-
What is the difference between external and internal respiration?
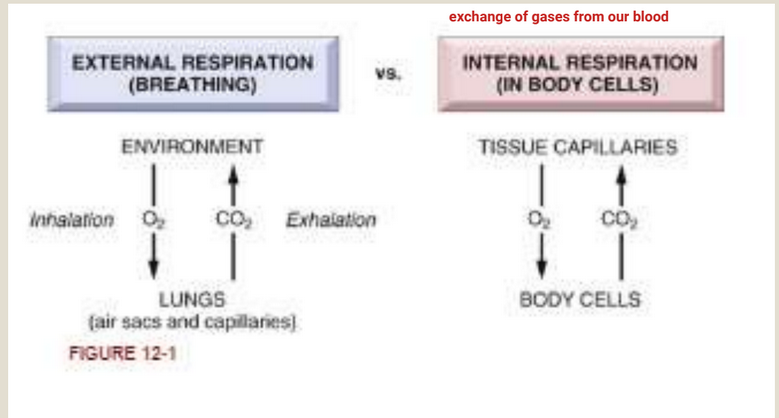
External is breathing; taking in O2 and breathing out CO2. Internal is breathing but done through our tissues and body cells.
-
What is the conducting zone?
The zone in which different body structures take in air and breathe out CO2.
-
What body parts our responsible for conducting air?
- Nose
- Nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses
- Pharynx (throat)
- Larynx (voice box)
- Trachea (wind pipe)
-
What are the cavities and sinuses responsible for?
Warms and moistens incoming air; so lung tissue remains wet instead of drying out.
-
What structures are responsible for the exchange of gases.
- Bronchioles
- Alveoli
- Lung capillaries
-
What is the arrangement of epithelial cell are the alveoli made of?
simple squamos; allows easy diffusion
-
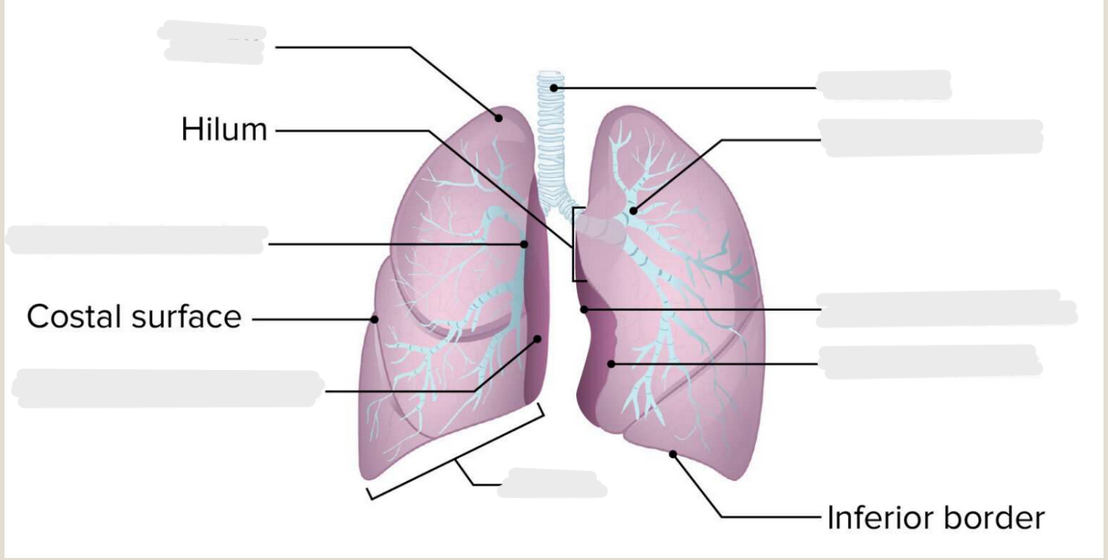
Label the diagram
-
Describe the flow of O2; how it enters and the structures associated with it.
- Nose > cavities and sinuses (warms up wets air for lungs) > pharynx (throat) > larynx (voice box) > trachea (wind pipe) > bronchi > bronchioles (small branches of the bronchi) > alveolar sacs > alveoli > lung capillaries (bloodstream)
-
What are adenoids?
The tonsils of the pharyngeal side (lower part of your mouth).
-
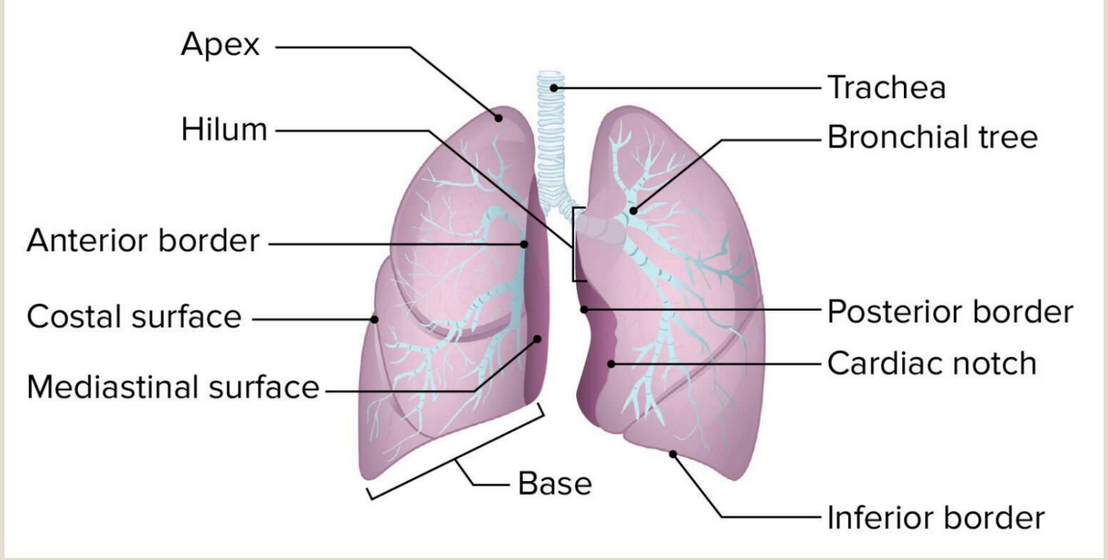
Where is the apex of the lung?
The uppermost tip of the lung.
-
What is the bronchus?
The branch of the trachea that is a passageway into the lung.
-
What sort of epithelial cells line the upper respiratory tract? It moves foreign substances to either be coughed up or swallowed, and produces mucus to protect from foreign substances from entering the lungs.
Ciliated simple columnar
-
What does the diaphragm do when it pulls air into the lungs, and when it pushes air out of the lungs?
It contracts when pulling air, and relaxes when pushing air out.
-
What structure prevents food from entering the larynx and trachea when eating?
The epiglottis
-
What area of the lungs do the bronchi enter?
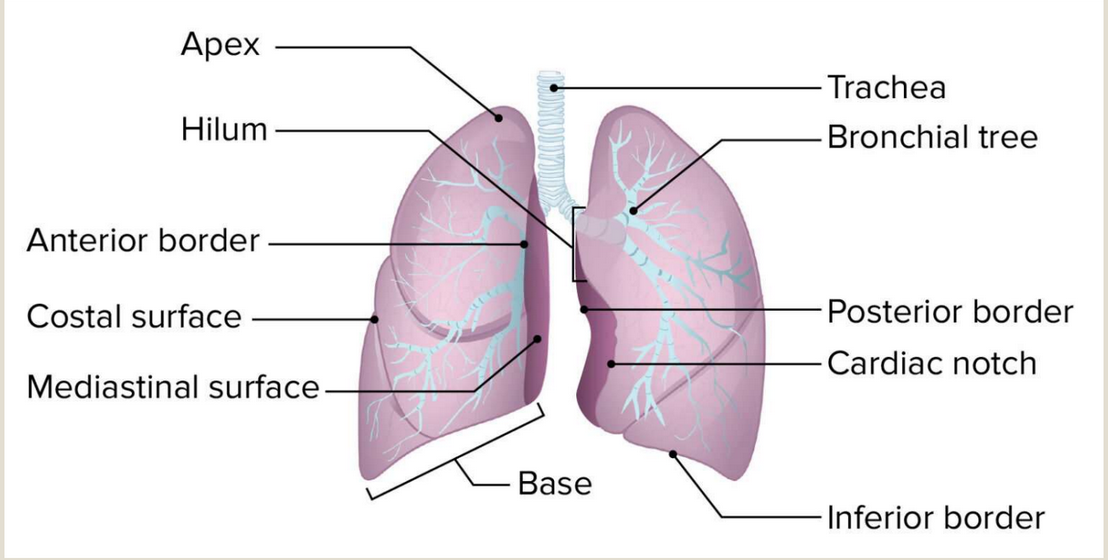
The hilum
-
Inspiration means to...
breathe in (inhale)
-
Expiration means to...
breathe out (exhale)
-
What structure contains the vocal cords?
Larynx
-
Where is the mediastinum located?
Between the lungs; contains the heart and the trachea.
-
What is the tip of uppermost portion of the lung?
Apex
-
combining form of nose
nas/o
-
orth/o
straight, upright
-
ox/o
oxygen
-
combining form of chest
pector/o
-
phon/o
voice
-
combining form of diaphragm
phren/o
-
pleur/o
pleura
-
pneum/o
air, lung
-
pneumon/o, pulmon/o
lung
-
combining form of sinus cavity
sinus/o
-
spir/o
breathing
-
combining form of chest (what cavity is the chest part of?)
thorac/o
-
combining form of trachea
trache/o
-
-ema
condition
-
-pnea (think of sleep apnea)
breathing
-
-ptysis
spitting
-
-thorax
pleural cavity, chest
-
What does atelectasis refer to?
Collapse of the lung
-
What does epistaxis refer to?
nosebleed
-
Pertussis is ___.
coughing
-
What does bronchiectasis refer to?
Chronic dilation of a bronchus; over stretching of the bronchus, makes it harder to breathe because of the size.
-
What does pulmonary edema refer to?
Fluid in the lungs
-
What does pneumonia refer to?
Infection of the lungs
-
Pleural effusion is...
accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.
-
Pleuritis/pleurisy is....
inflammation of the pleura
-
What does pneumothorax refer to?
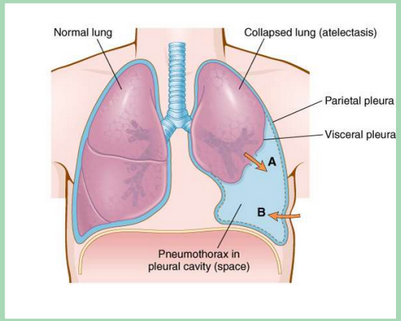
collection of air in the pleura space.
-
Bacilli refers to...
the shape of bacteria.
-
What does exudate mean?
The leaking from a wound, which tends to indicate an infection (mucus or pus).
-
Water in the chest cavity is?
Hydrothorax
-
What is the general term for chronic bronchitis and emphysema?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
-
Paroxysmal means..
something that come and goes.
-
What is the term for when the blood flow towards the lungs is blocked?
Pulmonary infarction
-
What does purulent mean?
Thick, yellow/green mucus
-
What occurs during a bronchoscopy?
An endoscope is inserted into the bronchial tubes for diagnosis, biopsy or collection of the secretions.
-
What occurs during an endotracheal intubation?
A tube is placed from the mouth to the trachea to establish airway.
-
What occurs during a thoracentesis?
Fluid is aspirated
-
What occurs during a tube thoracostomy?
A tube is inserted into the chest.

