-
How is Clostridium tetani: Diagnosis within a patient?
–Characteristic muscular contraction
-
The treatments for Clostridium tetani are as followed:
–Cleansing of wounds to remove endospores
–Administer immunoglobulin against tetanus toxin
–Administer antimicrobial drugs
–Active immunization with tetanus toxoid
-
How can Clostridium tetani be Prevented?
–Immunization with tetanus toxoid
-
Common signs of lockjaw are:
–Initial tightening of the jaw and neck muscles
•Commonly called lockjaw
-
Symptoms of Clostridium tetani are
–Spasms and contractions can spread to other muscles
–Unrelenting contraction of the diaphragm can cause death
-
Why are people in underdeveloped countries so susceptible to Clostridium tetani?
•Due to inadequate medical care and lack of vaccination
–Recovery requires the growth of new neuronal terminals
–The mortality rate is about 50%
-
The action of tetanospasmin (tetanus toxin) on a pair of antagonistic muscles.
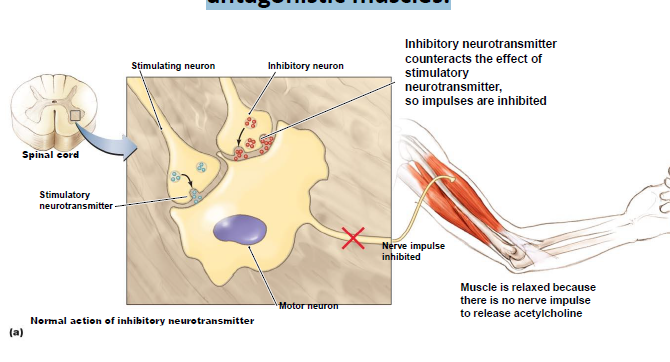
Inhibitory neurotransmitter counteracts the effect of
stimulatory neurotransmitter, so impulses are inhibited Muscle is relaxed because there is no nerve impulse to release acetylcholine.
-
The action of tetanospasmin (tetanus toxin) on a pair of antagonistic muscles.
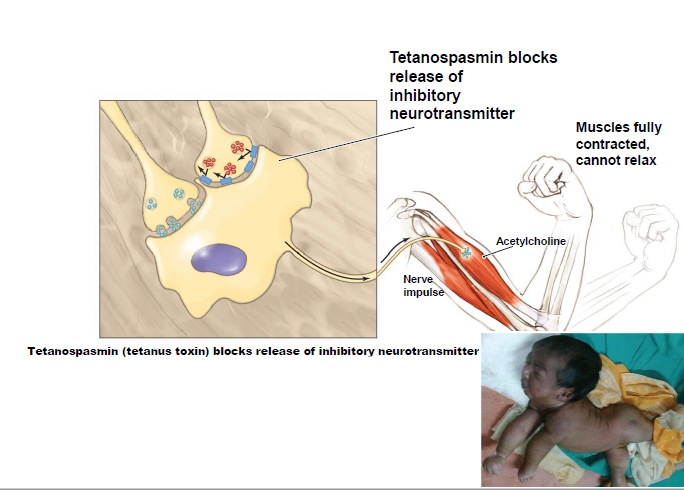
Tetanus toxin causes hyperactivity of voluntary muscles in the form of rigidity and spasms. Rigidity is the tonic, involuntary contraction of muscles, while spasms are shorter lasting muscle contractions that can be elicited by stretching of the muscles or by sensory stimulation; they are termed reflex spasms.
-
Pathogenesis of Clostridium tetani
–Tetanospasmin toxin (tetanus toxin)
•Released by C. tetani cells when they die
•Potent neurotoxin
•Causes continuous muscle contractions
-
Characteristics of Clostridium tetani are as follows:
–Anaerobic, endospore-forming bacillus
–Common in soil and water
–Botulism results when the endospores germinate and produce botulism toxins
-
Clostridium botulinum: Diagnosis
•Motile, obligately anaerobic bacilli with a terminal endospore
•Ubiquitous in soil, dust, and GI tract of animals and humans
•Tetanus results when endospores germinate and produce tetanus toxin
–Symptoms are diagnostic
-
Proper canning of food and Infants under 1 year should not consume honey are all forms of
–Symptoms are diagnostic
Preventing Clostridium botulinum
-
Clostridium botulinum can be prevented by
–Washing intestinal tract to remove Clostridium
–Administering neutralizing antibodies against botulism toxin
–Administering antimicrobial drugs in infant and wound botulism cases
-
Foodborne botulism is intoxication from Clostridium botulinum that
•Death can result from asphyxiation
•Slow recovery from the growth of new nerve cell endings
-
Results from ingestion of endospores, however paralysis and death are rare this is a case of:
Infant botulism
-
Wound botulism is a Contamination of a wound by endospores and has similar Symptoms to:
Foodborne botulism
-
The Pathogenesis of Clostridium botulinum occurs in these steps:
–Botulism toxins
•C. botulinum strains produce seven distinct toxins
•Among the deadliest known toxins
•Bind neurons and prevent muscle contractions
-
Ture or false, Clostridium botulinum is anaerobic, endospore-forming Bacillus and is common in soil and water
Ture
-
We can Diagnosis Clostridium perfringens by minimum bacterial load in food or feces and:
–Appearance of gas gangrene is usually diagnostic
-
Treatment for Clostridium perfringens are successful when
–Food poisoning is self-limited
–Gas gangrene requires removal of dead tissue and administration of antitoxin and penicillin
-
To prevent Clostridium perfringens we could refrigerate foods to reduce food poisoning and properly clean wounds to prevent gas gangrene. Is this statement true.
Yes
-
Toxins that cause irreversible damage to the body are known as
Pathogens of Clostridium perfringens
-
The epidemiology of Clostridium perfringens grows in the digestive tracts of animals and humans.
True
-
–Food poisoning •Abdominal cramps and watery diarrhea –Gas gangrene
•Trauma introduces endospores into the body •Endospores germinate and cause necrosis, which are all symptoms that occur in the Disease.
Clostridium perfringens
-
Clostridium perfringens could be define as:
–Large, nonmotile bacillus
–Clostridium is most frequently isolated from clinical specimens
-
The characteristic of Clostridium are
•Anaerobic, endospore-forming
•Ubiquitous in soil, water, and gastrointestinal tracts of animals and humans
•Endospores allow for survival in harsh conditions
-
Ture or false, Botulism results when the endospores germinate and produce botulism toxins.
Ture
-
How botulism toxin acts at a neuromuscular junction.
Intramuscular administration of botulinum toxin acts at the neuromuscular junction to cause muscle paralysis by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine from presynaptic motor neurons.
-
How does botulinum affect the nervous system?
Botulism causes paralysis by affecting the nerves which allow the brain to stimulate muscles and part of the central nervous system.

