-
What does the cardiovascular system do?
It delivers oxygen and nutrients to cells of body tissue.
-
Blood vessels are the ___.
fuel line and transportation network of the nutrients.
-
What are the combining forms of vessel?
vascul/o, angi/o
-
What vessel leads away from the heart and transports oxygenated blood?
arteries (red)
-
Where do veins deliver blood to?
The heart
-
What do the valves do?
Keep the blood flowing in the right direction, and makes sure they don't go backwards.
-
What vein delivers blood from the upper half of the body to the heart?
Superior vena cava
-
Deoxygenated blood first enters the heart from the vena cava into the ___.
Right atrium
-
Deoxygenated blood enters the pulmonary valve and goes to the ___ through the pulmonary artery.
left and right lungs
-
Where does gas exchange occur?
The lungs
-
After the blood has been oxygenated, what veins does it enter to get to the heart?
Pulmonary veins
-
What atrium does the oxygenated blood go to after it's return from the lungs?
The left atrium
-
Blood exits the left atrium to go into the left ___ and exits the heart through the ___.
ventricle, aorta
-
Of the 3 blood vessels in the body, which of them has a valve and why?
The vein has a valve; it's sending deoxygenated blood to the heart, and the valve is there to make sure it doesn't go backwards.
-
What are the 2 phases of the heartbeat and what do they mean?
- Diastole: relaxation phase of the heartbeat
- Systole: contraction
-
The sphygmomanometer is an instrument that measures what?
People's blood pressure.
-
Where is the apex of the heart located?
The lower tip of the heart.
-
The arteriole is a ___.
small artery
-
Detail the journey of CO2 in the cardiac system.
Enters the heart via veins, and then goes to the lungs to be exhaled.
-
Where are the coronary arteries located?
Outside the heart; branch out from the aorta and covers the heart, carries oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle so that it can function.
-
The endocardium is the ___.
inner lining of the heart
-
The endothelium is the ___.
innermost lining of blood vessels
-
The myocardium is the ___.
muscular, middle layer of the heart
-
What is pulmonary circulation?
The flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart.
-
The pulse is the result of the ___.
beating of the heart felt through the walls of the arteries
-
What is the septum?
The wall dividing the two ventricles and atria.
-
What does systemic circulation refer to?
The flow of blood from the body tissue to the heart and back (the entire system).
-
What is the largest vein in the body?
The vena cava (superior and inferior)
-
What is a venule?
A small vein
-
aort/o
aorta
-
artery (2)
arteri/o, arter/o
-
yellowish plaque
ather/o
-
atrium
atri/o
-
heart (2 possible)
cardi/o, coron/o
-
cyan/o
blue
-
oxygen
ox/o
-
phleb/o
vein
-
chest (think what instrument is used to listen to your heart)
steth/o
-
sphygm/o
pulse
-
clot
thromb/o
-
What happens when blood stops moving?
It clots
-
valve (2)
valv/o, valvul/o
-
vessel (2)
vas/o, vascul/o
-
ventricle
ventricul/o
-
What is atherosclerosis, and break down the word.
Plaque (ather/o), stiffening, hardening (-sclerosis); The build up of plaque and fat creating a blockage.
-
What is a thrombotic occlussion?
Blockage caused by a clot.
-
Necrosis is ___.
tissue death
-
What is an infarction?
When blood supply to an organ or tissue is blocked; usually by a thrombus, causing local death of the tissue.
Tldr; blockage of blood supply
-
What are the symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS)?
- Unstable angina: chest pain that doesn't stop with rest; can lead to myocardial infarction
- Myocardial infarction: blockage of the coronary arteries; a heart attack, the blood stops flowing to the heart muscle and dies as a result.
-
What is an aneurysm?
Vessel is ruptured due to bloating (expansion).
-
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Blood clotting in deeper veins (legs, thighs).
-
What is HTN and what does it stand for?
Hypertension; high blood pressure.
-
What is PVD and what does it stand for?
Peripheral Vascular Disease; disease outside (peripheral) the heart.
-
What happens to the veins when somebody has varicose veins?
Their valves aren't working properly and end up making the veins bulge.
-
What is a coronary artery bypass graft, what happens during it?
Where a section of the vein from a leg, or the chest is removed and a coronary artery is attached to bypass an area of blockage.
-
What is a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)?
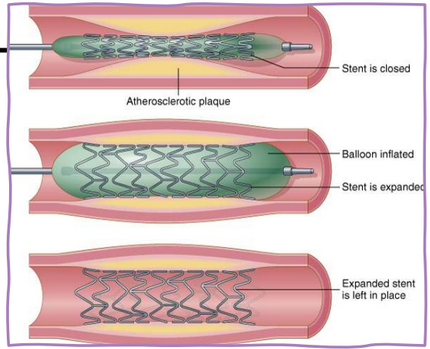
The placement of a stent to dilate and open a blocked vessel.
-
isch/o
to hold back
-
myx/o
mucus
-
muscle
my/o
-
rhythm
rrhythm/o
-
-constriction
narrowing
-
-lysis (think of hydrolysis, and what happens there)
breakdown, separation, loosening
-
suffix for enlargement
-megaly
-
-stenosis
tightening, structure
-
prefix for slow
-brady
-
de-
lack of, down, less, removal of
-
dys-
bad, painful, difficult
-
What is the term for paralysis of the heart.
cardi/o/plegia
cardi/o (the heart), -plegia (paralysis)
-
What is the term for cutting a vein?
phleb/o/tomy
phleb/o (vein), -tomy (to cut, make an incision)
-
What is the singular form of atrium?
atria
-um --> -a
-
The procedure where a thin tube is inserted into the heart and is used to diagnose and treat heart conditions is called?
Cardiac Catheterization
-
What is the procedure that involves the recording of the vessels of the heart?
Coronary Angiogram
Coronary - heart
Angi/o (vessels), -gram (record, recording of)
-
What does pericardiocentesis mean and what occurs in this procedure?
Pericardi/o (the pericardium), -centesis (a puncture, perforation, usually to remove fluid)
Puncturing the pericardium to remove fluid
-
What procedure involves dilating a vessel (stent)?
angioplasty
-
What is the difference between atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis - build of plaque, fats and other materials along the arterial walls and can block blood flow.
Arteriosclerosis - a general term for changes to the arterial walls (hardening, or stiffening that can restrict blood flow).

