-
Energy refers to a system’s ability to _____ or—more broadly—to _____.
do work
make something happen.
-
Different forms of energy have the capacity to perform _____.
different actions.
-
Mechanical energy can cause objects to _____.
move or accelerate
-
An ice cube sitting on the kitchen counter at room temperature will absorb _____ through heat.
thermal energy
-
Kinetic energy is the energy of _____.
motion
-
Kinetic energy equation
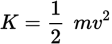
where K is kinetic energy, m is the mass in kilograms, and v is speed in meters per second.
-
The SI unit for kinetic energy, as with all forms of energy, is the _____, which is equal to _____.
joule (J)
kg * m^2 * s^-2
-
Kinetic energy is related to _____ and not _____.
speed
velocity
-
An object has the same kinetic energy regardless of the direction of its _____.
velocity vector
-
Potential energy refers to energy that is associated with a given object’s _____ or other _____.
position in space
intrinsic qualities of the system
-
Gravitational potential energy depends on an object’s position with respect to some level identified as the _____.
datum ("ground zero")
-
The datum is usually chosen out of _____.
convenience
-
Gravitational potential energy equation
U = mgh
...where U is the potential energy, m is the mass in kilograms, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above the datum.
-
When a spring is stretched or compressed from its equilibrium length, the spring has _____.
elastic potential energy
-
Elastic potential energy equation
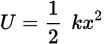
...where U is the potential energy, k is the spring constant (a measure of the stiffness of the spring), and x is the magnitude of displacement from equilibrium. Note the similarities between this equation and the formula for kinetic energy.
-
The sum of an object’s potential and kinetic energies is its _____.
total mechanical energy
-
Total mechanical energy equation
E = U + K
...where E is total mechanical energy, U is potential energy, and K is kinetic energy.
-
The first law of thermodynamics accounts for the _____, which posits that energy is never _____ — it is merely _____.
conservation of mechanical energy
created nor destroyed
transferred from one form to another
-
The total mechanical energy equation _____ obey the first law of thermodynamics.
Why?
does not (necessarily)
there are other forms of energy
-
In the absence of nonconservative forces, such as frictional forces, the sum of the kinetic and potential energies will be _____.
constant
-
Conservative forces are those that are _____ and that _____.
path independent
do not dissipate energy
-
Conservative forces have _____ associated with them.
potential energies
-
Perfectly elastic springs have _____, but non-ideal springs produce _____.
conservative energies
friction
-
What are two ways to determine if a force is conservative?
pathing between two points (same energy change regardless) and pathing in a circle (net 0 energy change)
-
When the work done by nonconservative forces is zero, or when there are no nonconservative forces acting on the system, the total mechanical energy of the system remains _____.
constant
-
Conservation of mechanical energy in a conservative system
ΔE = ΔU + ΔK = 0
...where ΔE, ΔU, and ΔK are the changes in total mechanical energy, potential energy, and kinetic energy, respectively.
-
When nonconservative forces, such as friction, air resistance, or viscous drag (a resistance force created by fluid viscosity) are present, total mechanical energy is _____.
not conserved
-
Nonconservative work equation
Wnonconservative = ΔE = ΔU + ΔK
...where Wnonconservative is the work done by the nonconservative forces only.
-
Nonconservative forces, unlike conservative forces, are _____.
path dependent

