-
What is the difference between microbial growth in the lab and in the wild?
Microbial growth in the lab is under optimal conditions
-
What are biofilms?
Organized communities stuck on surfaces
-
What is the difference between biofilm and planktonic?
Biofilm grows slower have water channels, more resistant, harder to remove
-
How do bacteria create biofilms?
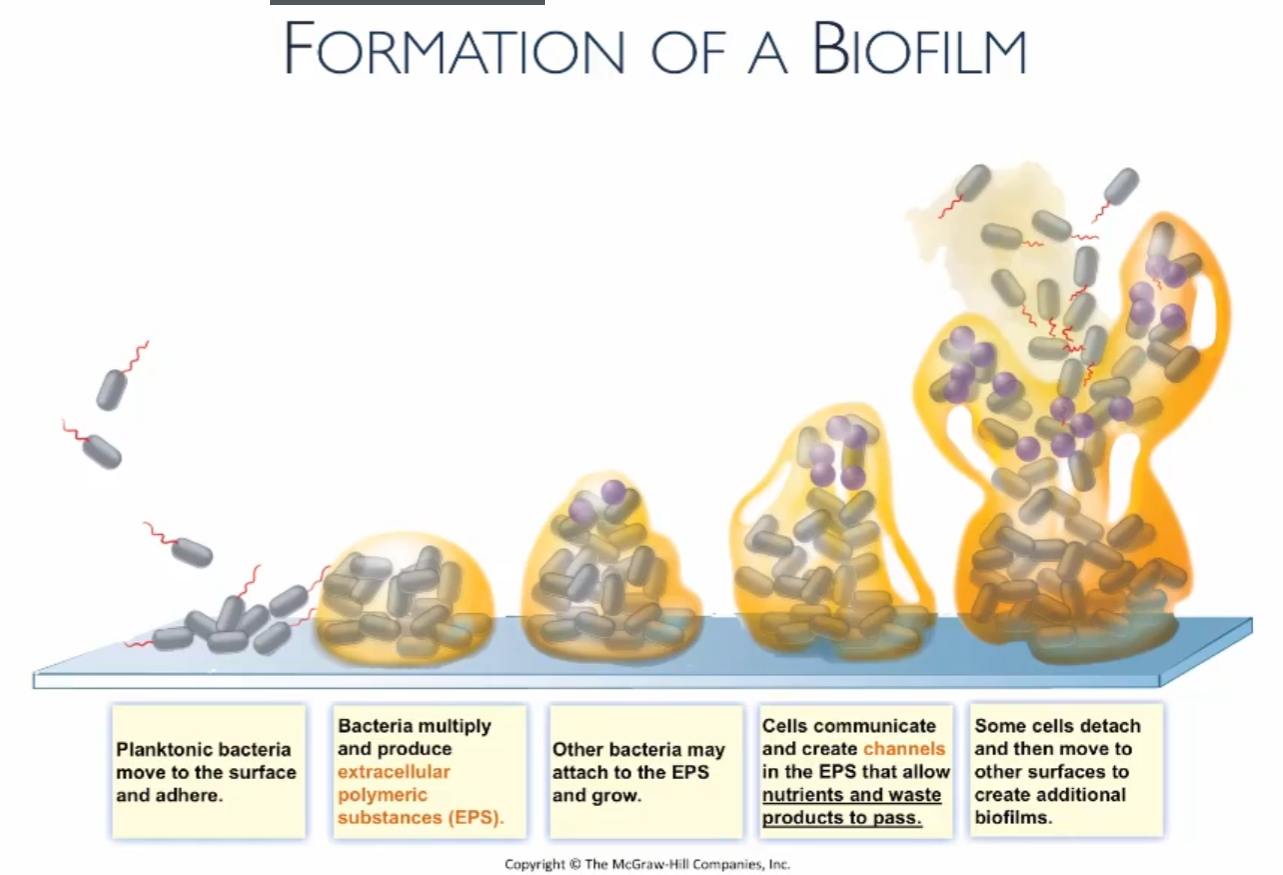
Some gather on a surface, they multiply and produce EPS (extracellular polymeric substances), more bacteria come, create water channels, some leave to make more biofilm.
-
How does bacteria Quorum Sensing work?
Controlled by chemicals called autoinducers which bacteria create. When there's enough concentration of autoinducers they switch behaviour modes.
-
How do mixed microbial environments work?
Some interactions are cooperative (eat waste of another organism) but mostly competitive (synthesize toxins targeted at other microbes)
-
What are the factors that influence microbial growth?
Temperature, oxygen , pH, and water availability
-
What are the temperature ranges for all the philes
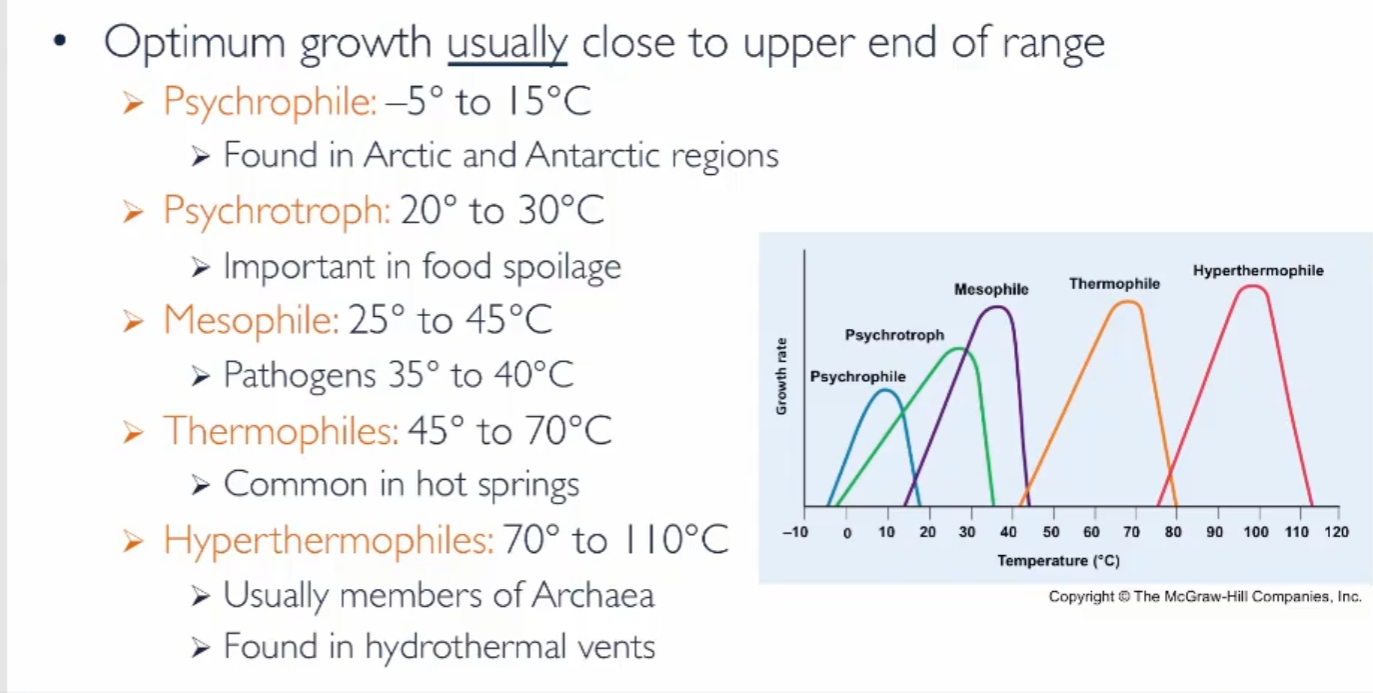
-
How do thermophiles resists protein denaturing?
Amino acid sequence of proteins
-
What are the type of aerobes for bacteria?
1.Obligate aerobes only grow in oxygen
2. Facultative aerobes can use oxygen for energy
3. Obligate anaerobes cannot use or tolerate oxygen
4. Aerotolerant anaerobes do not use oxygen but tolerate it
5. Microaerophiles grow in presence of low oxygen
-
What is produced in aerobic respiration?
ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) like O2- (superoxide) and H2O2 hydrogen peroxide
-
How do bacteria counter ROS?
They make superoxide dismutase which converts superoxide into hydrogen peroxide then they use catalase which turns that into hydrogen and oxygen
-
What are the terms for pH philes?
Acidophiles grow optimally under 5.5 pH
Alkaliphiles grow optimally over 8.5
Neutrophiles grow optimally around 7 pH
-
How does salt limit microbial growth?
Reduces amount of water available
-
What is halotolerant and halophiles?
Halotolerant means it can grow in water up to 10% salt concentration, halophiles require high salt concentration
-
What are BSL levels?
Biosafety levels, 4 levels, higher the level the more safety required(more dangerous)
-
What are endospores?
Super resistant microbial seeds that sprout under right conditions
-
What are pseudomonas?
Grow in disinfectant
-
What are naked viruses?
More resistant to detergent and disinfectants but still susceptible to chlorine
-
What is decimal reduction time?
Gauges disinfectant effectiveness (time required to kill 90% of a microbe)
-
What is an autoclave?
Machine that steams water thus increasing temperature and pressure killing microbes. (121C)
-
What is a retort?
Supa sized industrial autoclave
-
what is pascalization?
Super high pressures (130k psi)
-
Classes of chemical disinfectants?
Alcohols, Aldehydes, Biguanides, Ethylene oxide(gas), Halogens, Ozone (O3), Peroxygens, phenolic compounds, Quats

