-
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to the spreading out of light as it passes through a narrow opening or around an obstacle.
-
Diffraction and interference are significant evidence for the _____.
wave theory of light
-
When light passes through a narrow opening (an opening with a size that is on the order of _____), the light waves seem to _____.
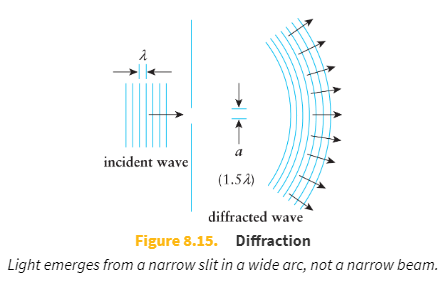
light wavelengths
spread out (diffract)
-
As a slit is narrowed, the light passing through the slit _____.
spreads out more
-
Location of dark fringes (minima) in a single slit experiment equation
a sin θ = nλ
a is the width of the slit
θ is the angle between the line drawn from the center of the lens to the dark fringe and the axis of the lens
n is an integer indicating the number of the fringe
λ is the wavelength of the incident wave
Note that bright fringes are halfway between dark fringes.
-
If a lens is placed between a narrow slit and a screen, a pattern is observed consisting of a _____ central fringe with _____.
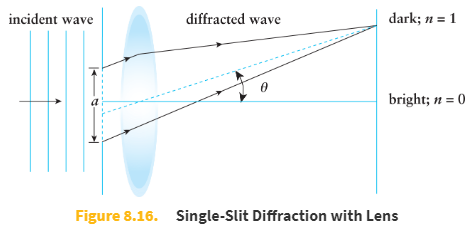
bright
alternating dark and bright fringes on each side.
-
Interference (light)
When waves interact with each other, the displacements of the waves add together in a process called interference.
-
Who performed the double slit experiment?
Thomas Young
-
What did the double split experiment show?
That light behaves like a wave
Note: this did not prove that it is a wave (there is a difference)
-
When monochromatic light passes through two parallel slits, an _____ is observed on a screen placed behind the slits. Regions of _____ between the two light waves appear as bright fringes (maxima) on the screen. Conversely, in regions where the light waves interfere _____, dark fringes (minima) appear.
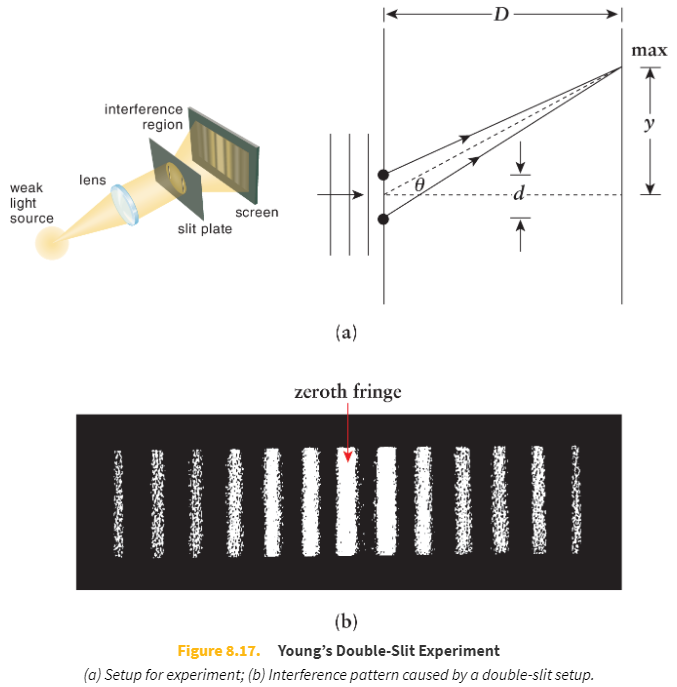
interference pattern
constructive interference
destructively
-
Huygens-Fresnel principle
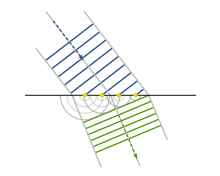
Every point on a wavefront is itself the source of spherical wavelets, and the secondary wavelets emanating from different points mutually interfere.
-
What principle does the single-slit experiment rely on?
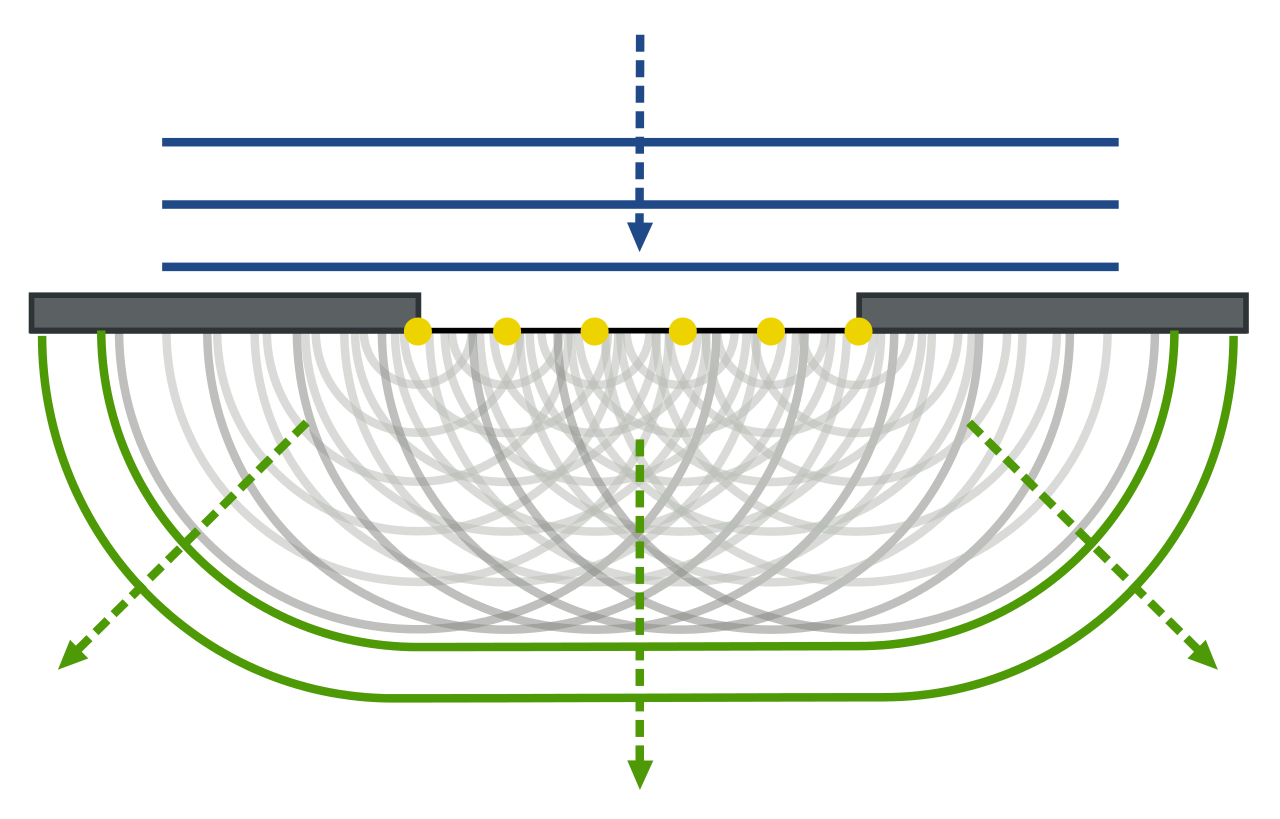
Huygens-Fresnel principle
-
Single slit and lens diffraction pattern
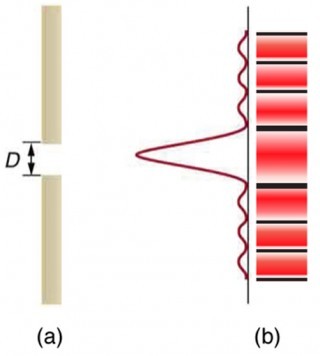
-
Double slit interference pattern
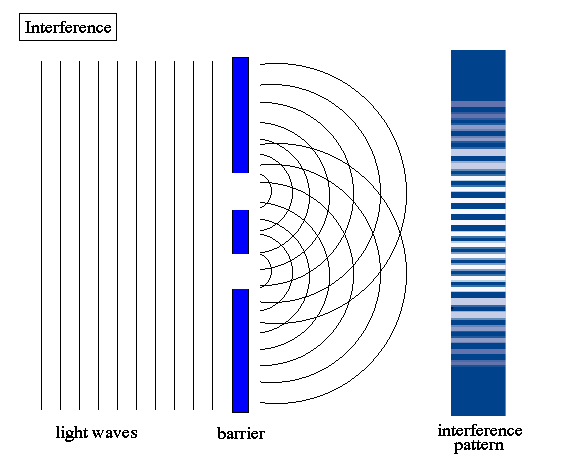
-
Location of minima in a double slit experiment equation
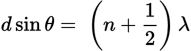
d is the distance between the two slits
θ is the angle between the line drawn from the midpoint between the two slits to the dark fringe and the normal
n is an integer indicating the number of the fringe
λ is the wavelength of the incident wave
-
IMPORTANT: the dingle and double slit experiments use _____ light.
monochromatic
-
Diffraction gratings
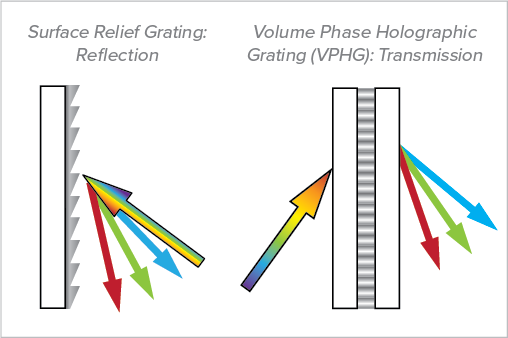
Diffraction gratings consist of multiple slits (or ramps) arranged in patterns
-
Thin films may also cause interference patterns because light waves _____ interfere with light waves _____.
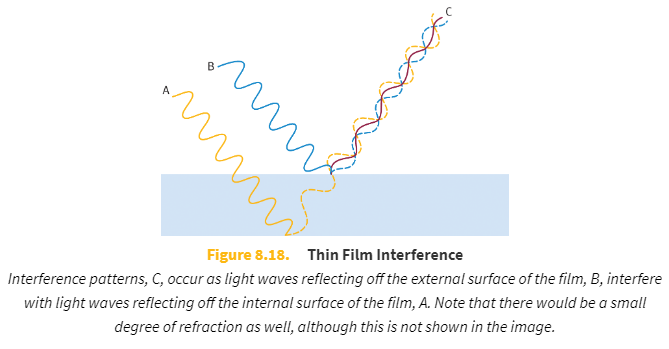
reflecting off the external surface of the film
reflecting off the internal surface of the film
-
The interference in a thin film is not between _____ rays, but between _____ rays.
diffracted
reflected
-
X-ray crystallography (general scope)
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information.
-
X-ray crystallographic produce _____.
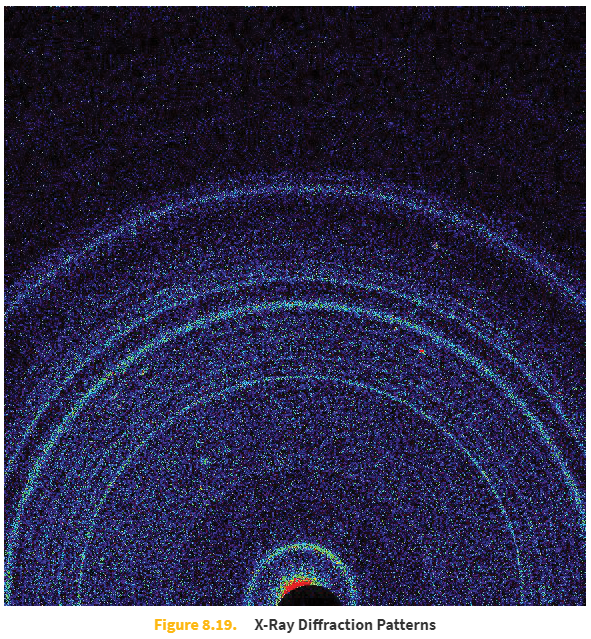
complex two dimensional images
-
X-ray crystallography is commonly used to analyze the structure of _____.
proteins
-
What would be the diffraction pattern of a single slit without a lens?
The light just spreads out.
-
When light is diffracted through a reflection-type grating, _____ is diffracted the farthest away from the normal
red light
-
When light is diffracted through a transmission-type grating, _____ is diffracted the most.
red light
Remember from 376k: mλ = dsinθ -> as wavelength increases, the angle must also increase
-
Equation for the location of light through a transmission-type diffraction grating
mλ = dsinθ
m is an integer describing the order of the light
λ is the wavelength of the desired light
d is the distance between the slits
θ is the angle at which the light comes off of the grating
-
Equation for the location of light through a reflection-type diffraction grating
mλ = d * (sinα ± sinβ)
m is an integer describing the order of the light
λ is the wavelength of the desired light
α is the angle of the incident light
β is the angle of the resulting light
-
When light is dispersed through a prism, _____ is dispersed the most.
violet light

