-
The SI unit for force is the _____, which is equivalent to _____
newton (N), 1 kg*m*s-2
-
Every change in velocity is motivated by a ...
force
-
Force is a _____ quantity
vector
-
Gravity
an attractive force that is felt between objects with mass
-
gravitational acceleration at earth's surface
g = ~10 m/s2 (really 9.8, but there's no calculator on the MCAT)
-
The gravitation forces felt between two objects are _____
equal in magnitude, opposite in direction due to Newton's third law
-
The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects
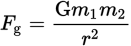
-
G (universal gravitational constant)
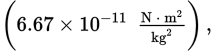
-
The magnitude of Fg is proportional to the distance between two objects how?
Fg α 1/r2
-
The magnitude of Fg is proportional to the mass of the two objects how?
Fg α m1
Fg α m2
-
6.67 ≈ ?
20/3
-
Friction is a type of force that...
opposes the movement of objects
-
There are two types of friction: _____ and _____
static and kinetic
-
Static friction (fs) exists between...
a stationary object and the surface upon which it rests
-
Static friction (fs) inequality
0 ≤ fs ≤ μsN
-
μs
coefficient of static friction
-
N
magnitude of normal force
-
Normal force
The component of the force between two objects in contact that is perpendicular to the plane of contact between the object and the surface upon which it rests
-
One should not assume that objects that are stationary are...
experiencing a maximal static force of friction
-
Kinetic friction (fk) exists between...
a sliding object and the surface over which the object slides
-
Does a wheel experience kinetic friction? Why or why not?
No, the surface of the wheel does not actually slide across the ground (ideally). Instead, the wheel experiences static friction.
-
Kinetic friction (fk) equation
fk = μkN
-
Kinetic friction does not depend on _____ nor _____
how much surface area is in contact
the velocity of the sliding object
-
The value of _____ is always larger than the value of _____. What implication does this have on objects?
μs > μk
Objects will “stick” until they start moving, and then will slide more easily over one another.
I.e. It always requires more force to get an object to start sliding than it takes to keep an object sliding.
-
Mass (m)
a measure of a body’s inertia—the amount of matter in the object
-
Weight (Fg)
a measure of gravitational force (usually that of the Earth) on an object’s mass
-
Mass is a _____ quantity, while weight is a _____ quantity
scalar, vector
-
Weight units
newtons (N)
-
Relation between mass and weight (equation)
Fg = m*g
g = ~10 m/s
-
The weight of an object can be thought of as being applied at a single point in that object called the _____.
center of mass, center of gravity
-
Center of mass of a system equations
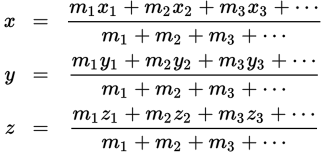
-
The center of mass of a uniform object is at the...
geometric center of the object
Note: this is not the case for all objects
-
Acceleration (a)
the rate of change of velocity that an object experiences as a result of some applied force
-
Acceleration is a _____ quantity
vector
-
Acceleration units
m/s2
-
Average acceleration equation
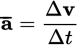
-
Instantaneous acceleration equation
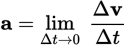
-
On a graph of velocity vs. time, the _____, which corresponds to the _____, indicates the instantaneous acceleration
tangent to the graph at any time t
slope of the graph at that time
-
If the slope is positive, then the acceleration is _____. If the slope is negative, then the acceleration is _____.
positive and in the same direction as the velocity
negative and in the opposite direction of the velocity (this is a deceleration)

