MCAT Physics and Math 1.7: Mechanical Equilibrium
MCAT Physics and Math 1.7: Mechanical Equilibrium
-
Dynamics
The study of forces and torques
-
Free body diagram
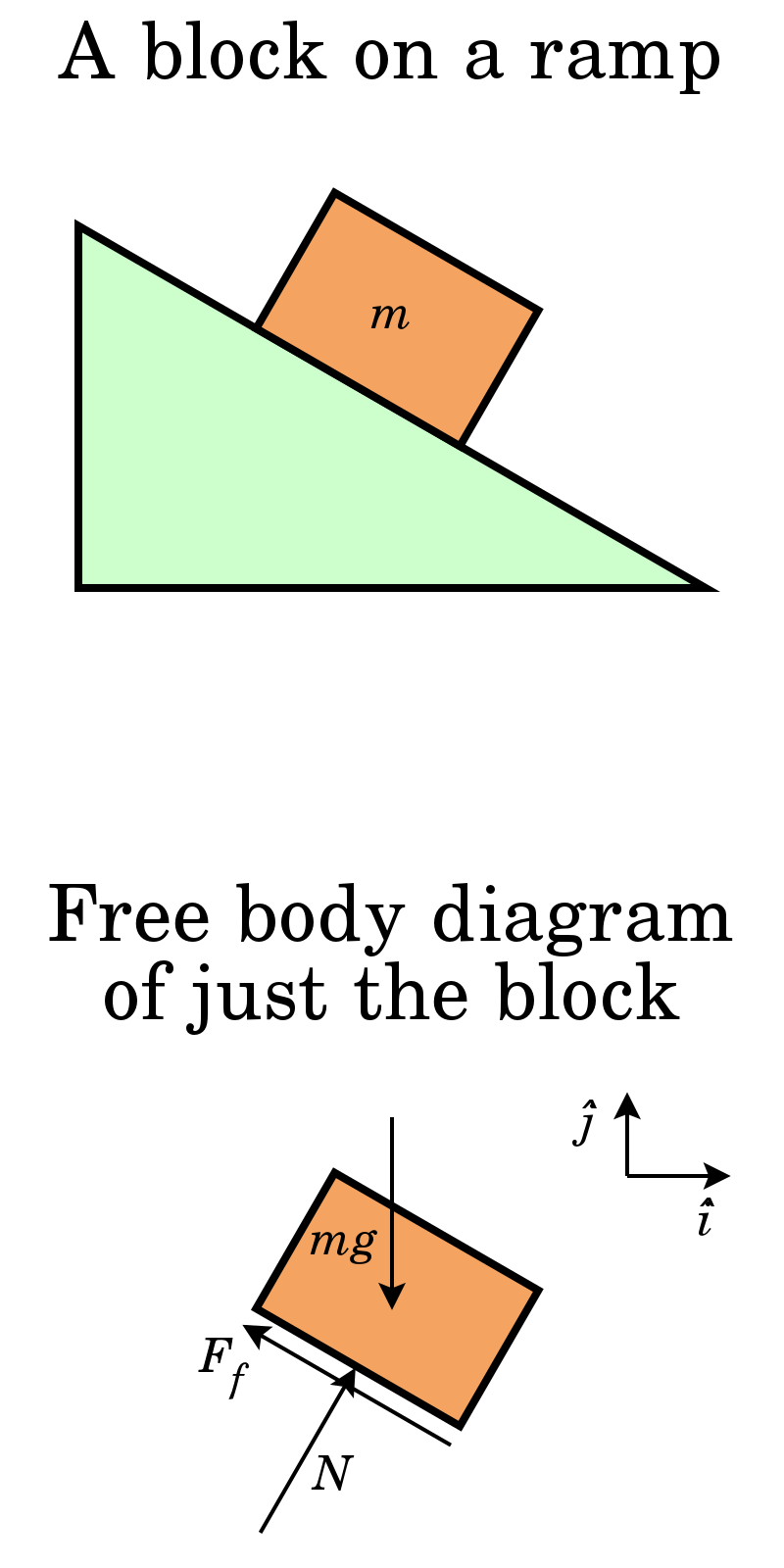
A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it.
-
Translational motion occurs when _____.
forces cause an object to move without any rotation
-
Translational equilibrium exists only when the _____.
vector sum of all of the forces acting on an object is zero.
(this is the second condition of equilibrium)
-
When dealing w/ mechanics, always _____.
draw out the free body diagrams!
-
Rotational motion occurs when forces are applied against an object in such a way as to cause the object to _____, also known as the _____.
rotate around a fixed pivot point
fulcrum
-
Formula for torque
τ = r × F = rF sinθ
...where r is the length of the lever arm, F is the magnitude of the force, and θ is the angle between the lever arm and force vectors
-
Rotational equilibrium exists only when the _____.
vector sum of all the torques acting on an object is zero.
(this is the second condition of equilibrium)
-
Torques that generate clockwise rotation are considered _____, while torques that generate counterclockwise rotation are _____.
negative
positive
-
_____ is the angular equivalent of _____.
torque (τ)
force (F)

