-
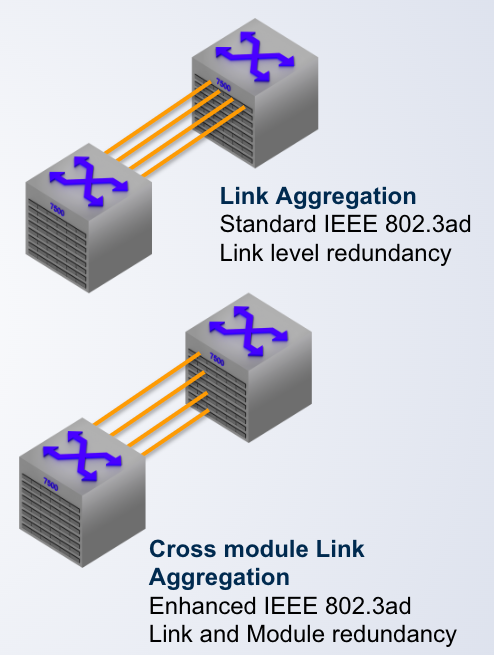
Link Aggregation Group
- Dynamic LAG IEEE _____
- Multiple physical links to act as a single logical link
- New bandwidth is aggregate of all the links in the group
- Traffic is shared across the links in the group
- In the event of link failure, the data traffic is moved to another link in the group providing seamless failover
803.2ad
-
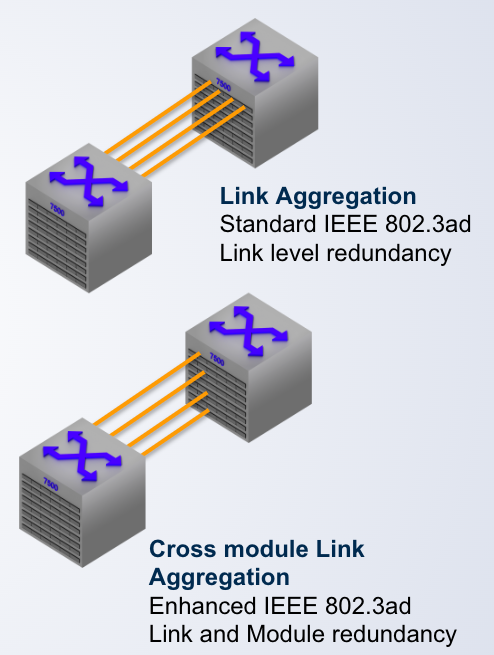
Link Aggregation Group
- Dynamic LAG IEEE 803.2ad
- Multiple physical links to act as a single ____ link
- New bandwidth is aggregate of all the links in the group
- Traffic is shared across the links in the group
- In the event of link failure, the data traffic is moved to another link in the group providing seamless failover
logical
-
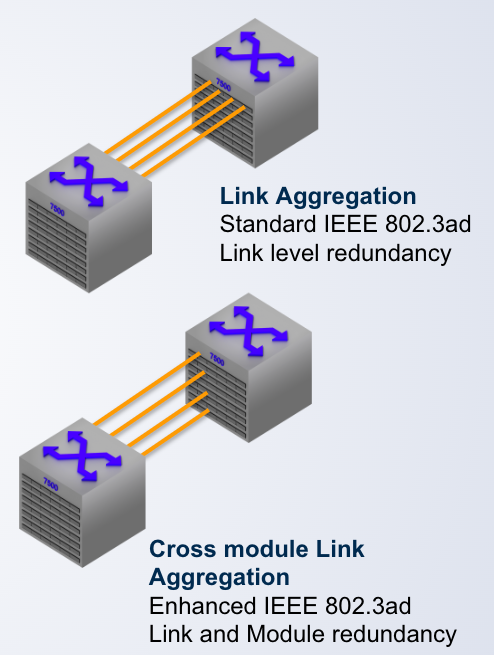
Link Aggregation Group
- Dynamic LAG IEEE 803.2ad
- Multiple physical links to act as a single logical link
- New bandwidth is _____ of all the links in the group
- Traffic is shared across the links in the group
- In the event of link failure, the data traffic is moved to another link in the group providing seamless failover
aggregate
-
Multi-Chassis LAG (MLAG)
- Enhancement to standard LAG
- Splits the LAG group across different nodes
- Providing link, ____ and ___ redundancy
- No layer 2 loop thus an Active-Active topology
- Sub-second failover based on the physical link failure
module, node
-
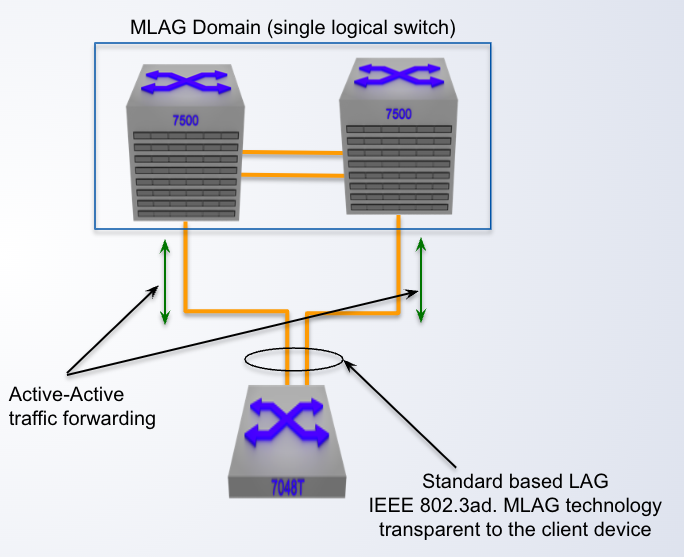
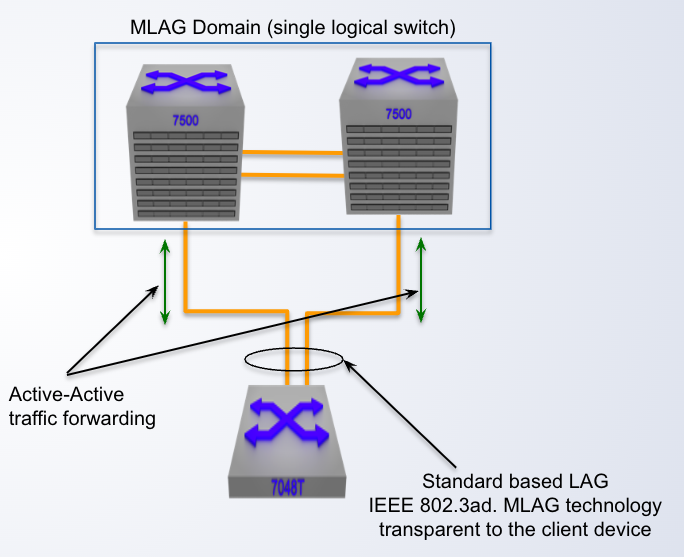
Multi-Chassis LAG (MLAG)
- Enhancement to standard LAG
- Splits the LAG group across different nodes
- Providing link, module and node redundancy
- No layer 2 loop thus an Active-____ topology
- Sub-second failover based on the physical link failure
active
-
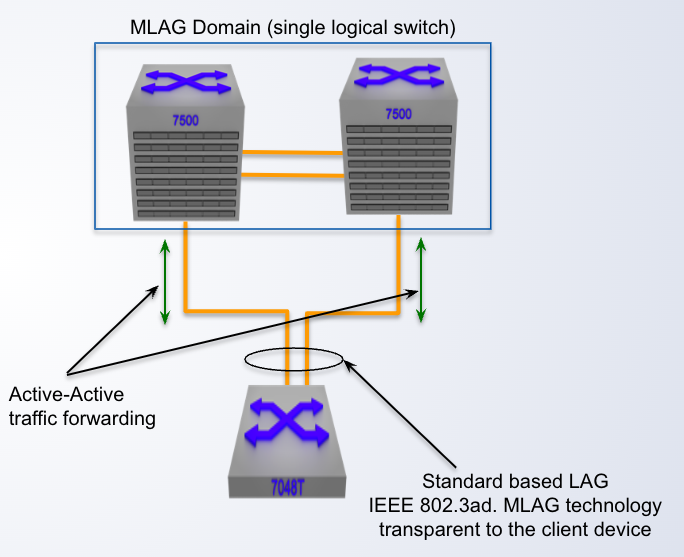
Multi-Chassis LAG (MLAG)
- Enhancement to standard LAG
- Splits the LAG group across different nodes
- Providing link, module and node redundancy
- No layer 2 loop thus an Active-Active topology
- Sub-___ failover based on the physical link failure
second
-
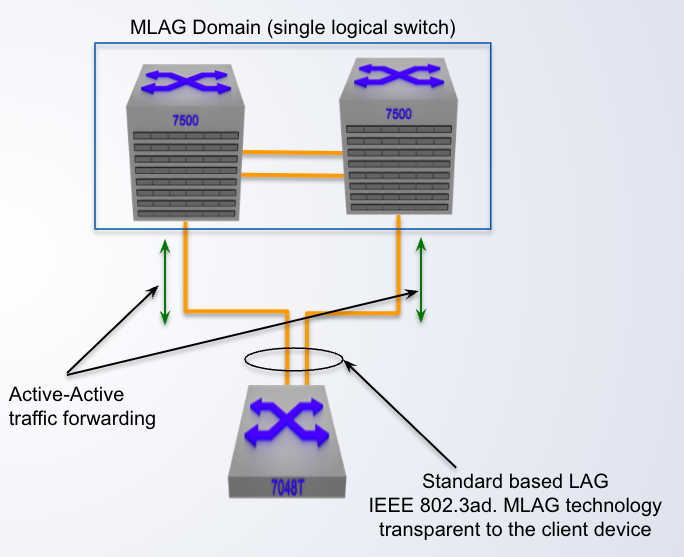
MLAG is Standard ____ based
802.3ad
-
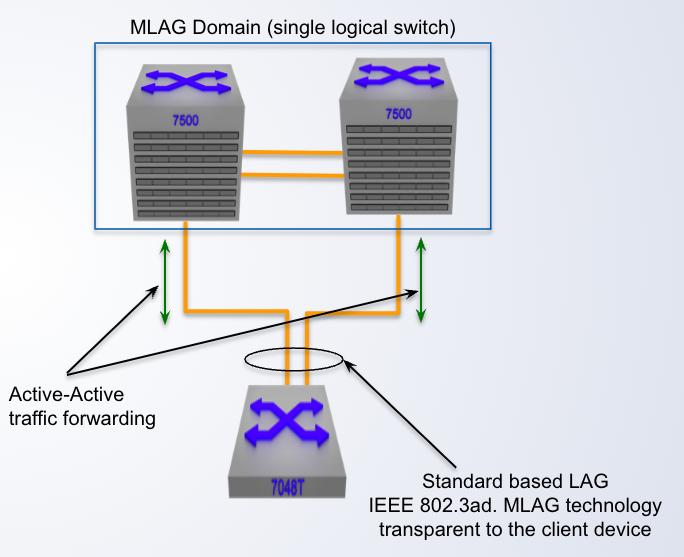
MLAG is standard 802.3ad based:
- Dynamic LACP or ____ configuration
- Transparent to attached client device
- Support for third-party vendors and servers
static
-
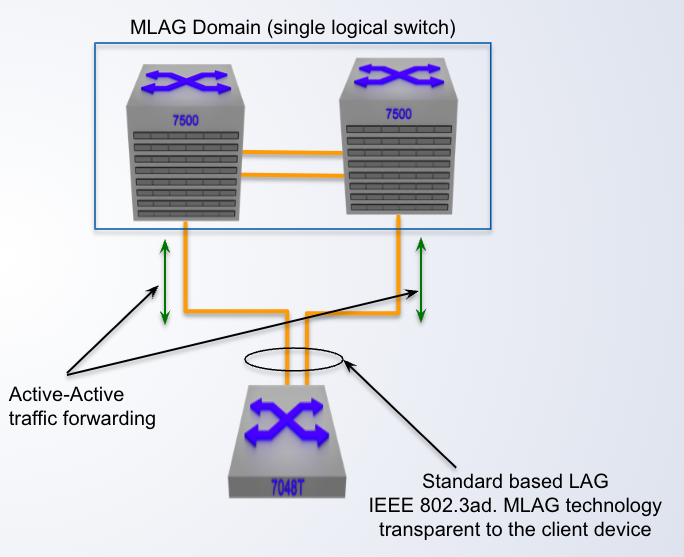
MLAG is standard 802.3ad based:
- Dynamic LACP or static configuration
- _____ to attached client device
- Support for third-party vendors and servers
transparent
-
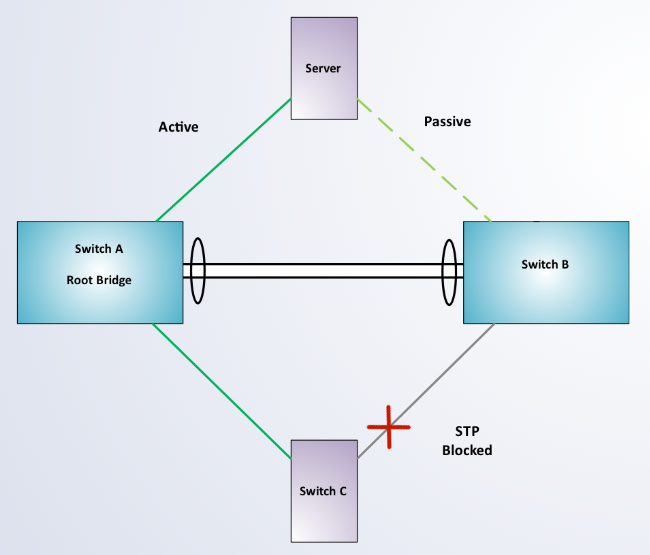
Without MLAG, redundant connections from end host devices would either be configured in an ____ scenario or blocked via spanning-tree reducing the total bandwidth used.
active/passive
-

Without MLAG, redundant connections from end host devices would either be configured in an active/passive scenario or blocked via ____ reducing the total bandwidth used.
spanning-tree
-
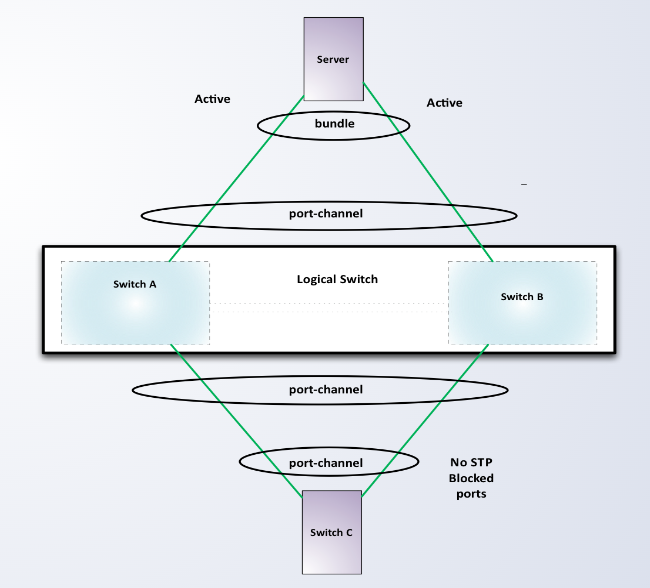
Using MLAG, all redundant links to downstream devices/hosts can be ___ into a single LAG to utilize the entire bandwidth available.
bundled
-
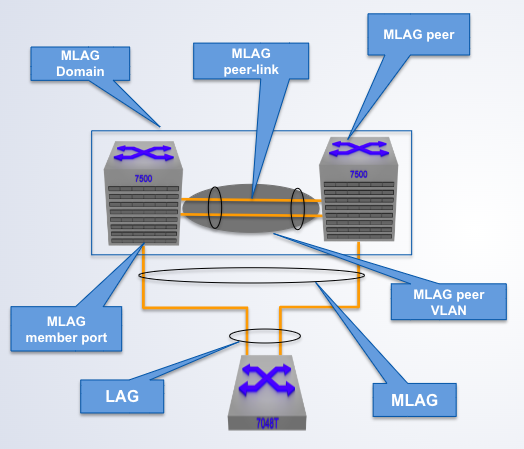
A pair of physical switches
MLAG Domain
-
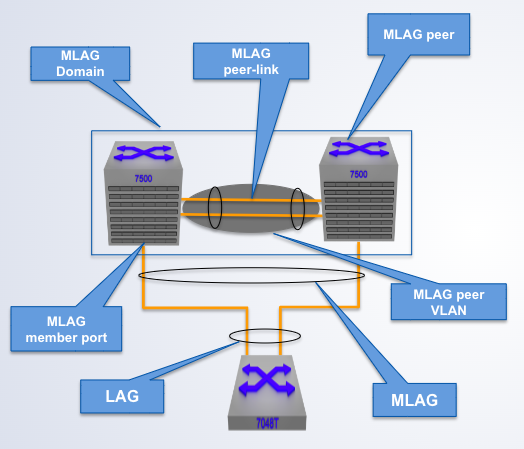
A single switch within an MLAG domain
MLAG Peer
-
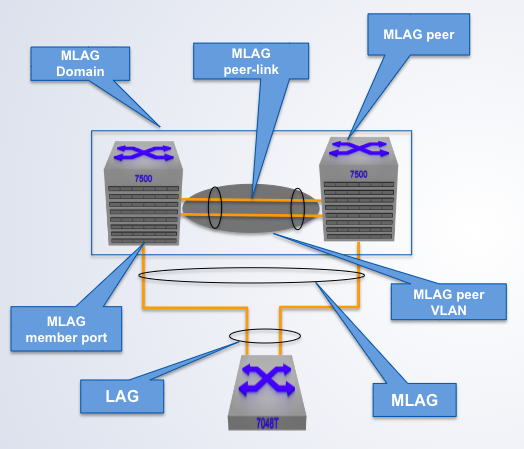
Non-proprietary Ethernet physical link between MLAG peers required to synchronize state between MLAG peers and carry user data
MLAG peer-link
-
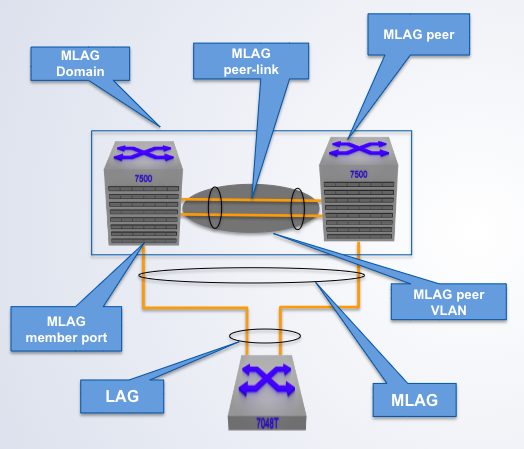
One or more user-facing physical ports that forms an MLAG
MLAG member port
-
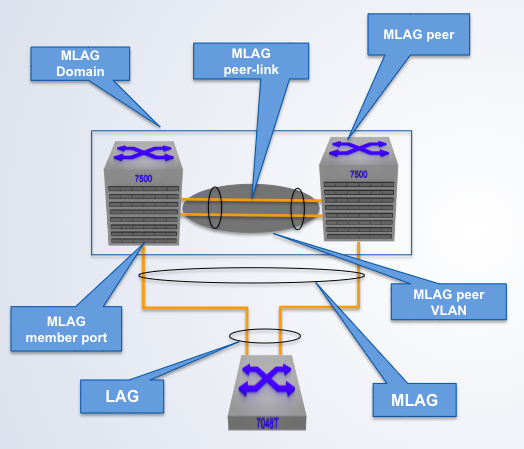
This is a combined user-facing port-channel between MLAG peers consisting of MLAG member ports on both MLAG peers
MLAG port-channel
-
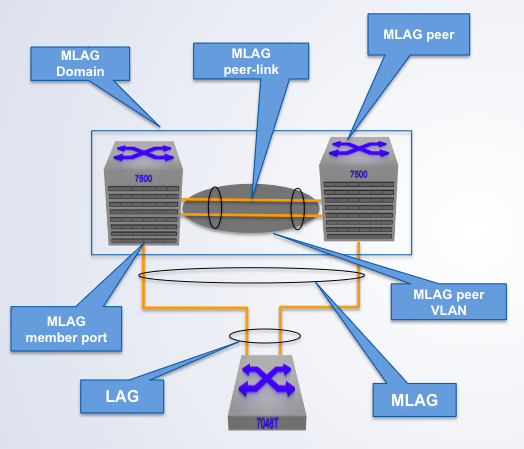
A VLAN used exclusively on the MLAG peer-link, in order to aid control-plane communication between MLAG peers.
MLAG VLAN
-
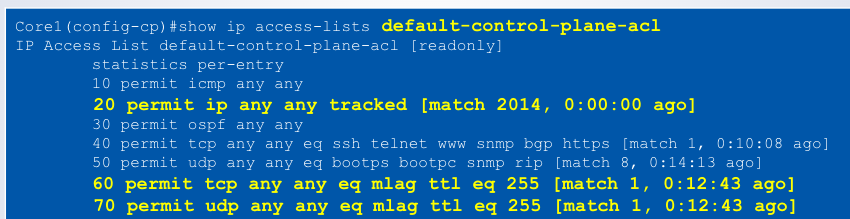
To permit the MLAG communication between peers,
appropriate MLAG-related UDP and TCP entries should be present in the default control plane ACL or in a custom ACL if one is used instead:
- permit ip any any tracked
- permit tcp ___
- permit udp ___
any any eq mlag ttl eq 255
-
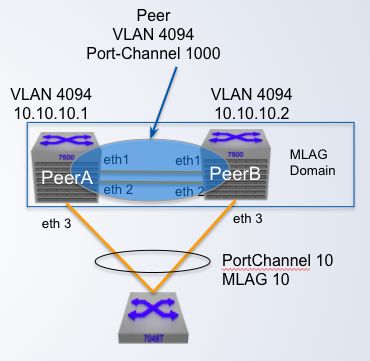
MLAG Configuration
Step 1: Configure the Peer link
Configure the peer link as a standard _____
- Any Ethernet port on the switch of enough capacity
- Recommended minimum of two ports for redundancy
- Under steady state conditions data traffic doesn't flow across the peer link
- Bandwidth not required to be large under the steady conditions
port-channel
-
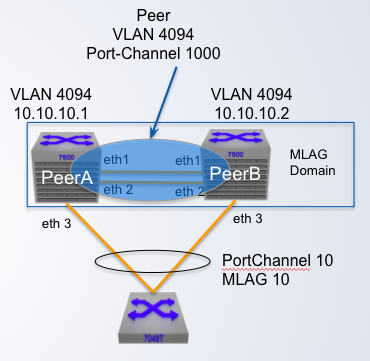
MLAG Configuration
Step 1: Configure the Peer link
Configure the peer link as a standard port-channel
- Any Ethernet port on the switch of enough capacity
- Recommended minimum of two ports for _____
- Under steady state conditions data traffic doesn't flow across the peer link
- Bandwidth not required to be large under the steady conditions
redundancy
-
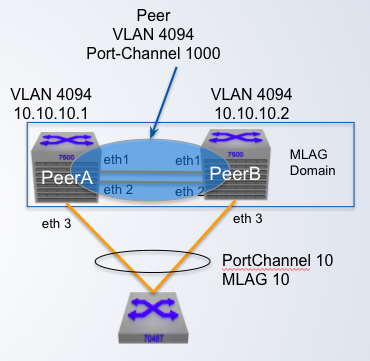
MLAG Configuration
Step 1: Configure the Peer link
Configure the peer link as a standard port-channel
- Any Ethernet port on the switch of enough capacity
- Recommended minimum of two ports for redundancy
- Under steady state conditions _____ doesn't flow across the peer link
- Bandwidth not required to be large under the steady conditions
data traffic
-

Create the port-channel as a ____ port.
trunk
-
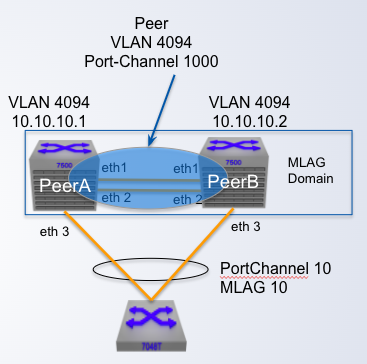
MLAG Configuration
Step 2: Create the Peer link VLAN
- VLAN used for MLAG _____ session
- SVI needs to be created for the VLAN
- Spanning tree must be disabled on the VLAN
- Peer link VLAN recommended to be configured within a "trunk group"
- Trunk group needs to be explicitly configured on the peer link
TCP/UDP
-
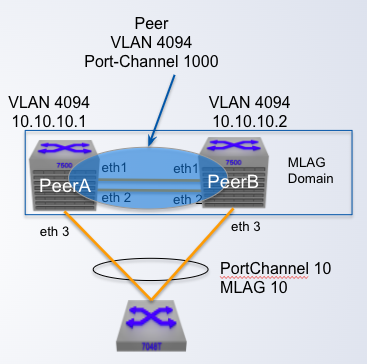
MLAG Configuration
Step 2: Create the ____
- VLAN used for MLAG TCP/UDP session
- SVI needs to be created for the VLAN
- Spanning tree must be disabled on the VLAN
- Peer link VLAN recommended to be configured within a "trunk group"
- Trunk group needs to be explicitly configured on the peer link
peer link VLAN
-

MLAG Configuration
Step 2: Create the Peer link VLAN
- VLAN used for MLAG TCP/UDP session
- SVI needs to be created for the VLAN
- Spanning tree must be ____ on the VLAN
- Peer link VLAN recommended to be configured within a "trunk group"
- Trunk group needs to be explicitly configured on the peer link
disabled
-
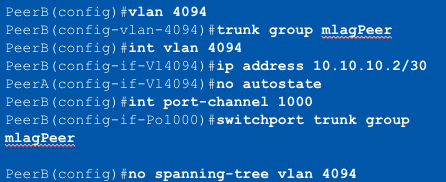
MLAG Configuration
Step 2: Create the Peer link VLAN
- VLAN used for MLAG TCP/UDP session
- SVI needs to be created for the VLAN
- Spanning tree must be disabled on the VLAN
- Peer link VLAN recommended to be configured within a ____
- ____ needs to be explicitly configured on the peer link
trunk group
-
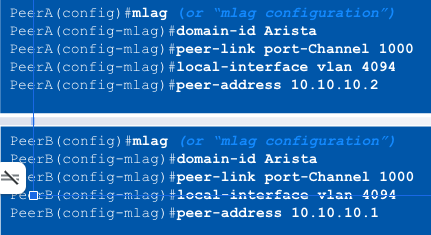
MLAG Configuration
Step 3: Configure the MLAG domain
- All MLAG configuration achieved under the “mlag” context
- Define the MLAG domain-ID, must be identical on both switches (____)
- Define the port-channel to be used for the peer link
- Define the local interface to be used for the MLAG session
- Define the remote peer’s IP address for creating the MLAG session
case sensitive
-
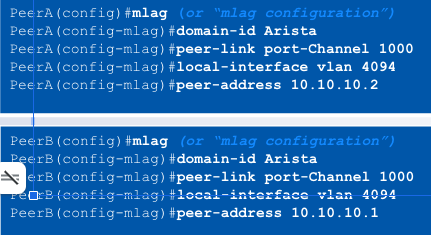
MLAG Configuration
Step 3: Configure the MLAG domain
- All MLAG configuration achieved under the “mlag” context
- Define the MLAG domain-ID, must be identical on both switches (case
sensitive)
- Define the port-channel to be used for the ____
- Define the local interface to be used for the MLAG session
- Define the remote peer’s IP address for creating the MLAG session
peer link
-
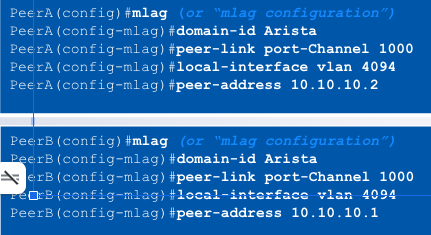
MLAG Configuration
Step 3: Configure the MLAG domain
- All MLAG configuration achieved under the “mlag” context
- Define the MLAG domain-ID, must be identical on both switches (case sensitive)
- Define the port-channel to be used for the peer link
- Define the ____ to be used for the MLAG session
- Define the remote peer’s IP address for creating the MLAG session
local interface
-
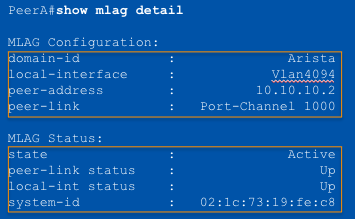
MLAG Configuration
Step 3: Configure the MLAG domain
- All MLAG configuration achieved under the “mlag” context
- Define the MLAG domain-ID, must be identical on both switches (case
sensitive)
- Define the port-channel to be used for the peer link
- Define the local interface to be used for the MLAG session
- Define the remote peer’s ____ for creating the MLAG session
IP address
-
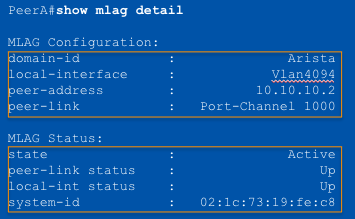
MLAG Configuration
Step 3: Configure the ____
- All MLAG configuration achieved under the “mlag” context
- Define the MLAG domain-ID, must be identical on both switches (case
sensitive)
- Define the port-channel to be used for the peer link
- Define the local interface to be used for the MLAG session
- Define the remote peer’s IP address for creating the MLAG session
MLAG domain
-
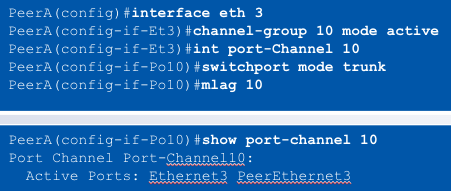
MLAG Configuration
Step 4: Create the MLAG port members
- MLAG port members created as standard port-channels
- Port-channel created on each MLAG peer
- Static, passive or active ____ configurable on each port-channel
- The port-channel can contain one or multiple ports on each peer switch
- The “MLAG <#>” statement binds the port-channel on the peers together
LACP
-
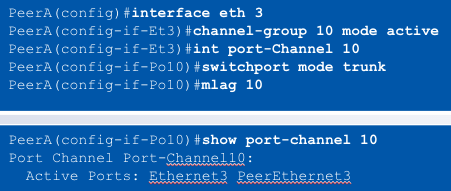
MLAG Configuration
Step 4: Create the MLAG port members
- MLAG port members created as standard port-channels
- Port-channel created on each MLAG peer
- Static, passive or active LACP configurable on each port-channel
- The port-channel can contain one or multiple ports on each peer switch
- "____" command binds the port-channel on the peers together
MLAG <#>
-
Link Aggregation Groups provide ____ and ____ redundancy
link, module

