-
Electromagnetic spectrum
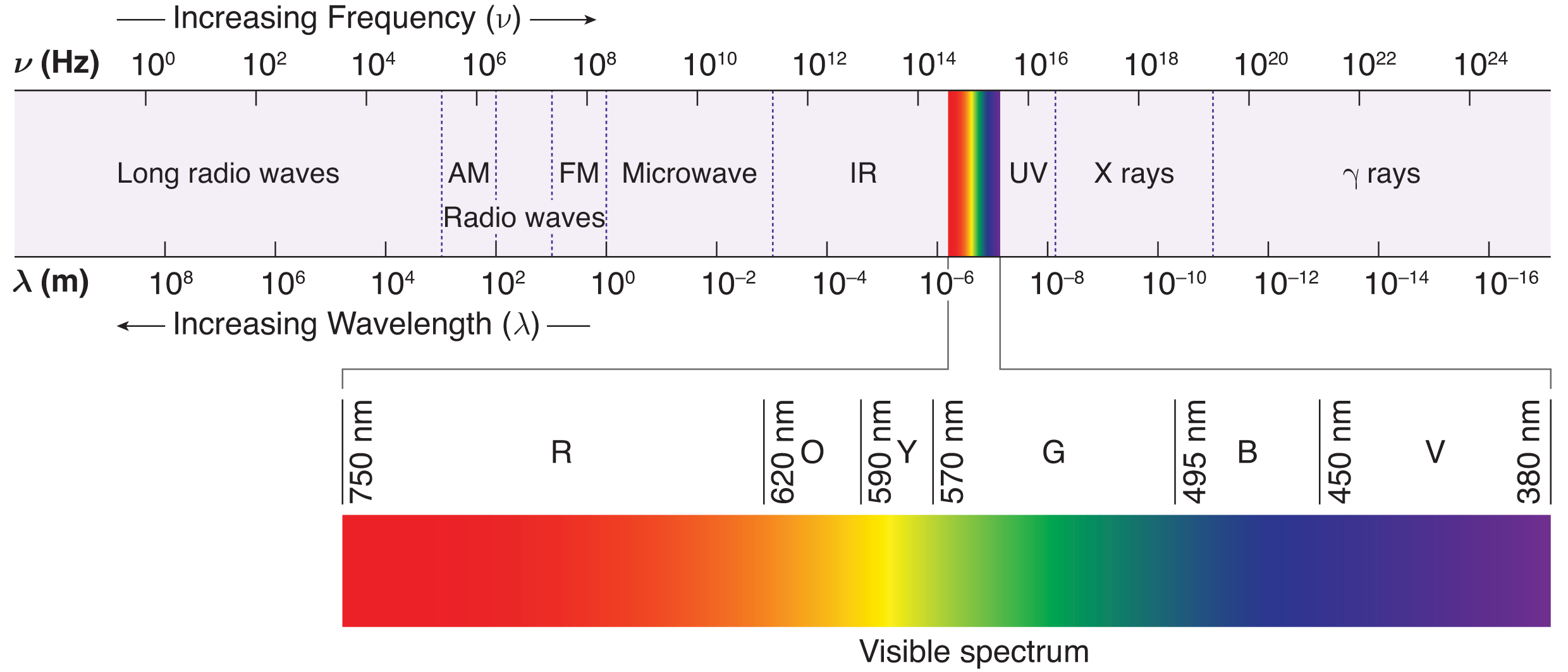
The range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
-
List the categories of light from low energy to high energy
radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
-
Electromagnetic waves are _____ waves because the oscillating electric and magnetic field vectors are _____ to the direction of propagation
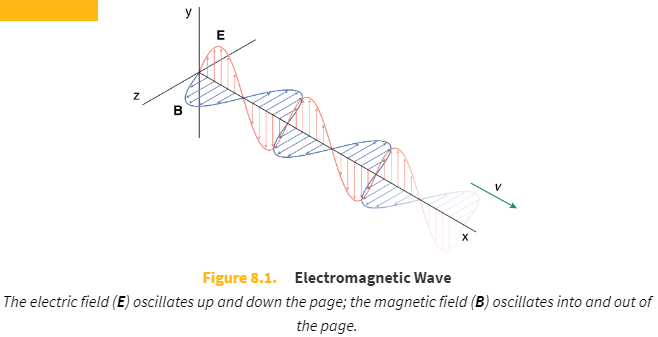
transverse
perpendicular
-
With electric and magnetic fields, each oscillating field causes oscillations in the other field completely independent of _____. This means that electromagnetic waves can _____.
matter
travel through a vacuum
-
Electromagnetic waves
Classically, electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves, which are synchronized oscillations of electric and magnetic fields.
-
The electric field and the magnetic field are _____ to each other.
perpendicular
Note: this is true in In homogeneous, isotropic media
-
Wavelength of radio waves
109–1 m
-
Wavelength of microwaves
1 m–1 mm
-
Wavelength of infrared
1 mm–700 nm
-
Wavelength of visible light
700–400 nm
(more accurately, about 380 to about 750 nanometers)
-
Wavelength of ultraviolet
400–50 nm
-
Wavelength of x-rays
50–10–2 nm
-
Wavelength of gamma rays
less than 10–2 nm
-
In a vacuum, all electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed, called the _____.
speed of light
-
Speed of light in a vacuum
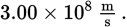
-
To a first approximation—and for the purposes of all MCAT-related equations—electromagnetic waves travel in air at _____.
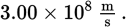
-
Electromagnetic wave equation
c = fλ
c is the speed of light in a vacuum and, to a first approximation, also in air
f is the frequency
λ is the wavelength
-
The only part of the spectrum that is perceived as light by the human eye is the _____.
visible region
-
Violet wavelength
~400 nm
-
Red wavelength
~700 nm
-
Light that contains all the colors in equal intensity is perceived as _____.
white
-
The color of an object that does not emit its own light is dependent on _____.
the color of light that it reflects
-
Blackbody
The term blackbody refers to an ideal absorber of all wavelengths of light, which would appear completely black if it were at a lower temperature than its surroundings.

