-
Coulomb’s law
Coulomb’s law quantifies the magnitude of the electrostatic force Fe between two charges.
-
Coulomb’s law euqation
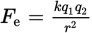
Fe is the magnitude of the electrostatic force
k is Coulomb’s constant
q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the two charges
r is the distance between the charges
-
Coulomb’s constant (also called the electrostatic constant) (with units)
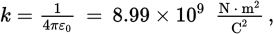
ε0 represents the permittivity of free space
-
Permittivity of free space value
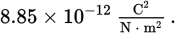
-
The electrostatic force always points along ...
... the line connecting the centers of the two charges
-
In both the equation for Coulomb's Law and the equation for gravitational force, the force magnitude is ...
... inversely proportional to the square of the distance of separation.
-
What is the ratio of electrostatic force to gravitational force for an electron/proton pair?
~2.27 x 1039
-
Electric field (with units)
An electric field is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them.
The units for an electric field are newtons per coulomb (N/C)
-
Test charge (with variable)
The charge placed in the electric field
q (little q)
-
Source charge (with variable)
The charge which actually creates the electric field
Q (big Q)
-
Electric fields are produced by source charges (Q). When a test charge (q) is placed in an electric field (E), it will experience an electrostatic force (Fe) equal to _____.
qE
-
Electric field equation
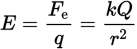
E is the electric field magnitude in newtons per coulomb
Fe is the magnitude of the force felt by the test charge q
k is the electrostatic constant
Q is the source charge magnitude
r is the distance between the charges
-
The electric field is a _____ quantity.
vector
-
There are two different methods for calculating the magnitude of the electric field at a particular point in space:
1) Place a test charge q at some point within the electric field, measure the force exerted on that test charge, and define the electric field at that point in space as the ratio of the force magnitude to test charge magnitude. This method requires a test charge.
2) Use the magnitude of the source charge and the distance between the source charge and point in space at which we want to measure the electric field to calculate E. This method requires knowledge of the magnitude of the source charge.
-
By convention, the direction of the electric field vector is given as the direction that a _____ would move in the presence of the source charge.
positive test charge
-
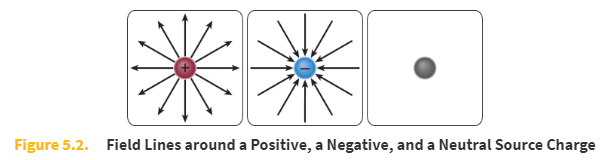
Field lines
Field lines are imaginary lines that represent how a positive test charge would move in the presence of the source charge.
-
Where the field lines are _____, the field is stronger; where the lines are _____, the field is weaker.
closer together
farther apart
-
A collection of charges will exert a net electric field at a point in space that is equal to ...
... the vector sum of all the electric fields.
-
If the test charge within a field is positive, then the force will be in the _____ direction as the electric field vector of the source charge; if the test charge is negative, then the force will be in the _____ direction to the field vector of the source charge.
same
opposite

