-
Plane-polarized (or linearly polarized) light
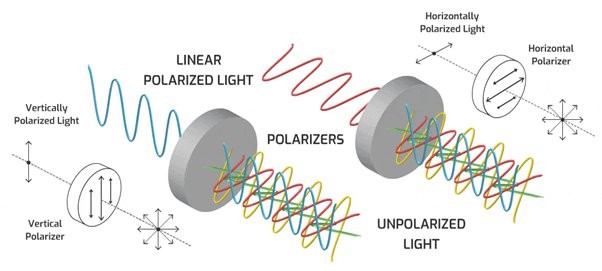
Plane-polarized (or linearly polarized) light is light in which the electric fields of all the waves are oriented in the same direction (that is, their electric field vectors are parallel).
-
Aside from their electric fields being parallel, the _____ in plane-polarized light are also parallel. The plane of the _____ identifies the plane of polarization due to convention.
magnetic fields
electric field
-
Unpolarized light has _____ orientation of its electric field vectors.
random
-
Specific rotation
The change in orientation of monochromatic plane-polarized light as the light passes through a sample of a chiral compound in solution.
-
The optical activity of a compound, due to the presence of _____, causes plane-polarized light to rotate clockwise or counterclockwise by a given number of degrees relative to its _____.
chiral centers
concentration
-
Amyloidosis is diagnosed by ...
... biopsy and staining the tissue with Congo red stain; a bright “apple green” color is seen under plane-polarized light.
-
Gout
The precipitation of monosodium urate crystals into tissues throughout the body (fucking wherever, apparently)
-
Pseudogout
The precipitation of calcium pyrophosphate crystals
-
Amyloidosis
The buildup of misfolded amyloid proteins in the heart, kidneys, liver, or other organs.
-
Gout and pseudogout are differentiated by their _____.
precipitate colors under polarized light
-
Monosodium urate appears _____ when the axis of the crystal is aligned with a polarizer.
yellow
-
calcium pyrophosphate appears _____ when the axis of the crystal is aligned with a polarizer.
blue
-
MNEMONIC: Monosodium urate is _____, just like _____.
yellow
urine
-
Polarizers
There are filters called polarizers which allow only light with an electric field pointing in a particular direction to pass through.
-
If one passes a beam of light through a polarizer, it will only let through that portion of the light _____.
parallel to the axis of the polarizer
-
When two polarizers are placed perpendicular to each other, ...
... no light gets through at all.
-
Circular polarization
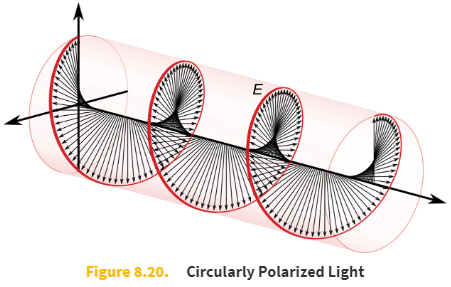
Circular polarization is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave. This results in a helical orientation in the propagating wave.

