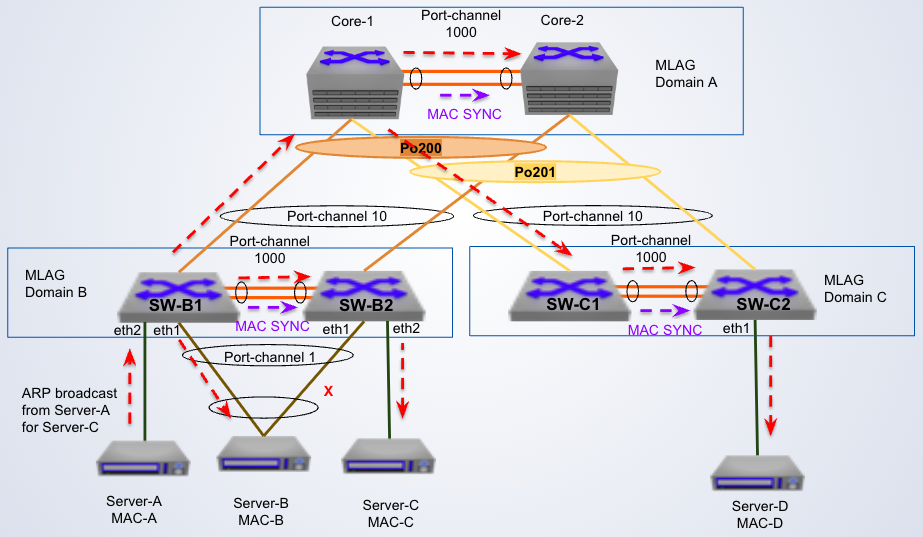
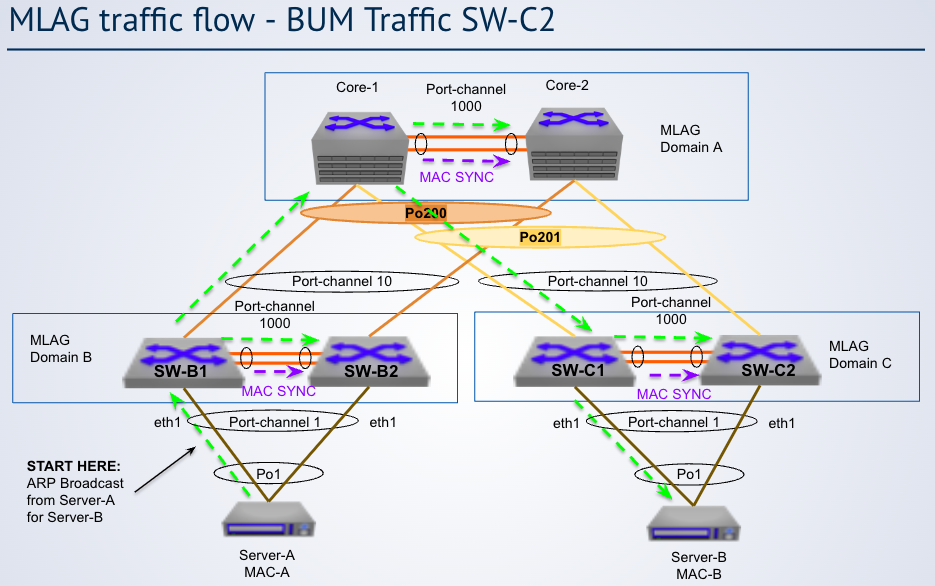
BUM traffic for single homed devices
In the diagram, switch SW-B1 broadcasts locally to the dual-attached ___ and to the upstream
Server B
-
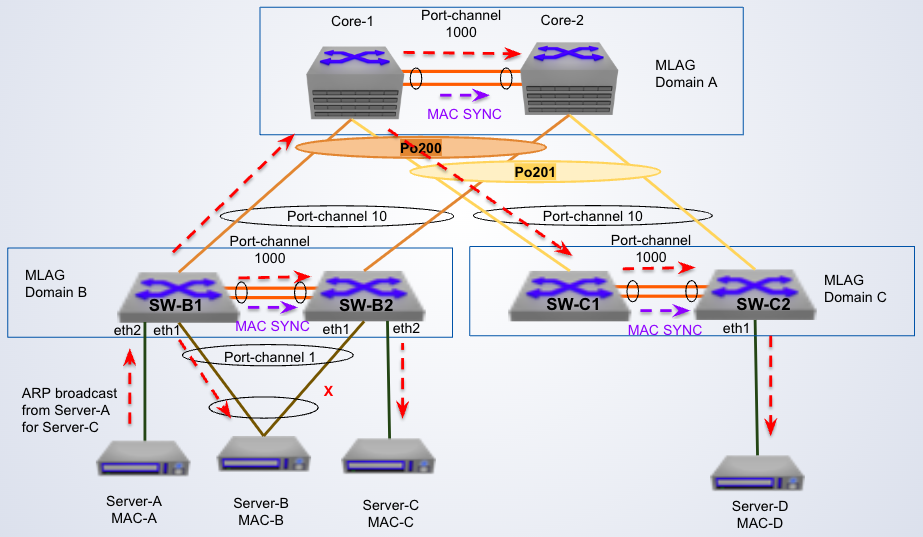
BUM traffic for single homed devices
In the diagram, switch SW-B2 broadcasts locally only to the those hosts that are ___ on the peer switch
not active
-
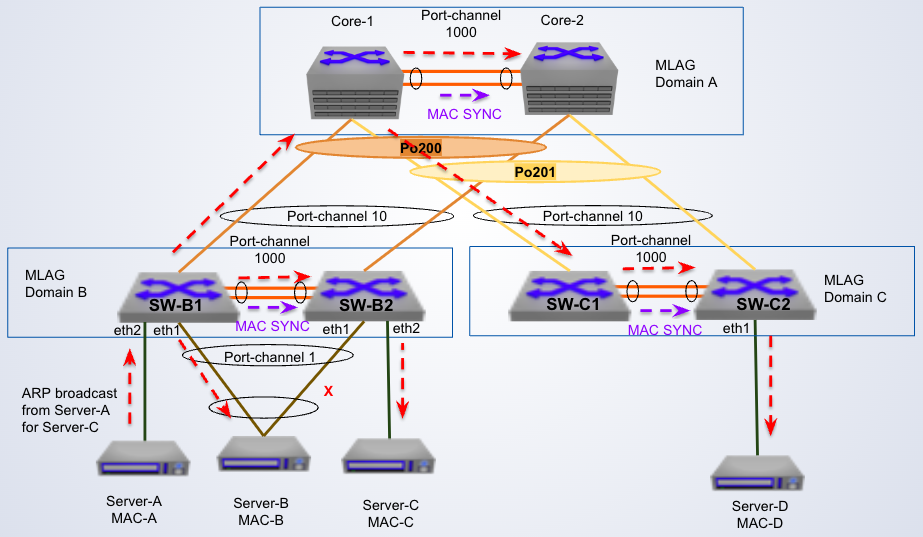
BUM traffic for single homed devices
In the diagram, switch Core-2 does not forward the broadcast on its local MLAG links because ___
MLAG port (in Po201) is active on Core-1
-
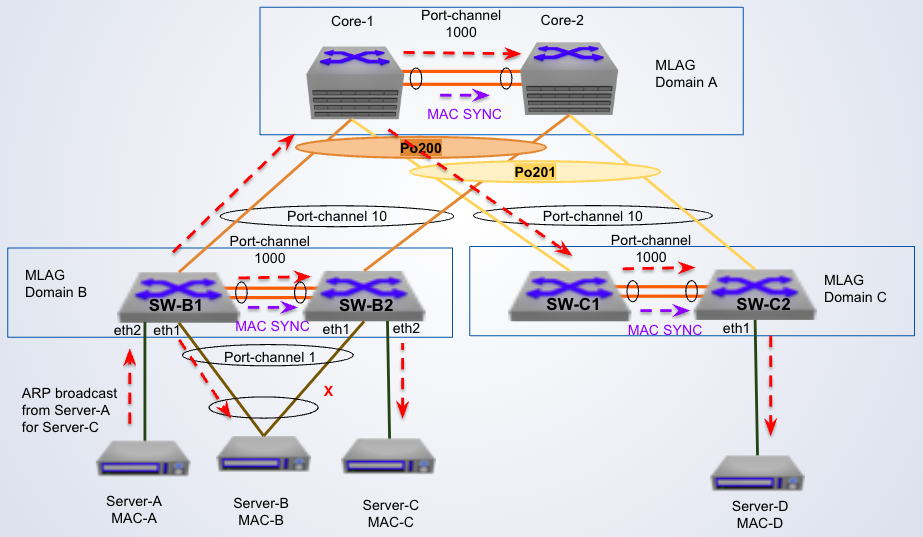
BUM traffic for single homed devices
In the diagram, switch SW-C2 floods broadcast traffic out any __ links
partial-active or single-homed
-
MLAG provides ___ L2 topology
active-active
-
MLAG peer switches run ___ layer 3 control planes
separate
-
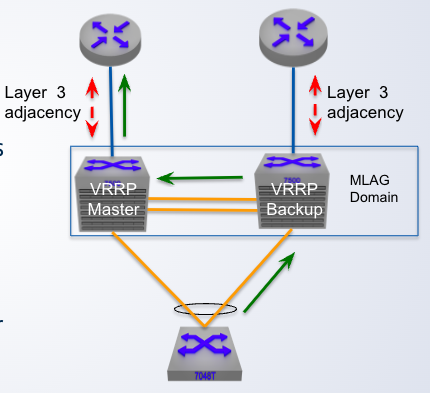
MLAG + VRRP
VRRP could be deployed to provide ___ redundancy
default gateway
-
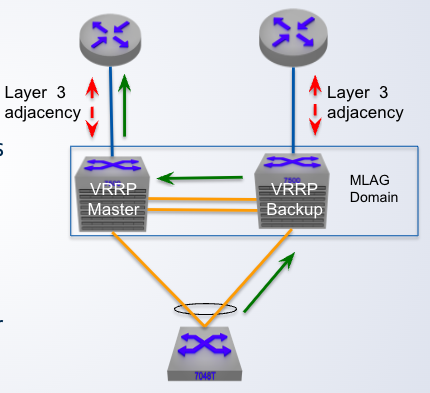
MLAG + VRRP
Only one active ____ in the MLAG domain
default gateway
-
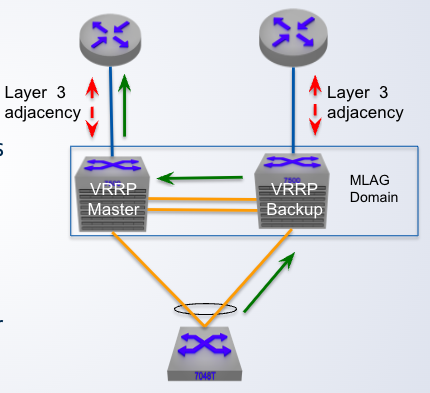
MLAG + VRRP
Only one active default gateway in the MLAG domain which results in ___ Layer 3 forwarding
active-standby
-
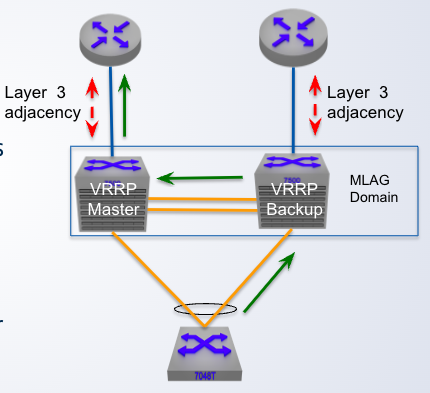
MLAG + VRRP
Traffic is ___ across the peer link under normal operation
forwarded
-
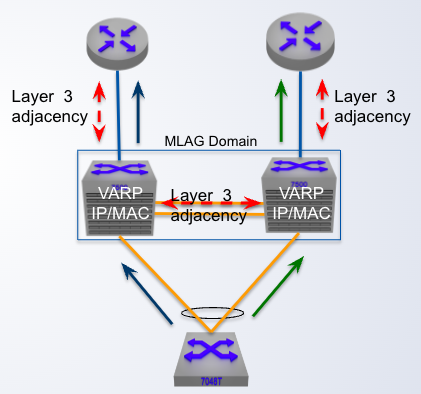
MLAG + VARP
VARP is used to achieve ___ default gateway forwarding
active-active
-
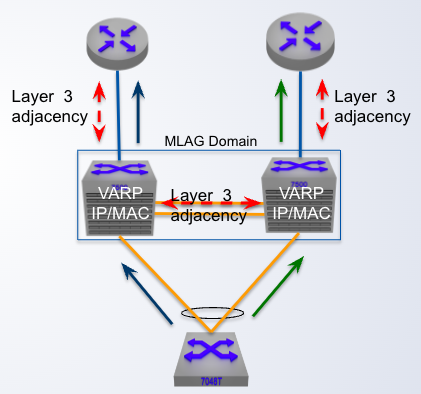
MLAG + VARP
Two VARP peers share a ___ VARP address
single
-
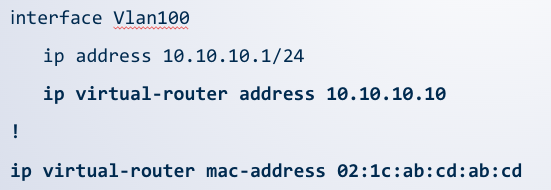
MLAG + VARP
A ____ consists of a Virtual IP address and MAC address (global)
VARP address
-
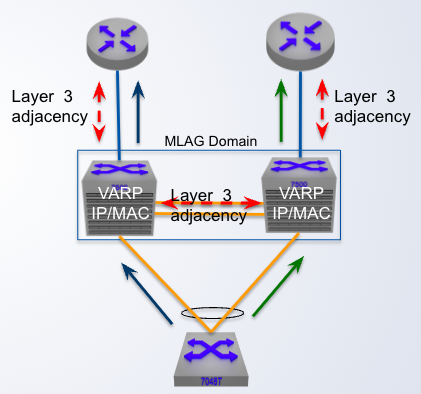
MLAG + VARP
Peer locally forwards traffic sent to the VARP MAC address locally, thus no need to forward traffic across the ____
peer link
-
MLAG + VARP
Each peer is responsible for ___ of local nodes
ARP
-
MLAG + VARP
GARP is sent periodically to refresh ____
MAC tables
-
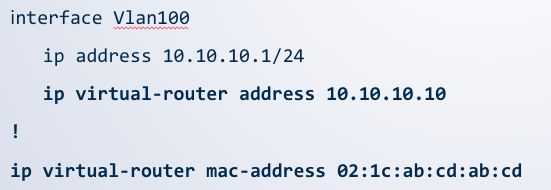
MLAG + VARP
End nodes configured with the VARP IP as their ____
default gateway

