-
Current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space between two points at different electrical potentials.
-
Because of historical conventions, current is considered the flow of _____—even though only _____ are actually moving.
positive charge
negative charges
-
Conductivity can be divided into two categories: _____, as seen in _____ and _____, or _____, as seen in _____.
metallic conductivity, solid metals and the molten forms of some salts
electrolytic conductivity, solutions
-
Conductance
Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance
-
SI unit(s) for conductance
siemens (S) or sometimes siemens per meter (S/m)
-
Electrical conductors
Some materials allow free flow of electric charge within them; these materials are called electrical conductors.
-
Metal atoms can _____ one or more of their outer electrons, which are then free to _____.
easily lose
move around in the larger collection of metal atoms
-
Most metals are good _____.
electrical and thermal conductors
-
Metallic bonding
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions (cations).
-
The metallic bond has often been visualized as a ...
... sea of electrons flowing over and past a rigid lattice of metal cations.
Note: while this model is generally appropriate for the MCAT, metallic bonding is more accurately described as an equal distribution of the charge density of free electrons across all of the neutral atoms within the metallic mass.
-
Metals are found on the _____ side of the periodic table.
left
-
While not substantially different from metallic conductivity, it is important to note that electrolytic conductivity depends on the _____.
strength of a solution
-
Distilled deionized water has such a low ion concentration that it may be considered an _____.
insulator
-
Conductivity in an electrolyte solution is measured by ...
Because _____ and conductivity are directly related, this method is often used to determine _____, such as _____.
... placing the solution as a resistor in a circuit and measuring changes in voltage across the solution.
concentration
ionic concentrations in solutions
blood
-
Electrical insulator
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely.
-
Conductivity in nonionic solutions is always _____ in ionic solutions. While the concentration of total dissolved solids does relate to conductivity, the contribution of nonionic solids is _____.
lower than
much, much less important than ion concentration
-
Current formula
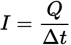
I is current
Q is the amount of charge passing through the conductor per unit time, ∆t
-
SI unit of current (with base units)
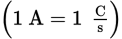
ampère
-
Charge is transmitted by a flow of _____ in a conductor, and because _____ are _____ charged, they move from a point of _____ electrical potential to a point of _____ electrical potential.
electrons
electrons
negatively
lower -> higher
-
By convention, the direction of current is the direction in which _____ would flow (from _____ potential to _____ potential). Thus, the direction of current is _____ to the direction of actual electron flow.
positive charge
higher -> lower
opposite
-
The two patterns of current flow are _____ and _____.
direct current (DC)
alternating current (AC)
-
Direct current (DC)
Charge flows in one direction only
-
Alternating current (AC)
Flow of electrons changes direction periodically
-
Direct current is produced by _____, while the current supplied _____ is alternating current.
household batteries
over long distances to homes and other buildings
-
Our discussion of circuits will assume _____, which is tested on the MCAT to the exclusion of alternating current.
direct current
-
Electromotive force (with abbr.)
When no charge is moving between the two terminals of a cell that are at different potential values, the voltage is called the electromotive force (emf or ε).
-
Electromotive force is not _____; it is a _____ and has units of _____.
a force
potential difference (voltage)
joules per coulomb
-
It may be helpful to think of emf as a “_____” that results in current, in much the same way that a pressure difference between two points in a fluid-filled tube causes the fluid to flow.
pressure to move
-
The standard batteries in flashlights and remote controls are examples of _____.
galvanic (voltaic) cells
-
Currents (and circuits in general) are governed by _____. _____ and _____ must be fully accounted for at all times and can be neither created nor destroyed.
the laws of conservation
Charge and energy
-
Kirchhoff’s laws
Two rules that deal with the conservation of charge and energy within a circuit
-
Kirchhoff’s junction rule
At any point or junction in a circuit, the sum of currents directed into that point equals the sum of currents directed away from that point.
Iinto junction = Ileaving junction
-
Kirchhoff’s junction rule is an expression of _____.
conservation of electrical charge
-
Kirchhoff’s loop rule
Around any closed circuit loop, the sum of voltage sources will always be equal to the sum of voltage (potential) drops.
Vsource = Vdrop
-
Kirchhoff’s loop rule is an expression of _____.
conservation of energy
-
Although Kirchhoff’s loop rule is a consequence of the law of conservation of energy, this law is in terms of , not just _____.
voltage (joules per coulomb)
energy (joules)
-
When considering circuits, it is important to remember that energy can be _____.
changed from one form to another
-
If all of the voltage wasn’t “used up” in each loop of the circuit, then the voltage would _____, which is impossible.
build after each trip around the circuit

