-
Capacitors
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other.
-
Perhaps the most important capacitor you’ll encounter in the clinics is the _____.
defibrillator
-
The MCAT focuses on a particular type of capacitor called a _____.
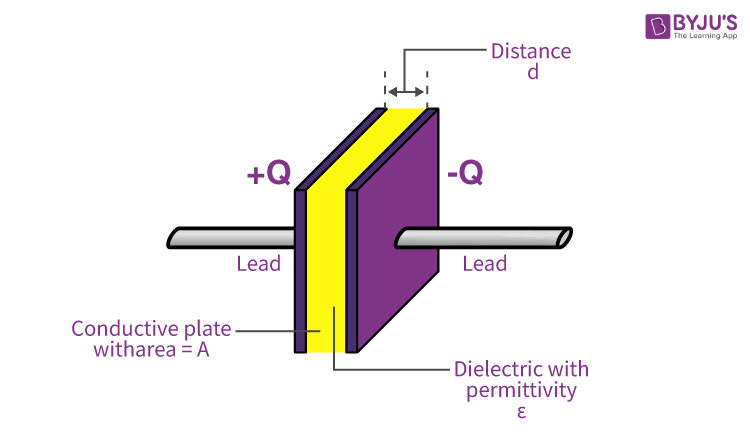
parallel plate capacitor
-
When two electrically neutral metal plates are connected to a voltage source, positive charge builds up on the plate connected to the _____, and negative charge builds up on the plate connected to the _____.
positive (higher potential) terminal
negative (lower potential) terminal
-
capacitance
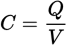
The capacitance of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of the charge stored on one plate to the potential difference (voltage) across the capacitor.
-
SI unit for capacitance
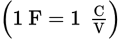
farad
-
One farad is a _____, relatively speaking. Capacitances are usually given in _____ or _____.
very large capacitance
microfarads (1 μF = 1 × 10–6 F) or picofarads (1 pF = 1 × 10–12 F)
-
Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor equation
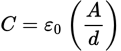
ε0 is the permittivity of free space
A is the area of overlap of the two plates
d is the separation of the two plates
-
The separation of charges sets up a _____ between the plates with parallel field vectors.
uniform electric field
-
Electric field in a parallel plate capacitor equation
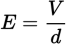
The direction of the electric field at any point between the plates is from the positive plate toward the negative plate.
-
The function of a capacitor is ...
... to store an amount of energy in the form of charge separation at a particular voltage.
-
Potential energy stored in a capacitor equation
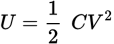
-
Dielectric material
The term dielectric material is just another way of saying insulation.
-
Dielectric constant
When a dielectric material, such as air, glass, plastic, ceramic, or certain metal oxides, is introduced between the plates of a capacitor, it increases the capacitance by a factor called the dielectric constant (κ).
-
A vacuum has a dielectric constant of _____, by definition.
1
-
Capacitance due to a dielectric material equation
C′ = κC
C′ is the new capacitance with the dielectric present
C is the original capacitance
-
MNEMONIC: Incorporating the dielectric constant into Equation 6.14 reveals that capacitors are _____ with charge.
CAκεd with charge (C = Aκε0/d)
-
A dielectric material can never _____; thus, κ can never be _____.
decrease the capacitance
less than 1
-
When a dielectric material is placed in an isolated, the ...
... voltage across the capacitor decreases.
-
When a dielectric material is placed in a charged capacitor within a circuit—that is, still connected to a voltage source—the ...
... charge on the capacitor increases.
-
The stored energy in a capacitor is only useful if it is allowed to _____.
discharge
-
Stored charge in a capacitor can be released from the plates either by _____ or _____.
discharging across the plates
through some conductive material with which the plates are in contact
-
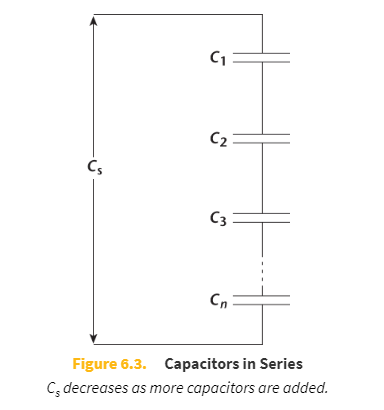
Capacitors can be arranged in _____ and in _____.
series
parallel
-
Capacitors in series
-
Capacitance of capacitors in series equation
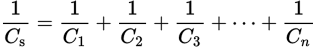
-
Capacitance of capacitors in parallel equation
Cp = C1 + C2 + C3 + ⋯ + Cn
-
Cs _____ as more capacitors are added, while Cp _____ as more capacitors are added
decreases
increases
-
The voltage across each parallel capacitor is _____.
the same
-
The total voltage of capacitors in series is _____.
the sum of the individual voltages

