-
Resistance
Resistance is the opposition within any material to the movement and flow of charge.
-
Materials that offer almost no resistance are called _____, and those materials that offer very high resistance are called _____. Conductive materials that offer amounts of resistance between these two extremes are called _____.
conductors
insulators
resistors
-
The resistance of a resistor is dependent upon certain characteristics of the resistor, including _____, _____, _____, and _____.
resistivity, length, cross-sectional area, and temperature
-
Resistance equation
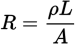
ρ is the resistivity
L is the length of the resistor
A is its cross-sectional area
-
resistivity
The number that characterizes the intrinsic resistance to current flow in a material is called the resistivity (ρ).
-
SI unit of resistivity
ohm–meter (Ω · m)
-
The resistance of a resistor is directly proportional to its _____. This factor scales _____: if a resistor doubles its length, it will _____its resistance.
length
linearly
double
-
Conduction pathways
The number of pathways through a resistor
-
The equation for resistance demonstrates an _____ proportionality between resistance and the cross-sectional area of the resistor: if a resistor’s cross-sectional area is doubled, its resistance will be _____.
inverse
cut in half
-
Most conductors have greater resistance at _____ temperatures. A few materials do not follow this general rule, including _____.
higher
glass, pure silicon, and most semiconductors.
-
Why do resistors have a greater resistance at higher temperatures?
Increased thermal oscillation of the atoms in the conductive material, which produces a greater resistance to electron flow
-
Ohm's Law
V = IR
V is the voltage drop
I is the current
R is the magnitude of the resistance
-
Electrical resistance results in _____, which reflects a drop in _____.
an energy loss
electrical potential
-
SI unit of resistance
ohms (Ω)
-
For a given resistance, the magnitude of the current will be proportional to the ...
... magnitude of the emf (voltage) impressed upon the circuit
-
For a given magnitude of resistance, the voltage drop across the resistor will be proportional to the ...
... magnitude of the current.
-
As current moves through a set of resistors in a circuit, the voltage _____; the current (or sum of currents for a divided circuit) is _____.
drops some amount in each resistor
constant
-
No charge is gained or lost through a resistor; thus, if resistors are connected in series ...
... all of the current must pass through each resistor.
-
Conductive materials, such as copper wires, act as _____, causing a _____.
weak resistors
drop in electrical potential (voltage)
-
Even the very sources of emf, such as batteries, have some small but measurable amount of _____.
internal resistance
-
Internal resistance, rint.
Internal resistance refers to the opposition to the flow of current offered by the cells and batteries themselves resulting in the generation of heat.
-
Actual voltage supplied to a circuit (equation)
V = Ecell – irint
V is the voltage provided by the cell
Ecell is the emf of the cell
i is the current through the cell
rint is its internal resistance
-
If a cell is not actually driving any current, then the internal resistance is _____, and the voltage of the cell is _____. For cases when the current is not zero, the internal resistance is _____, and voltage will be _____.
zero, equal to its emf
not negligible, less than emf
-
_____ are the one major exception to the rules of internal resistance.
Superconductors.
When these elements and compounds are cooled to very low temperatures (usually well below 100 K, but the exact threshold varies by material), the resistivity of the material (ρ) completely dissipates, dropping to zero.
-
When a cell is discharging, it supplies _____ which flows from the _____ of the cell around the circuit to the _____.
current
positive, higher potential end
negative, lower potential end
-
Secondary batteries
A type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or primary battery, which is supplied fully charged and discarded after use.
-
When secondary batteries are being recharged, an external voltage is applied in such a way to drive current _____.
toward the positive end of the secondary battery
-
In electrochemical terms, a secondary battery acts as a _____ when it discharges and as an _____ when it recharges.
galvanic (voltaic) cell
electrolytic cell
-
Power
Power is measured as the ratio of work (energy expenditure) to time
-
Power equation
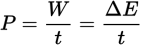
-
In electric circuits, energy is supplied by the cell that houses a _____, which when allowed to proceed (by the closing of a switch, for example), generates a _____. These electrons, which have _____, convert that energy into _____ as they move around the circuit, driven by the _____ of the cell.
spontaneous oxidation–reduction reaction
flow of electrons
electrical potential energy
kinetic energy
emf
-
Resistors convert the kinetic energy of electrons to _____.
some other form, depending on the particular configuration of the resistor (it's usually heat or light on the MCAT)
-
Power of a resistor equation
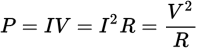
I is the current through the resistor
V is the voltage drop across the resistor
R is the resistance of the resistor
-
Resistors can be connected into a circuit in one of two ways: either in _____ or in _____.
series
parallel
-
Resistors in series
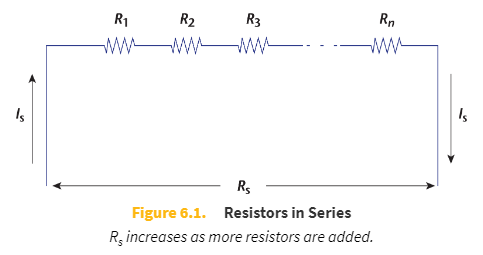
All current must pass sequentially through each resistor connected in a linear arrangement
-
Resistors in parallel
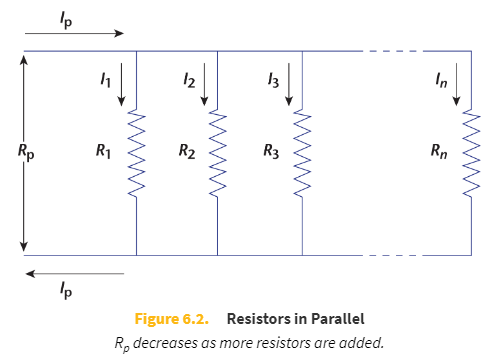
Current will divide to pass through resistors separately.
-
For resistors in series, the voltage drops are _____.
additive
-
Equation for the voltage drop of resistors in series
Vs = V1 + V2 + V3 + ⋯ + Vn
-
The resistances of resistors in series are _____
additive
-
Equation for the resistance of resistors in series
Rs = R1 + R2 + R3 + ⋯ + Rn
-
Equivalent or resultant resistance
The set of resistors wired in series can be treated as a single resistor with a resistance equal to the sum of the individual resistances, termed the equivalent or resultant resistance.
-
Equation for the current through resistors in series
I = I1 = I2 = I3 = ⋯ = In
-
Rs will _____ as more resistors are added, while Rp will _____ as more resistors are added
always increase
always decrease
-
Equation for the voltage drop of resistors in parallel
Vp = V1 = V2 = V3 = ⋯ = Vn
-
Remember Kirchhoff’s loop rule: if every resistor is in parallel, then the voltage drop across _____ must be equal to the voltage of the source.
each pathway alone
-
Equation for the resistance of resistors in parallel
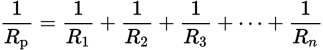
-
Equation for the current through resistors in parallel
I = I1 + I2 + I3 + ⋯ + In
-
The current will be largest through the pathways with the _____. In fact, there is an _____ between the portion of the current that travels through a particular pathway and the resistance offered by that pathway.
lowest resistance
inverse relationship
-
The configuration of resistors in parallel allows for a greater _____, and the effect of connecting resistors in parallel is a _____ in the equivalent resistance.
total number of conduction paths
reduction
-
If a circuit divides into two branches and one branch has twice the resistance of the other, the one with twice the resistance will have _____ the magnitude of current compared to the other.
half
-
When n identical resistors are wired in parallel, the total resistance is given by _____.
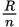
-
When n identical resistors are wired in parallel, the current at each resistor is given by _____.
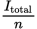
-
When approaching circuit problems, the first things you need to find are the _____.
total (circuit) values

