-
How do microscopes give us a magnified image of an object?By using 2 lenses - they eye piece lens and the objective lens.
-
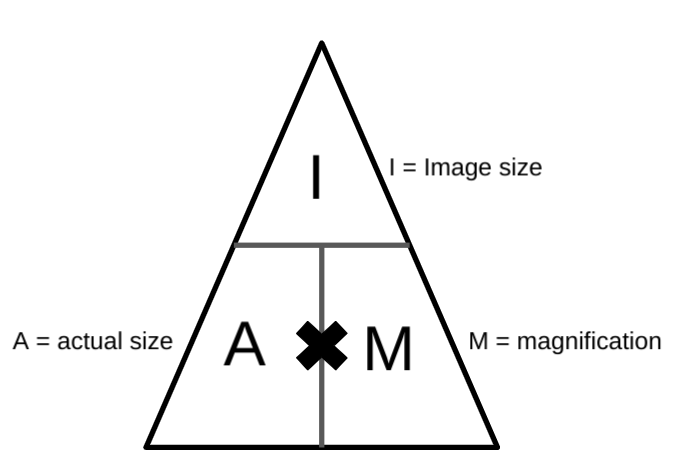
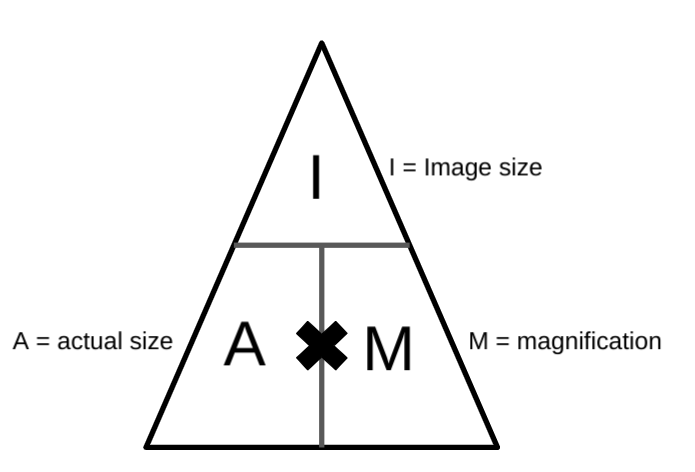 How is the total magnification calculated?By multiplying both together. E.g: if the eye piece is x40 and the objective lens is x100 the total magnification is 4000.
How is the total magnification calculated?By multiplying both together. E.g: if the eye piece is x40 and the objective lens is x100 the total magnification is 4000. -
Light raysLight rays have a long wave length (400-700nm). This is fine for studying human hair, which is about 100 times bigger than the wavelenght of light, but not for a bacterium that is 200nm in length or a protein molecule that is just 10nm.
-
Seeing detailed objectsIf you want to see in detail objects that are smaller than the wavelength of light, you need to use electrons.
-
ElectronsElectrons have a very short wavelength (1nm) which allows us to see objects much smaller than the wavelenght of light.
-
Electron microscopeIn an electron microscope, a beam of electrons is used instead of light rays. When the electrons reach the specimen, some pass through and some bounce off - the electrons that pass through are detected and displayed as an image on a flourescent screen.
-
Electron microscope magnificationElectron microspcopes have much higher magnification and resolving power (the ability to see 2 points as being separate) than a microscope. This means that cells can be studied in much finer detail and biologists can now see many more sub-cellular structures.