-
benzothiadiazine
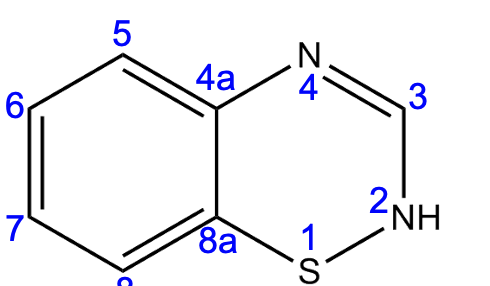
What heterocycle is this?
-
a
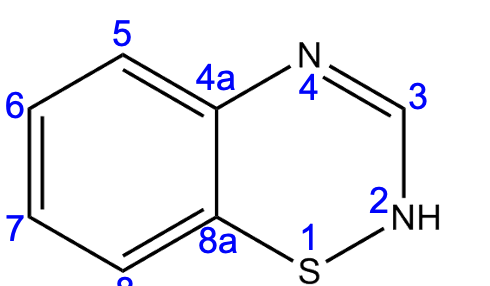
An alkyl placed at position ____ will increase lipophilicity and duration of action.
a) position 2
b) position 3
c) position 3-4
d) position 6
e) position 7
-
b
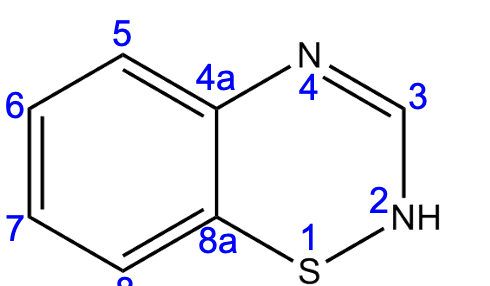
A lipophilic group placed at position ______ will increase potency.
a) position 2
b) position 3
c) position 3-4
d) position 6
e) position 7
-
c
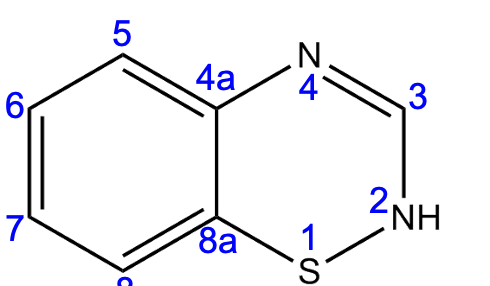
Saturation at position _____ will increase activity 10x.
a) position 2
b) position 3
c) position 3-4
d) position 6
e) position 7
-
d
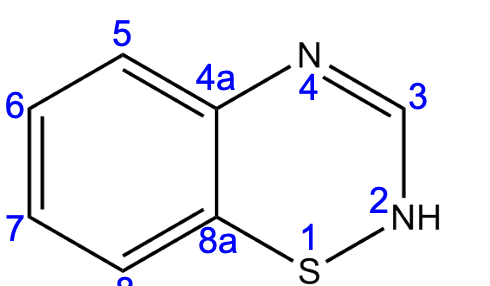
The electron-withdrawing group must be at position ______.
a) position 2
b) position 3
c) position 3-4
d) position 6
e) position 7
-
e
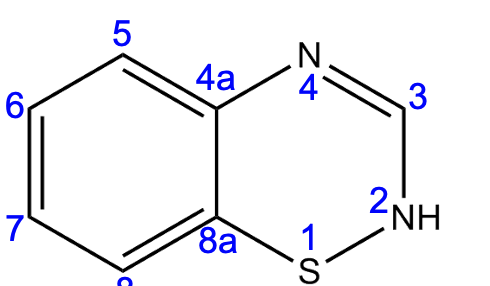
Position ____ increases activity but leads to hypersensitivity.
a) position 2
b) position 3
c) position 3-4
d) position 6
e) position 7
-
chlorobenzensulfonamide
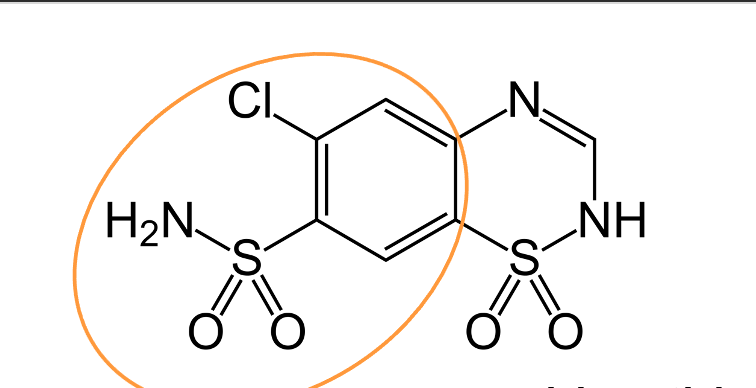
What is the highlighted structure?
-
3-4; saturated bond= increased activity
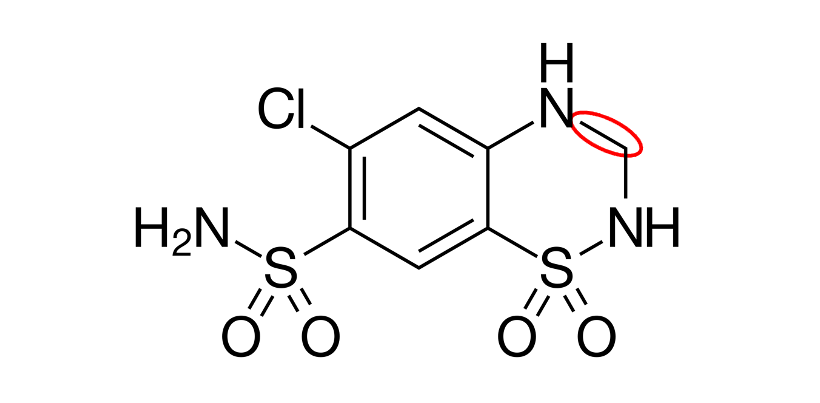
This is HCTZ. What is the position of the red circle? What does this change do to the structure?
-
phthalimide ring
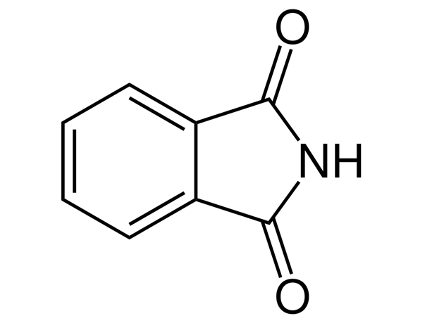
What structure is this?
-
phenoxy; acts as electron-withdrawing group
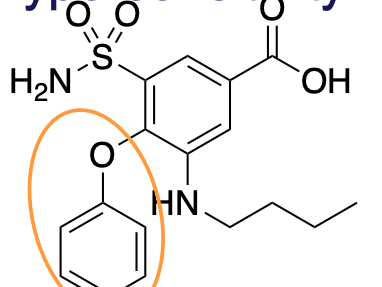
What is this group?
What does this addition do?
-
benzensulfonamide
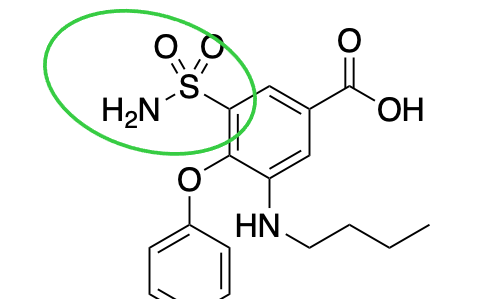
What is the name of this group?
-
butyl amine; increases lipophilicity; assists hepatic metabolism
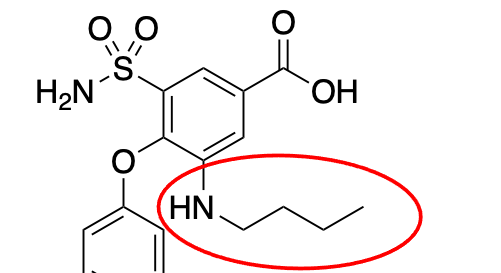
What is the name of this group?
What does it do?
-
pyridine
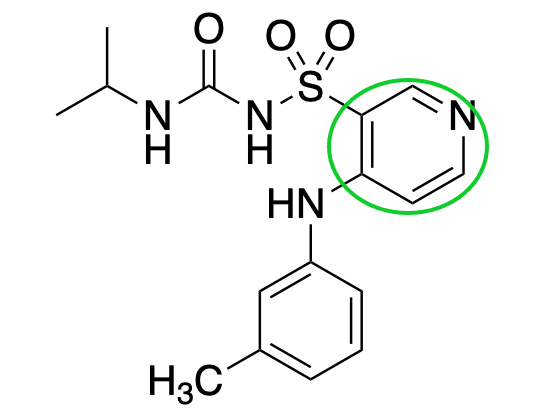
What is the name of this group?
-
aniline
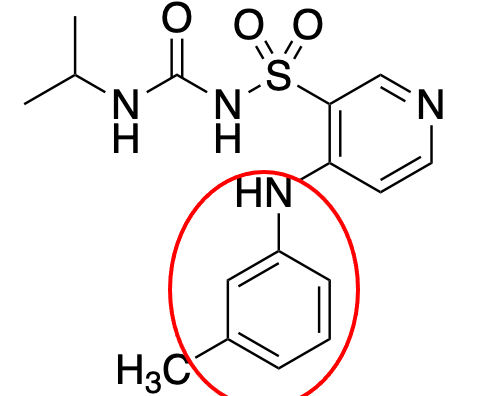
What is the name of this group?
-
sulfonylurea
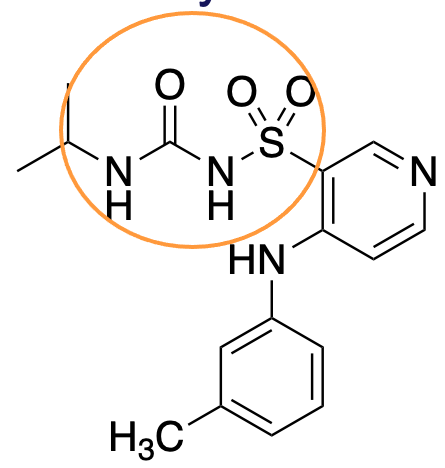
What is the name of this group?
-
chlorothiazide, HCTZ, chlorthalidone, indapamide, furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide
Which drugs have a sulfonamide in their structures? (7)
-
irreversible inhibitor that covalently binds Na/K/Cl cotransporter, unsaturated lactone nucleophile that reacts with sulfhydryl groups of cysteine receptor; phenoxyacetic acid;
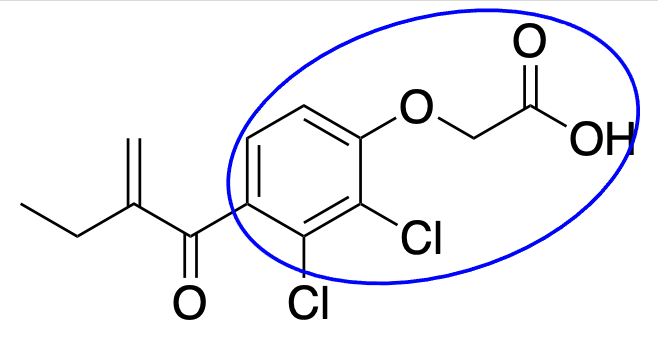
This is Ethacrynic acid.
What is unique about its MOA?
What is the name of this group?
-
antagonist for aldosterone; spironolactone, aldosterone
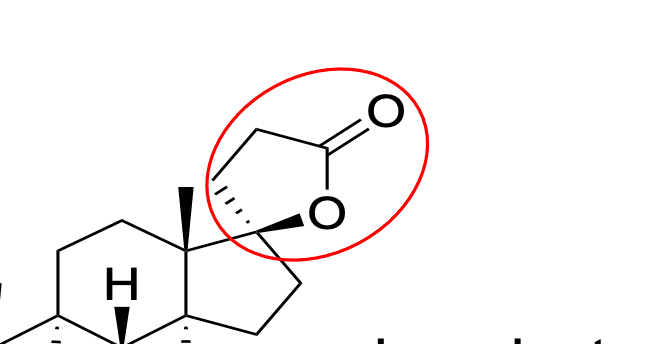
What does this structure do? What drugs is it found in?
-
triamterene
Which drug contains 3 aromatic rings that are highly aminated?
-
the open ring and cl- group
Why is Amiloride 100x more potent than Triamteren?
-
catechol ring
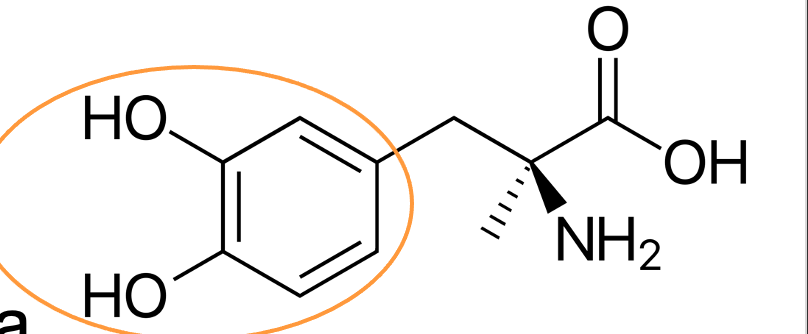
What is the highlighted structure?
-
dichlorobenzene; imidazole
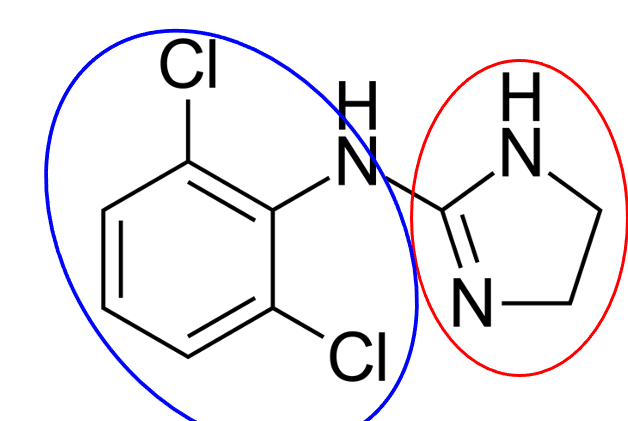
What is the blue structure?
What is the red structure?
-
piperazine
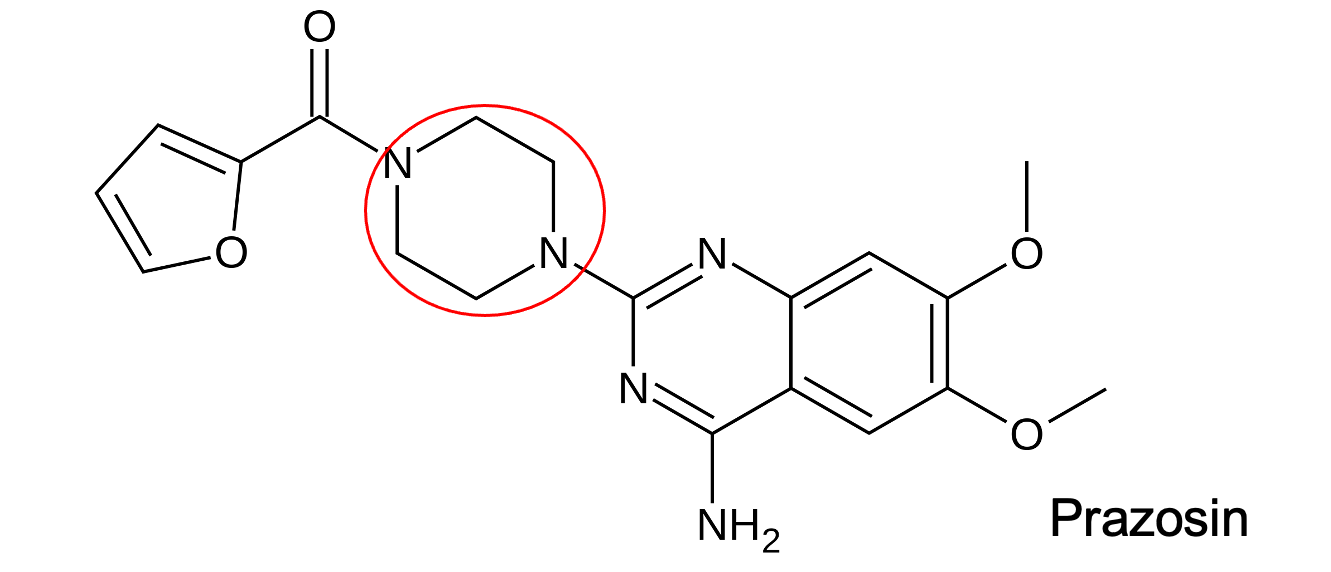
What is the red structure?
-
s
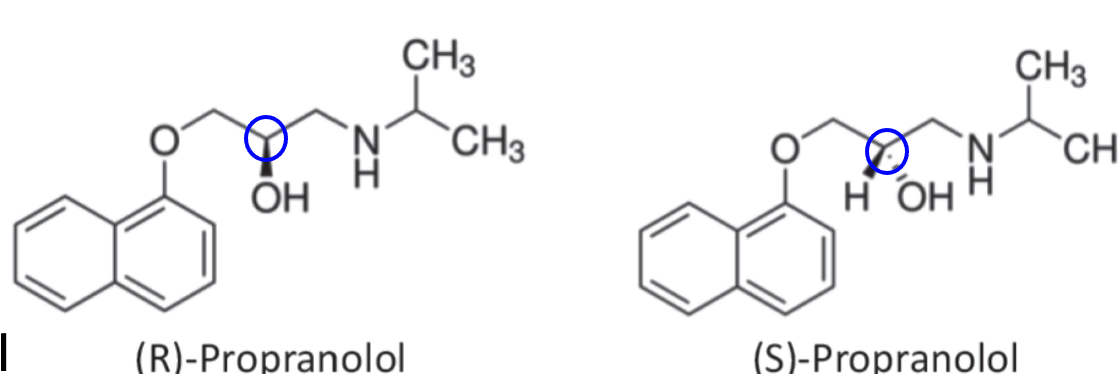
Which has more activity? S or R enantiomer?
-
a
Induces release of NO from the drug.
a) nitroprusside
b) hydralazine
-
b
Induces release of NO from the endothelium.
a) nitroprusside
b) hydralazine
-
d
Which activates the dopamine receptors?
a) minoxidil
b) hydralazine
c) nitroprusside
d) fenoldopam
-
r-isomer
Which is more active?
R-isomer of Fendolopam
S-isomer of Fendolopam
-
sulfhydryl; enhances potency in ACE inhibition
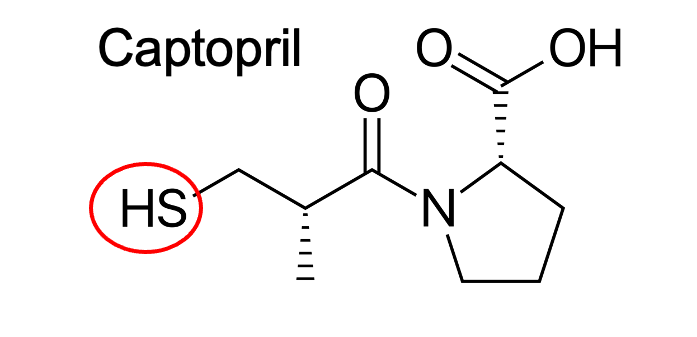
What is this red structure?
What does its addition do?
-
losartan
What was the first-marketed ARB?
-
carbon atom, position delta
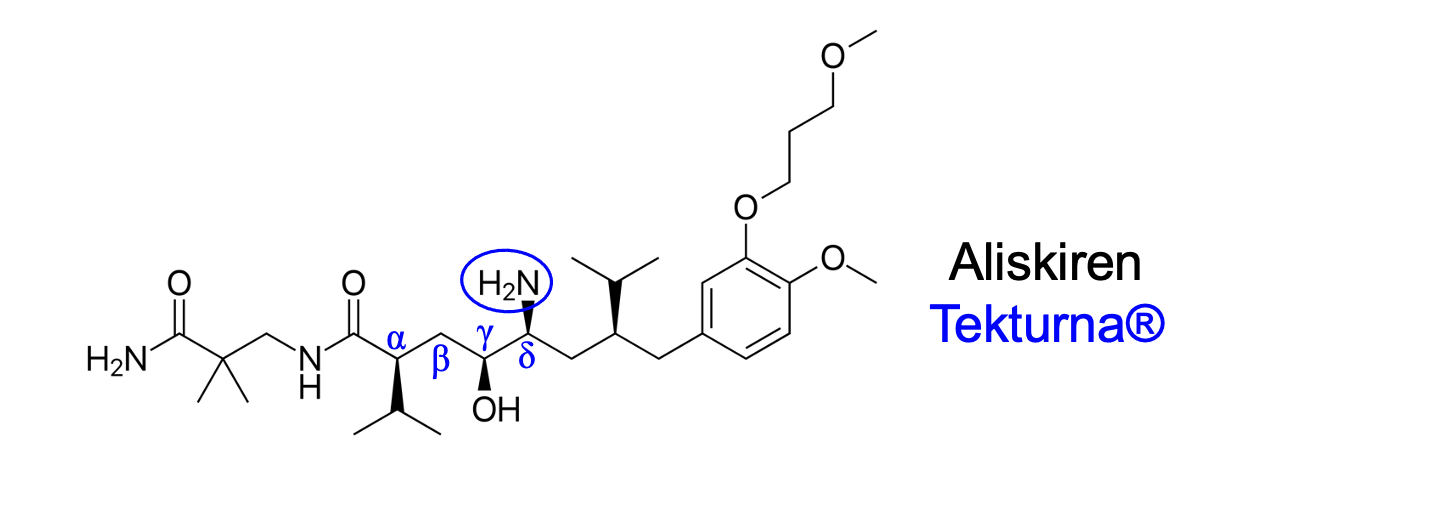
Where is the amine positioned?

