-
Atomic absorption
An electron can jump from a lower-energy to a higher-energy orbit by absorbing a photon of light of precisely the right frequency to match the energy difference between the orbits (E = hf).
-
Atomic emission
When an electron falls from a higher-energy level to a lower-energy level, a photon of light is emitted with an energy equal to the energy difference between the two orbits.
-
Bohr model
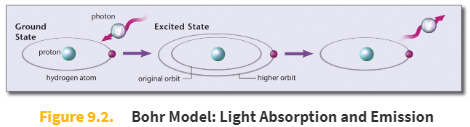
The Bohr model states that electron energy levels are stable and discrete, corresponding to specific orbits.
-
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy (with function)
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms.
-
UV–Vis spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
-
Absorption spectrum of the atmosphere
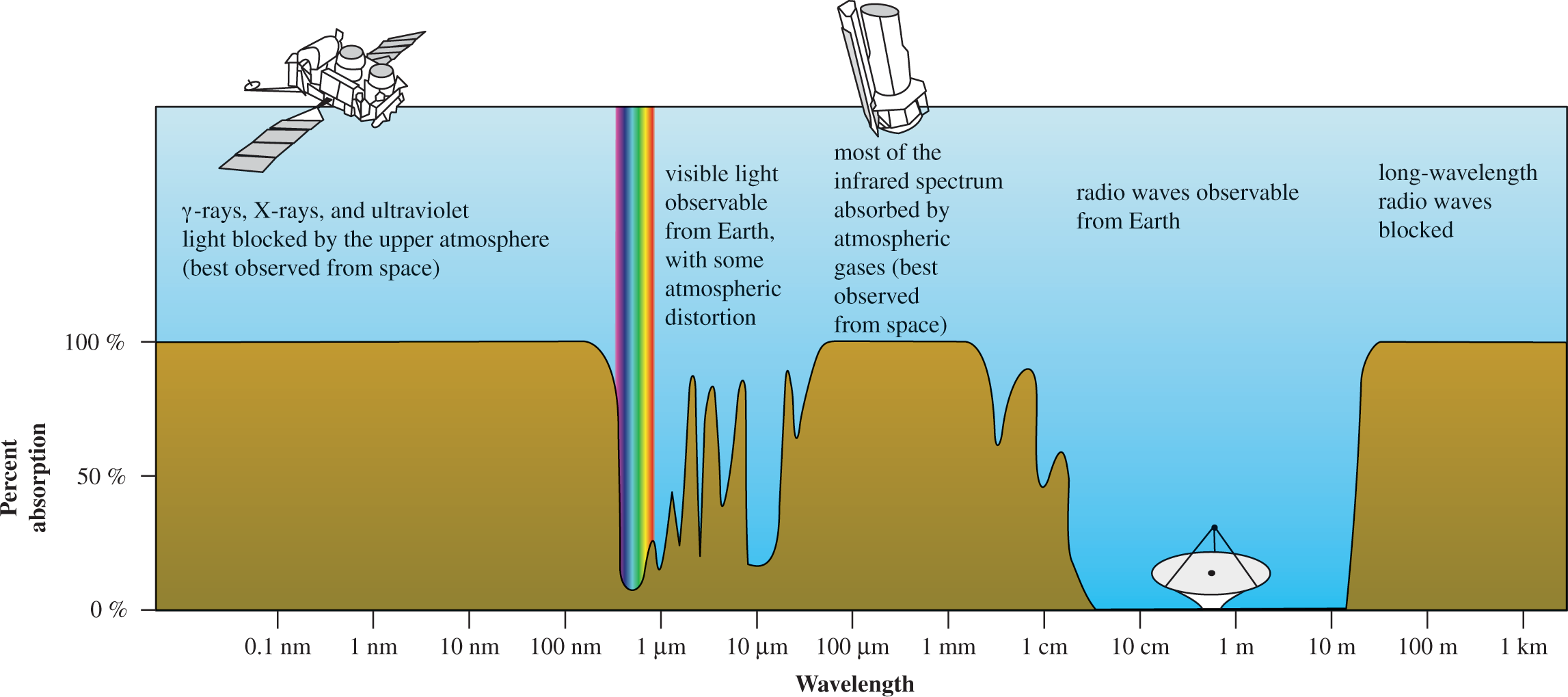
-
Phenolphthalein is _____ in basic solutions but _____ in acidic solutions.
pink
clear
-
Indicators often have _____ or _____, as this permits the absorption of light from photons in the visible range.
conjugated double bonds
aromatic ring systems
-
Fluorescence
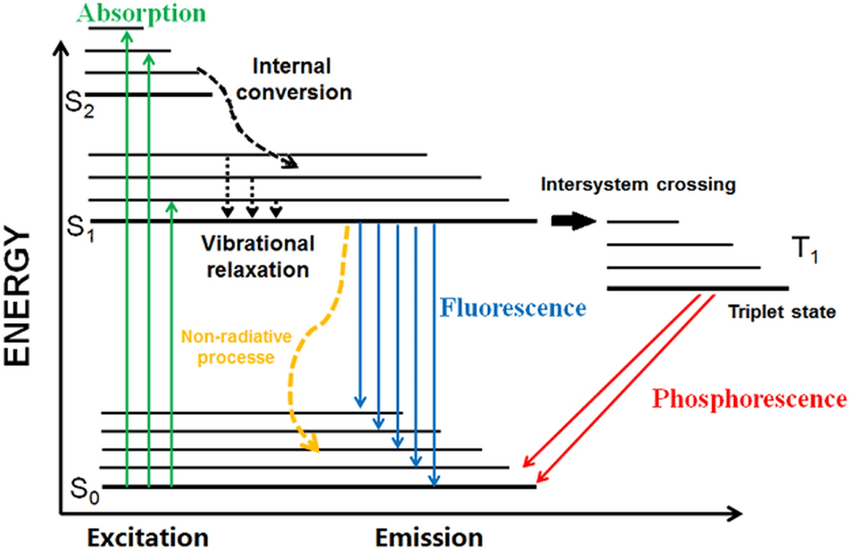
If one excites a fluorescent substance (such as a ruby, an emerald, or the phosphors found in fluorescent lights) with ultraviolet radiation, it will begin to glow with visible light.
-
In most cases, photons emitted by fluorescence are _____ than the exciting wavelength.
lower in energy
-
What determines the absorption spectrum of a material?
The energy differences between ground-state electrons and higher-level electron orbits determine the frequencies of light a particular material absorbs (its absorption spectrum).

