-
What is edema?
Swelling from too much fluid in the tissues.
-
What happens to the lymph nodes if you might be sick (infection)?
The nodes might swell.
-
What do the lymph nodes do?
Filter lymphatic fluid.
-
To determine if someone has breast cancer, what area of the armpit may they check the lymph nodes?
The armpit
-
What are the lymphatic organs?
- Liver
- Spleen
- Thymus
- Nodes
-
What are lymph nodes rich in?
Lymphocytes and monocytes
-
Where do lymph nodes originate at?
in blood
-
What do lymph nodes do in the intestine?
Absorb lipids in the intestine.
-
What are the 3 functions of the lymphatic system?
1. Tranportation of protein and fluid that leaked back to the bloodstream.
2. LV absorb lipids from intestines and bring them back to the bloodstream.
3. Lympho/monocytes protect the body by attack foreign cells and organisms (creates antibodies).
-
What is interstitial fluid?
Fluid around cells and tissues; usually from substances leaking from the blood capillaries.
-
What are the structures of interstitial fluid and lymph capillaries?
- B. capillaries
- L. capillaries
- L. vessel
- Interstitial fluid
- Tissue cells (lymphoid tissue)
-
Where does lymph filter out from?
B. capillaries and into the spaces between cells.
-
Fluid that surrounds body cells is called interstitial fluid, which passes continuously into thin-walled vessels called lymph capillaries that course through tissue spaces. True or false?
True
-
Where are lymph nodes located in the body?
- Cervical
- Axillary
- Mediastinal (chest)
- Mesentric (intestinal)
- Paraaortic (lumbar)
- Inguinal
-
What does the spleen do?
- destroys old rbcs
- filters foreign material out of blood
- activates lymphocytes during blood filtration
- stores blood
-
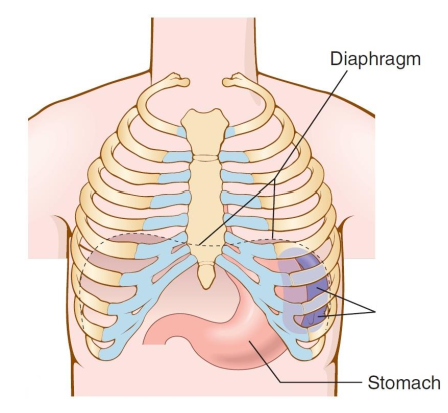
What is this organ?
The spleen
-
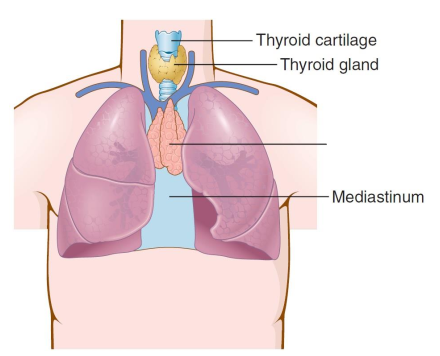
What structure is this?
Thymus gland
-
What does the thymus gland do?
- provides immunity in fetus' and in early years
- makes cells inmmunocompetent (strong) in early life
- early removal, prevents the body from making antibodies against antigens
- conditions T cells to react to foreign cells
-
What types of leukocytes are found in lymph fluid?
- neutrophils
- monocytes
- macrophages
-
What are adenoids?
Mass of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx.
-
What are antibodies?
Protein produced by B cells to destroy antigens.
-
What are antigens?
Foreign substance; evokes an immune response.
-
Axillary nodes are___.
L. nodes in the armpit.
-
What are B cells (B lymphocyte)?
Lymphocyte that matures into a plasma cell to secrete antibodies.
-
What happens to interstitial fluid in the L. capillaries?
Becomes lymph.
-
What is lymph?
Thin, watery fluid within lymphatic vessels and collected from tissues throughout the body.
-
What is a lymph vessel?
Carrier of lymph throughout the body.
-
Paraaortic nodes are ___.
lymph nodes near the aorta in the lumbar area of the body.
-
What is a plasma cell?
Lymphocyte that secretes antibodies; matures from B lymphocytes.
-
What do the lymphoid organs do?
Produce lymphocytes; nodes, spleen and thymus gland.
-
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Man-made antibody (compared to made in the body, like a vaccine) to attack antigens to destroy cells.
-
Where are the tonsils located?
Back of the oropharynx (back of the mouth, middle part of the throat).
-
immun/o
immunity, protection, safe
-
lymphaden/o
lymph node
-
splen/o
spleen
-
thym/o
thymus gland
-
tox/o (think toxic)
poison
-
prefix for again, anew
-ana (ana/phylaxis)
-
What is Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)?
Destroys helper T cells, weakening the immune system. CD4 cells (wbc) get destroyed extremely quickly that the body isn't able to regenerate them fast enough.
-
What is an allergy?
It's an abnormal sensitivity/reaction by exposure to an antigen.
-
What is rhinitis, anaphylaxis, and atopic dermatitis?
- Rhinitis (nose infection/inflammation aka nasal congestion)
- Anaphylaxis (severe allergic response and life-threatening, can cause the body to go into shock due to massive shift of fluids in body)
- Atopic dermatitis (Eczema; causes dry, itchy and inflammed skin)
-
What is urticaria?
Hives
-
What is lymphoma?
A malignant tumor made of the L. nodes and tissue.
-
What are the 2 types of lymphoma and describe them?
- Hodgkin lymphoma (Reed-sternberg cell)
- Non-hodgkin lymphoma (follicular, and large cell lymphoma)
-
What is multiple myeloma?
myel/o - bone marrow, -oma - tumor,
Malignant tumor of bone marrow cells.
-
axill/o
armpit (axillary)
-
cervic/o
neck; cervix (neck of the uterus)
-
Translate lymphadenopathy
lymph - lymph, aden/o - node(s), -pathy - disease condition
Lymphadenopathy - Disease of the lymph nodes (swelling)
-
-cytosis
condition of cells; increase in numbers (think leukocytosis)
-
-edema
swelling (lymphedema - swelling due to build up of lymph)
-
-globulin
protein (group of proteins made in the liver)
-
-oid
resembling (lymph/oid)
-
-penia
deficiency (leukopenia)
-
-poiesis
formation (erthyro/poiesis)
-
-stitial
to set; pertaining to standing or positioned (inter/stitial)
-
-suppression
to stop (immuno/suppression)
-
What is the name of the fluid that lies betweencells throughout the body?
Interstitial
-
Epinephrine is also called ___?
Adrenaline

