-
Vectors vs scalarVectors have both a magnitude and a direction Scalar quantities only have a magnitude
-
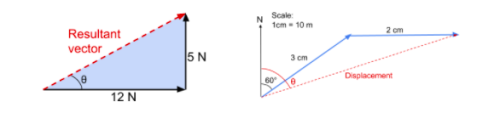
What can vector triangles determine?The resultant vector can determine whether the forces are balanced (with a resultant force or not)
-
vector diagrams
-
Resolving vectors
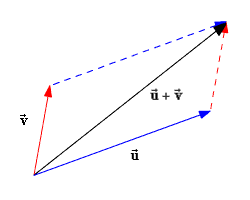 Split a vector into its horizontal and vertical components can be resolved using trigonometry or parallelogram method
Split a vector into its horizontal and vertical components can be resolved using trigonometry or parallelogram method -
What is a moment?The moment of a force about a point is the product of the force and the distance from its line of action to the point
-
Moment equationMoment (Nm) = Force (N) x Perpendicular distance (m)
-
When an object is in equilibriumThe moments on it about a point are balanced Total clockwise moment = total anticlockwise moment
-
What is a couple?
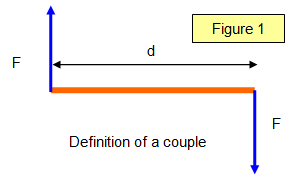 A pair of equal and opposite parallel forces acting on the same body that do not act in the same line
A pair of equal and opposite parallel forces acting on the same body that do not act in the same line -
moment of a couple equationMoment of a couple (Nm) = Force(N) x Perpendicular Distance Between Lines of Action (m)
-
Centre of massWhere the mass of an object can be considered to be concentrated
-
The line of actionacts from the centre of mass and shows how gravity is acting upon the object
-
How can the centre of mass be found?By suspending an object by a pin and then using a plum line to draw on the line of action-where they cross is the centre of mass
-
When will an object topple?If he line of action falls outside of the width of the base then the object will topple
-
Newton's first lawThe velocity of an object will not change unless a resultant force acts upon it
-
Newton's second lawF = ma force in N equals mass in kg times the acceleration in ms^-2
-
Newton's third lawEvery force has an equal and opposite force
-
In projectile motion...The horizontal and vertical components are treated seperately. Acceleration is due to gravity, hence only affects the vertical component and is positive if acting with the object and vegative if against it.
-
Frictiona force that oppoes motion when moving on a soliid
-
Draga force that opposes motion in a fluid, it usually increases with speed
-
Liftan upward force created on an object as it moves through a fluid due to the shape of an object
-
Terminal Velocityhappens when frictional forces equal the driving force, causing equilibrium and zero acceleration
-
principle of momentsprinciple of moments states that for a body to be in rotational equilibrium the sum of clockwise moments at any point must be equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments about that same point
-
terminal velocity for humans~ 240-290km/h
-
In a closed systemmomentum is conserved meaning that the product of velocity and mass is the same before and after occurs in both collisions and explosions
-
momentum equationp = mv
-
momentum is conservedp1 =p2 m1v1 = m2v2
-
inelastic collsion
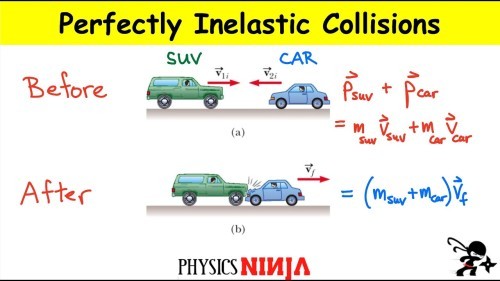 kinetic energy is not conserved -> so we can work out the change in kinetic energy and hence how much energy is dissipated in other forms change in energy = final kinetic energy - initial kinetic energy
kinetic energy is not conserved -> so we can work out the change in kinetic energy and hence how much energy is dissipated in other forms change in energy = final kinetic energy - initial kinetic energy -
Elastic collisionkinetic energy is conversed Final kinetic energy = Initial kinetic energy
-
Impulse equation
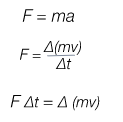
-
ImpulseThe change in momentum The produc of force and time
-
The area under a force-time graphis impulse
-
Power, work done and efficiency equations
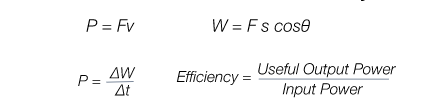
-
When is work donewhen a force is applied across a distance
-
What is one watt equal toOne joule per second
-
Density equation
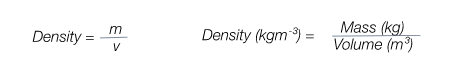
-
What is density?Density is the mass of a material per unit volume
-
Conservation of momentum
Total momentum before = total after
-

neutron will rebound / have velocity / momentum to the left
momentum transferred to the uranium will be greater
velocity of uranium will be greater

