-
Electric potential
Electric potential is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of a charge’s electric potential energy to the magnitude of the charge itself.
-
Electric potential equation
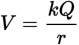
-
Units of electric potential
volts (V)
-
SI derived units for electric potential
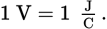
joules per coulomb (J/C)
-
Electric potential true equation
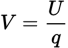
-
Electricity basic equations
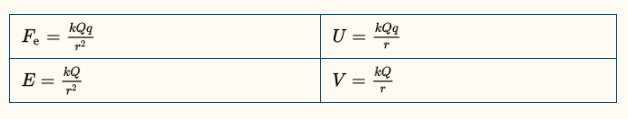
Take Coulomb's Law and manipulate it. From left to right, multiply by r; from top to bottom, divide by q.
-
Electric potential is a _____ quantity.
scalar
-
For a positive source charge, V is _____, but for a negative source charge, V is _____.
positive
negative
-
For a collection of charges, the total electric potential at a point in space is the ...
... scalar sum of the electric potential due to each charge.
-
Voltage
The difference between electric potentials at two points.
-
Voltage equation
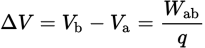
Wab is the work needed to move a test charge q through an electric field from point a to point b
-
Voltage is path _____.
independent
-
Like gravitational force, the electrostatic force is a _____ force.
conservative
-
MNEMONIC: The “plus” end of a battery is the high-potential end, and the “minus” end of a battery is the low-potential end. Positive charge moves _____ (the definition of current) while negative charge moves _____.
from + to –
from – to +
-
Charges, if allowed, will move spontaneously in whatever direction results in a _____. For a positive test charge, this means moving from a position of _____ electric potential to a position of _____ electric potential. The voltage is _____ in this case; because q is positive (for a positive test charge), thus, Wab must be _____, which represents a _____ in electric potential energy.
decrease in electric potential energy
higher -> lower
negative
negative
decrease
-
A negative test charge will spontaneously move from a position of _____ electric potential to a position of _____ electric potential. The voltage is _____ in this case; because q is negative (for a negative test charge), Wab must be _____, which again represents a decrease in electric potential energy.
lower -> higher
positive
negative
decrease
-
Positive charges will spontaneously move in the direction that _____ their electric potential (_____ voltage).
decreases
negative
-
Negative charges will spontaneously move in the direction that _____ their electric potential ( voltage).
increases
positive
-
In the case of a spontaneous movement of a particle (either positive or negative), the electric potential energy is _____.
decreasing
-
A test charge has a particular _____ at a given _____, depending on the magnitude of its charge.
electric potential energy
electric potential
-
Electric potential energy _____ the test charge, while electric potential _____.
depends on
does not
-
The value of electric potential does not determine whether a charged particle will move; _____ does.
voltage

