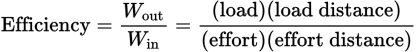-
Kinetic energy
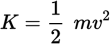
-
Gravitational potential energy
U = mgh
-
Elastic potential energy
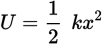
-
Total mechanical energy
E = U + K
-
Conservation of mechanical energy
ΔE = ΔU + ΔK = 0
-
Work done by nonconservative forces
Wnonconservative = ΔE = ΔU + ΔK
-
Definition of work (mechanical)
W = F · d = Fd cos θ
-
Definition of work (isobaric gas–piston system)
W = PΔV
-
Definition of power
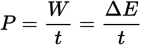
-
Work–Energy theorem
Wnet = ΔK = Kf – Ki
-
Mechanical advantage
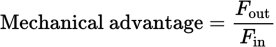
-
Efficiency