-
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is the study of stationary charges and the forces that are created by and which act upon these charges.
-
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle with a positive one elementary electric charge.
-
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge.
-
Opposite charges exert _____ forces, and like charges exert _____ forces.
attractive
repulsive
-
Unlike the force of gravity, which is _____, the electrostatic force may be _____ or _____ depending on the signs of the charges that are interacting.
always an attractive force
repulsive or attractive
-
While many of the particles we discuss in electrostatics are very, very tiny, do not forget that they still do _____.
have mass
-
Most matter is electrically _____, as a balance of positive and negative charges ensures a _____.
neutral
relative degree of stability
-
Ground
A means of returning charge to the earth
-
Static charge buildup or static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material or between materials.
-
Static charge buildup or static electricity is more significant in drier air because ...
...lower humidity makes it easier for charge to become and remain separated.
-
The SI unit of charge is the _____
coulomb (C)
-
Fundamental unit of charge (in coulombs)
e = 1.60 × 10−19 C
-
A proton and an electron each have one _____, although the proton is _____, while the electron is _____.
fundamental unit of charge
positively charged (q = +e)
negatively charged (q = −e)
-
Even though the proton and the electron share the same magnitude of charge, they do not share the same _____; the proton has a _____ than the electron.
mass
much greater mass
-
Law of conservation of charge
Charge can neither be created nor destroyed.
-
Insulator
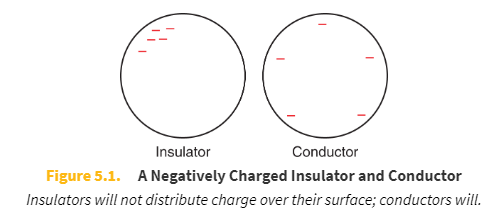
An insulator will not easily distribute a charge over its surface and will not transfer that charge to another neutral object very well—especially not to another insulator.
-
On a molecular level, the electrons of insulators tend to be _____. By extension, most _____ are insulators.
closely linked with their respective nuclei
nonmetals
-
Experimentally, insulators serve as _____ in capacitors, as well as in _____ to prevent grounding.
dielectric materials
isolating electrostatic experiments from the environment
-
Conductor behavior
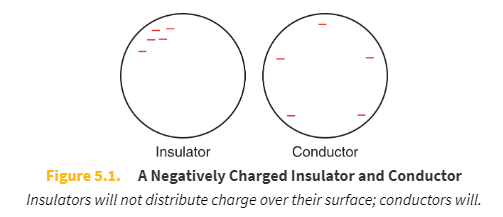
When a conductor is given a charge, the charges will distribute approximately evenly upon the surface of the conductor.
-
Conductors are able to _____ and are often used in circuits or electrochemical cells.
transfer and transport charges
-
Conductors are often conceptualized as nuclei surrounded by _____ and are only _____ associated with the positive charges.
a sea of free electrons that are able to move rapidly throughout the material
loosely
-
Conductors are generally _____, although _____ solutions are also effective conductors.
metals
ionic (electrolyte)
-
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton.

