-
What is taxonomy's opinion on phenotype?
ARBITRARY
-
How are microorganisms classified now?
DNA sequencing
-
What is the current classification system?
Three Domain System (Bacteria, Archaea, Eucarya)
-
What is the basic unit in taxonomy
Species
-
What are "strains" in taxonomy?
Level of categorization under species, identify specific isolates of a given species.
-
Modern way of seeing how related two microbes are?
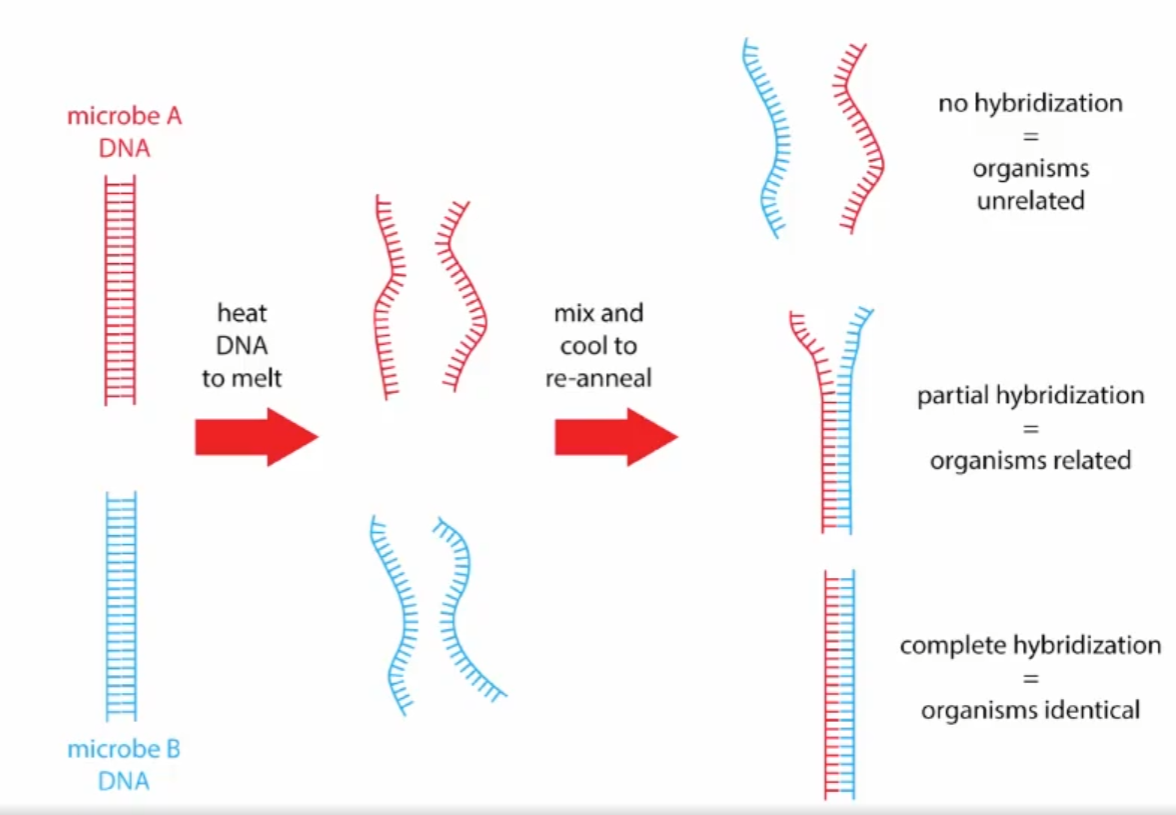
DNA DNA hybridization
-
What are the two types of tests?
Presumptive (Not exact, allows you to rule out some options)
Confirmatory(exact)
-
What are the phenotypic characteristics that help in the identification of pathogens?
-Microscopic morphology (stains, microscope)Sterile environments
-Culture Characteristics (Colony shapes, colours, smell)
-Metabolic capabilities (where it can grow, pH indicators, biochemical tests)
-Serology (Use of antibodies)
-Fatty Acid Analysis (Fatty acid methyl ester, microbes have unique fatty acids in membranes)
-Detecting specific nucleotide sequences (NAATS are several methods used to increase number of copies of specific DNA sequences, Nucleic acid probes)
-
What is a biovar or biotype?
Group of strains with a characteristic pattern of growth called a biovar or biotype
-
How do you characterize strain differences?
-Biochemical typing (biovar/biotype) OLD
-Serological Typing (Proteins & carbs that vary among strains can be used as markers)
-Molecular Typing(Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism, different RFLPs indicate different strains)
-Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (Sequence set of highly conserved genes and compare) need a database
-Phage typing (differences in bacterial strain susceptibility to bacteriophages) OLD
-Antibiograms (Antibiotic susceptibility patterns)
-
What can 16S rRNA gene sequencing do?
-Identify organisms taxonomic group
-Calculate relatedness between groups
-Describe new species and those that have never been successfully cultured
-
Why is 16s rRNA gene a good target for gene classification/identification?
1. Universal to all bacteria
2. Multi-copy
3. Conserved function and regions are very conserved
4. Although there are variable regions which are species specific
-
What are the advantages of 16s rRNA tests
Provide an answer when none is available
Do not need bacteria to be alive
-
What are the disadvantages of 16s rRNA tests
Cannot test antibiotic resistance
Can only use one bacterial species
Not sufficient to infer causation of infection
Negative foes not mean no bacteria present/no infection
-
Three stages in a clinal microbiology lab?
1. Pre-analytical (few hours)
specimen collection, transportation, sorting, and labeling
2. Analytical (days to months)
diagnostic testing
3.Post-analytical
Lab reporting
-
Advantages and disadvantages of MALDI-TOF MS?
Fast, cheap
Limited database of organisms
-
How does MALDI-TOF MS work?
Analyzes protein composition from intact cells or nucleic acid extract. Protein profile is then compared to database
-
Advantages and disadvantages of Real time PCR?
Rapid (3h)
Cheap
Requires prior sequence knowledge
-
Advantages and disadvantages of Whole genome sequencing?
Fast, Reliable
Requires strong infrastructure, expensive

