-
Normal distribution
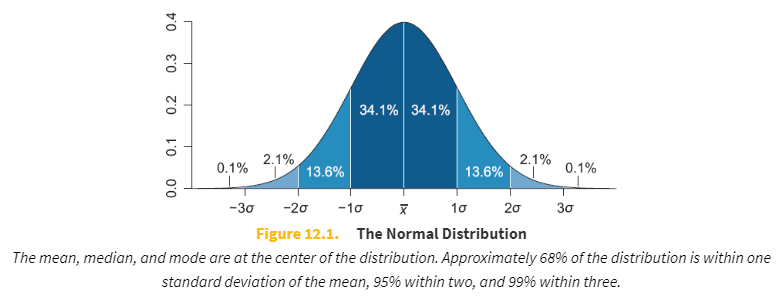
A normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable.
-
Standard distribution
A normal distribution with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one. This type of graph is often used to get information about probability or percentages of populations.
-
In the normal distribution, all of the _____ are the same.
measures of central tendency
-
Skewed distribution
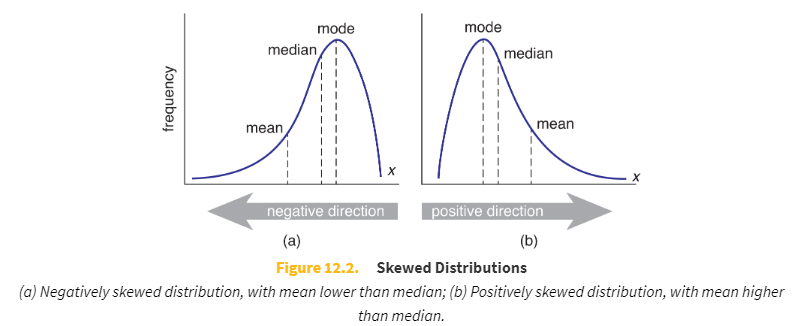
A skewed distribution is one that contains a tail on one side or the other of the data set.
-
A negatively skewed distribution has a tail on the _____ side.
left (or negative) side
-
A positively skewed distribution has a tail on the _____ side.
right (or positive) side
-
The mean of a negatively skewed distribution will be _____ the median.
lower than
-
The mean of a positively skewed distribution will be _____ the median.
higher than
-
The direction of skew in a sample is not determined by _____.
the bulk of the distribution.
-
Multimodal distribution
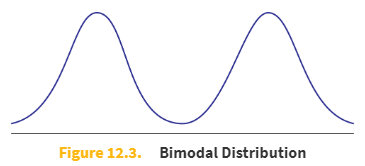
A multimodal distribution is a probability distribution with more than one mode. It is important to note that a multimodal distribution, strictly speaking, might have only one mode if one peak is slightly higher than the others. However, even when the peaks are of different sizes, we still call the distribution multimodal.
-
If there is _____, or a _____, bimodal distributions can often be analyzed as two separate distributions.
sufficient separation of the two peaks
sufficiently small amount of data within the valley region
-
Another name for a positively skewed distribution is a _____.
right-skewed distribution
-
Another name for a negatively skewed distribution is a _____.
left-skewed distribution

