-
Scientific method
The scientific method is a series of eight steps for the generation of new knowledge.
-
The initial steps (_____, _____, _____) focus on _____.
generate a testable question, gather data and resources, form a hypothesis
generating a hypothesis
-
The intermediate steps (_____, _____, _____) focus on _____.
collect new data, analyze the data, interpret the data and existing hypothesis
testing the hypothesis
-
The final steps (_____ and _____) relate to _____.
publish and verify results
providing the results for further testing of the hypothesis
-
The FINER method assesses the _____ on the basis of whether or not it is _____.
value of a research question
feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant
-
Basic science research uses _____ and is _____.
chemicals, cell cultures, or animal subjects (NOT HUMANS)
experiment-based
-
During research, we manipulate _____ and observe changes in the _____.
independent variables
dependent variable
-
Controls
Controls are used to correct for any influences of an intervention that are not part of the model. Controls may be positive or negative.
-
Positive controls
Positive controls ensure that a change in the dependent variable occurs when expected.
Positive controls are used to assess the test validity of the experimental protocol or equipment by producing the expected result.
-
Negative controls
Negative controls ensure that no change in the dependent variable occurs when none is expected.
The essential purpose of a negative control is to reproduce a condition that cannot involve the hypothesized causal mechanism, but is very likely to involve the same sources of bias that may have been present in the original association. (i.e. detect confounding variables)
-
Basic science research is often the best type for demonstrating causality because ...
... the experimenter has the highest degree of control over the experimental conditions.
-
Error in basic science research most often results from errors in _____.
measurement
-
Accuracy (validity)
Accuracy (validity) is the quality of approximating the true value.
-
Precision (reliability)
Precision (reliability) is the quality of being consistent in approximations.
Note: Determining precision requires more than one measurement
-
Human subjects research is subject to _____ that are generally absent in basic science research.
ethical constraints
-
Experiments may still be performed in human subject research, but causal conclusions are harder to determine because _____.
circumstances are harder to control
-
There are three main types of observational studies in human subject research:
Cohort studies
Cross-sectional studies
Case–control studies
-
Cohort studies
Cohort studies record exposures throughout time and then assess the rate of a certain outcome.
-
Cross-sectional studies
Cross-sectional studies assess both exposure and outcome at the same point in time.
-
Case–control studies
Case–control studies assess outcome status and then assess for exposure history.
-
Causality in observational studies is supported by _____.
Hill’s criteria
-
Hill’s criteria
-Strength
-Specificity
-Consistency
-Coherence
-Biological Plausibility
-Analogy
-Temporality (critical)
-Dose-dependence
-Experiment
Sometimes, a tenth criteria, Reversibility, is included.
-
Error may be in the form of _____, _____, or _____.
bias, confounding, or random error
-
Bias is _____ and results from a problem during _____ or _____.
systematic
sampling or data collection
-
Selection bias
Selection bias, in which the sample differs from the population, is most common in human subjects research.
-
Detection bias
Detection bias arises from educated professionals using their knowledge in an inconsistent way by searching for an outcome disproportionately in certain populations.
-
Hawthorne effect
The Hawthorne effect results from changes in behavior—by the subject, experimenter, or both—that occur as a result of the knowledge that the subject is being observed.
-
Confounding
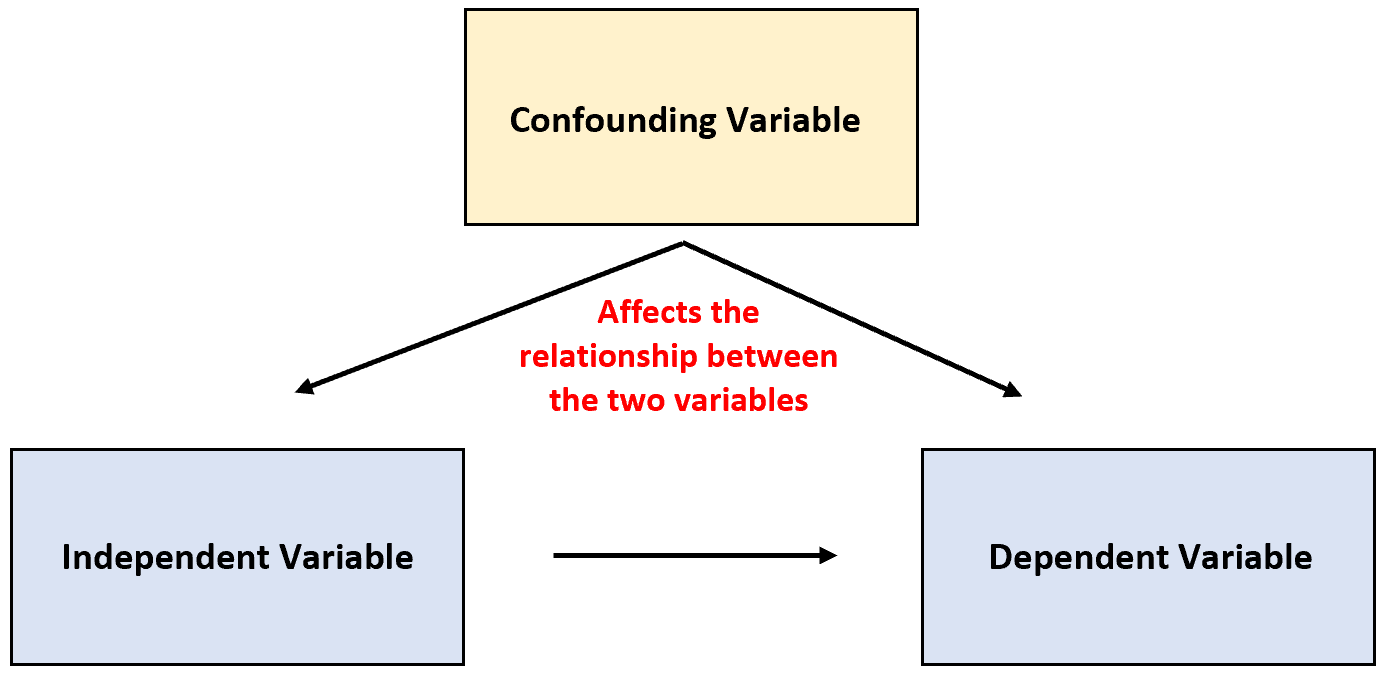
Confounding is an error in data analysis that results from a common connection of both the dependent and independent variables to a third variable.
-
Medical ethics generally refers to the four principles of _____, _____, _____, and _____.
beneficence, nonmaleficence, respect for patient autonomy, and justice
-
Research ethics established by the Belmont Report are:
Respect for persons
Justice
Beneficence
-
Respect for persons
Respect for persons includes autonomy, informed consent, and confidentiality.
-
Justice
Justice dictates which study questions are worth pursuing and which subjects to use.
-
Beneficence
Beneficence requires us to do the most good with the least harm.
-
Equipoise
We cannot perform an intervention without equipoise—a lack of knowledge about which arm of the research study is better for the subject.
-
Populations
Populations are all of the individuals who share a set of characteristics.
-
Parameters
Population data are called parameters.
-
Samples
Samples are a subset of a population that are used to estimate population data.
-
Statistics
Sample data are called statistics.
-
Internal validity
Internal validity refers to the identification of causality in a study between the independent and dependent variables.
-
External validity
External validity refers to the ability of a study to be generalized to the population that it describes.
-
In order to be supported, an intervention must display _____.
both statistical and clinical significance
-
Statistical significance
Statistical significance refers to the low likelihood of the experimental findings being due to chance.
-
Clinical significance
Clinical significance refers to the usefulness or importance of experimental findings to patient care or patient outcomes.

