-
Range
The range of a data set is the difference between its largest and smallest values
-
Range does not consider _____, nor does it consider the placement of any _____.
the number of items of the data set
measures of central tendency
-
The range of a data set is heavily affected by any _____.
outliers
-
In cases where it is not possible to calculate the standard deviation for a normal distribution because the entire data set is not provided, it is possible to approximate the standard deviation as _____.
one-fourth of the range
-
Interquartile range equation
IQR = Q3 – Q1
-
IQR criteria for an outlier
Any value that falls more than 1.5 interquartile ranges below the first quartile or above the third quartile is considered an outlier.
-
Standard deviation formula
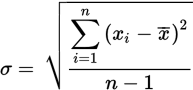
σ is the standard deviation
xi to xn are the values of all of the data points in the set
x̄ is the mean
n is the number of data points in the set
-
SD criteria for an outlier
If a data point falls more than three standard deviations from the mean, it is considered an outlier.
-
Approximately _____ of data points fall within 1 standard deviation of the mean.
68.2%
-
Approximately _____ of data points fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean.
95.5%
-
Approximately _____ of data points fall within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
99.7%
-
Between the mean and +1σ, approximately _____ of the data in a normal distribution can be found
36.1%
(same for the other side)
-
Between +1σ and +2σ, approximately _____ of the data in a normal distribution can be found
13.6%
(same for the other side)
-
Between +2σ and +3σ, approximately _____ of the data in a normal distribution can be found
2.1%
(same for the other side)
-
Outliers typically result from one of three causes:
A true statistical anomaly (e.g., a person who is over seven feet tall).
A measurement error (for example, reading the centimeter side of a tape measure instead of inches).
A distribution that is not approximated by the normal distribution (e.g., a skewed distribution with a long tail).
-
If there is a measurement error, the associated data point should be _____.
excluded from analysis
-
If an outlier is the result of a true measurement, but is not representative of the population, it may be _____ or _____ depending on the purpose of the study and preselected protocols.
weighted to reflect its rarity (included normally)
excluded from the analysis
-
The decision to include or exclude outliers should be made _____..
before a study begins—not once an outlier has been found

